The skin can itch quite often, because it is constantly exposed to external factors. Itching may also occur in the abdomen and sides. There can be many reasons for this. Some of them are harmless and such an unpleasant sensation can be easily eliminated. However, there are cases when a serious illness occurs with similar accompanying symptoms. Therefore, in this article we will discuss the causes of itching and possible treatment methods.
To find out why the sides of the abdomen itch, you must first pay attention to the causes of natural origin. These may be the following:
- Exposure to external stimuli. They can be woolen clothes worn on a naked body. Due to skin irritation by villi, itching occurs. It can also be uncomfortable, constricting clothing made from synthetic materials, which does not allow the skin to “breathe”.
- Allergic reaction. The cause may be the consumption of allergenic products, the use of household chemicals and cosmetics. Hypersensitivity can also be caused by components included in medications.
- Hot weather. During this period, increased sweating is observed, and the sebaceous glands work more efficiently. As a result, the normal condition of the skin of the abdomen is disrupted, and it begins to itch.
- Insect bites. Most often they are mosquitoes. They leave redness at the site of the bite, so it is easy to determine the cause of the itching. In addition, bedbugs may appear in apartments, and after their bite, the stomach or sides may also itch.
- Lack of hygiene. In the absence of water procedures, changing bed linen and clothes, the pores become very clogged, which causes itching.
- Pregnancy. In the last stages, a woman gains weight, her stomach grows, and her skin stretches intensely, forming stretch marks. It is because of them that the stomach itches.
There is no need to worry in these cases. The itching will stop immediately after the factor causing it is eliminated. This does not require drug treatment. There are no health consequences here.
Classification
Itchy skin is an external manifestation accompanied by irritation of the skin area and a strong desire to itch. This symptom can occur in anyone, regardless of age or gender. In medicine, there is a classification of skin itching, which is based on its individual characteristics.
According to the degree of prevalence, itchy skin is distinguished:
- Generalized. The phenomenon is typical for the skin of the entire body.
- Focal (localized). A clearly defined pathological area of skin is identified.
Depending on the causes:
- Dermatological. Develops as a symptom of skin diseases.
- Systemic as an external manifestation of pathologies of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, thyroid gland.
- Psychogenic. Occurs against the background of stressful situations that give rise to neuroses.
- Neuropathic. Formed as a result of diseases of the nervous system.
There are several specific types of skin itching:
- Aquagenic. Occurs when skin comes into contact with water.
- Senile. Itching appears in 60-70% of people after 70 years of age.
- Reflex. People who are overly emotional or excited have a desire to scratch if they hear or see a phenomenon or object that irritates them.
- High-rise. The symptom develops when a person rises to great heights.
Itching in various diseases
The occurrence of itching against the background of other diseases is a common occurrence, and therefore, to eliminate this problem, it is necessary to determine its cause and immediately begin treatment. Doctors identify several diseases that in most cases cause itchy skin:
- Neurodermatitis. This disease is neuropsychological in nature and occurs due to stress, short temper, choleric temperament, and inappropriate hot-tempered states. The main focus of treatment in this case is sedative procedures that reduce the activity of the nervous system.
- Xerosis. Excessive drying of the skin by harsh detergents or sunbathing is a common cause of itchy skin. The symptoms in this situation are obvious: cracked, dehydrated, dull and pale skin. Properly selected moisturizing cosmetics can quickly solve this problem.
- Diabetes. Blood sugar levels that are higher than normal indicate diabetes. This disease dehydrates the body in a short time and contributes to the occurrence of fungal infections. Such skin very often suffers from external irritants, and patients experience severe itching.
- Scabies. This disease occurs due to parasitic mites on the skin of the patient. They can be removed using special salicylic ointments.
Causes
The desire to scratch occurs as a result of a rush of blood to the receptors located in the upper layer of the skin. The blood may contain hormones, acids, and waste products, which contribute to irritation of the receptors.
Excessive release of certain compounds into the blood occurs under the influence of diseases or external phenomena. In this regard, several groups of factors can be identified that cause skin itching.
Dermatological diseases
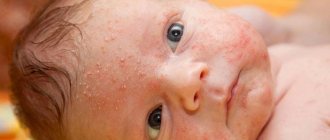
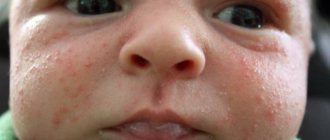
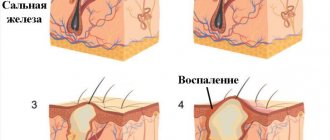
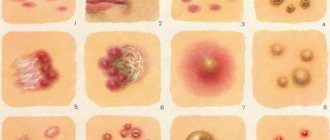
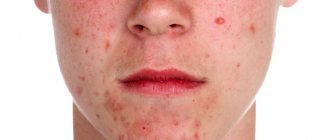
Skin diseases are often accompanied by severe itching. It can either concentrate in one or several areas or spread throughout the body. The skin itches unbearably with the following diseases:
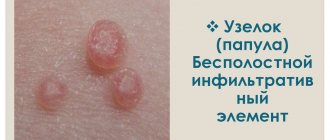
- Neurodermatitis. A disease of an allergic or nervous nature, in which the affected areas of the skin become covered with papules and itch unbearably.
- Hives. The pathology is of an allergic nature, itching is complemented by the formation of pink blisters.
- Scabies. A contagious skin disease caused by the scabies mite. Itching occurs as a result of the subcutaneous movement of the parasite; a rash of small papules appears on the body.
- Pediculosis. This is the name given to infestation by small lice, which prefer to live in the hairy part of the body, in particular on the pubis or under the arms.
- Xeroderma. A type of ichthyosis. Along with itching, flaking of the skin occurs, like small scales, which are found mainly on the limbs and buttocks.
- Lichen planus. Itching of the skin is accompanied by the formation of gray-white papules localized on the flexor side of the limbs and the sacrum.
- Dermatitis. A group of skin allergic diseases that occur as a result of exposure of the skin to aggressive environmental factors (chemicals, water, insect bites, etc.). With dermatitis, rashes appear that itch and thereby cause discomfort.
- Fungal diseases. This group of pathologies includes diseases such as epidermophytosis, trichophytosis, candidiasis, and ringworm. The causative agents are various representatives of fungal microorganisms.
- Folliculitis. An inflammatory process in the hair follicles that occurs as a result of damage by bacteria, viruses or fungi.
- Demodecosis. Infection of the skin with iron mites, which live in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
Internal diseases
Itching can be a symptom not only of skin diseases, but also of pathologies of internal organs. It is caused by the following diseases:
- Diseases of the liver and gall bladder (hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholestasis, pancreatic cancer and others), often accompanied by rash and itching. Since a diseased liver is not able to completely cleanse the body of toxic substances, some of its functions are taken over by the skin.
- Kidney failure and other kidney pathologies. The more pronounced the impairment of the excretory function of the kidneys, the more noticeable the skin itching.
- Thyroid diseases. The skin itches especially severely with diffuse goiter. The main reason is the strong blood flow to the epidermis. Another disease accompanied by increased itching is hyperthyroidism. Discomfort is caused by dry skin, which is one of the symptoms of this pathology.
- Diabetes. Itchy skin areas in diabetes are concentrated on the genitals. If the discomfort covers the whole body, then we are talking about a metabolic disorder due to renal pathology.
- Blood diseases. Anemia, lymphoma, leukemia, mastocytosis and other hematopoietic diseases cause painful itching. With lymphogranulomatosis, 30% of all patients complain about it. With polycythemia, the skin becomes very itchy after contact with water.
- Immunodeficiency virus. In 90% of cases, HIV infection is accompanied by itchy skin. The symptom intensifies in the cold season. As the disease progresses, the skin becomes dry, especially after contact with liquids.
- Pathologies of the nervous system. (sclerosis, brain tumor). With sclerosis, itching occurs suddenly and just as unexpectedly subsides. If there is a cerebral hemorrhage, the skin will itch on the injured side.
- Avitaminosis. A lack of vitamins A, E, and B in the body dries out the skin, which causes severe itching. The skin itches when there is a lack of zinc in the body.
- Intestinal helminths. Parasites living in the intestines interfere with the absorption of nutrients. During their life, helminths release large amounts of toxins into the body. If the internal organs cannot cope with intoxication, cleansing occurs through the skin.
- Periarteritis nodosa. An inflammatory process in the walls of blood vessels, leading to the formation of aneurysms. Impaired blood circulation affects skin receptors and causes itching.
Physiological reasons
Sometimes itchy skin is not associated with diseases:
- The period of menopause and pregnancy in women. Hormonal changes in the body provoke the release of hormones into the blood, which leads to irritation of receptors on the surface of the skin.
- Stressful situations. Overexcitation and stress contribute to a rush of blood to the epidermis, which provokes the desire to scratch.
- Taking medications. Some medications on the list of side effects have skin itching. It may be caused by an allergy to drugs.
- Senile itching. After 70 years, the functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, the skin does not retain moisture well and dries out. Lack of nutrition and loss of regenerative functions of the skin with age leads to regular scratching.
- Overheating, hypothermia or frequent contact with water. Natural factors contribute to dryness and cracking of the skin.
- Lack of hygiene. If a person rarely washes or uses aggressive washing products, the epidermis is affected and itching occurs.
Important! To establish the exact reason why the skin itches can only be based on a combination of several symptoms.
Dermatovenerologist M.G. Conte will tell you about the causes of skin itching. She will tell you in detail about diseases, one of the symptoms of which is the desire to scratch.
Diagnostics
Since there are more than 100 factors that can trigger itching, the dermatologist prescribes a whole range of diagnostic measures. The patient’s initial visit to a dermatologist includes:
- Obtaining anamnesis, including information about additional symptoms.
- An examination during which the dermatologist carefully examines the patient's skin.
The second stage of the examination involves:
- blood test, including biochemical;
- Analysis of urine;
- examination of stool for the presence of pathogenic bacteria;
- scraping from affected areas of the skin to determine the presence of pathogens.
If a disease of the internal organs is suspected, the doctor will refer the patient for examination by specialized specialists (endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, oncologist, etc.).
Skin itching without external signs: concept and nature of occurrence
In order to begin targeted treatment of skin itching, you need to determine it and find out the nature of its occurrence. Itching of the skin is one of the first signals about the presence of irritants (internal or external), which locally act on the nerve fibers of the deep layers of the skin, which is ultimately transmitted to the cortical centers of the brain. The nature of this disease is ambiguous, since there are more than a hundred causes and factors leading to its appearance. However, a reliable and indisputable fact is that an indifferent attitude to the treatment of skin itching is a quick and sure way to transform the body’s local protective reaction to certain pathogens into a standard reaction of the body in the form of a pathological phenomenon.
Scientists have proven that this disease is subjective in nature, since very often patients can be treated with hypnosis without additional medications. Also, absolutely healthy people were repeatedly convinced that they had itchy skin (placebo effect). Such cases require contacting not a dermatologist or immunologist, but a psychiatrist and neurologist.
Treatment
Methods for eliminating skin itching are selected depending on the reasons that gave rise to the unpleasant symptom.
Skin diseases
Treatment of itching in dermatological diseases is carried out not only with drugs for external use, but also with drugs for internal use.
- Neurodermatitis. The disease involves taking antihistamines (Astemizole, Loratadine) and sedatives (Phenazepam, Aminazine). For external treatment, ointments are used: antiseptic (zinc, ichthyol, tar), anti-inflammatory (Bepanten, Gistan), nourishing (Radevit), corticosteroid (Sinaflan, Advantan).
- Hives. Treatment involves limiting contact with the allergen, taking antihistamines (Claritin, Cetrin, Zyrtec), and hormonal medications (Nerobol, Retabolil). Externally, zinc and naphthalan ointments and hormonal creams (Flucinar, Fluorocort) are used.
- Scabies. The course of treatment is aimed at expelling the parasite, for which benzyl benzoate emulsion is rubbed into the skin. At the same time, the skin is treated with sulfur ointment and insecticidal liquids (Flicid, Lysol), and it is recommended to wash the skin with antiparasitic soap. Folk remedies that work well include ash lye, gasoline, and kerosene.
- Pediculosis. For hair in the pubic area and armpits, use tar soap, boric or mercury ointment. Shampoos and aerosols against lice (Veda, NOK, Sumitrin) help well.
- Xeroderma. To relieve itching and exfoliate scales, ointments with salicylic acid and urea (“Keratolan”, “Ureotop”) are used. Baths with collagen, salt and soda are useful. Compresses with a propylene glycol solution give good results.
- Lichen planus. The treatment is complex, it includes several groups of medications: immunosuppressants (Cyclosporin A, Chloroquine), systemic corticosteroids (Metypred, Prednisolone), interferons (Interferon-alpha 2b, Neovir), drugs with vitamin A (Tigazon, Acitretin), antihistamines (Zyrtec, Diazolin), antibiotics (Metacycline, Azithromycin).
- Dermatitis. To relieve symptoms, contact with the allergen is minimized, antihistamine ointments and creams (Zodak, Claritin, Cetrin), antifungal and antimicrobial medications (Candide, Terbix) are used.
- Fungal skin infection. To eliminate pathogens, antifungal drugs are used, both externally and internally (Exoderil, Pimafucin, Candide, Nizoral, Diflucan).
- Folliculitis. Depending on the causative agent of the disease, take antibiotics (Erythromycin, Cephalexin) or antifungal medications (Fluconazole, Terbinafine). Treat the affected areas of the skin with a solution of brilliant green, methylene blue, salicylic or boric alcohol.
- Demodecosis. Treatment is predominantly local, consisting of applying sulfur ointment or benzyl benzoate, treating skin areas with tar soap. To prevent secondary bacterial infection as part of complex therapy, use Trichopolum.
Internal diseases
In diseases of the internal organs, skin itching is only one of the many symptoms of the pathology. The course of treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause; topical medications only improve the condition of the skin and reduce itching.
- Diseases of the liver, gall bladder. To eliminate discomfort, for cholestasis and other diseases of the liver and gallbladder, medications are used that reduce the level of bile acids in the blood: ursodeoxycholic acid, Cholestyramine, Phenobarbital, Rifampicin, Naloxone, Tavegil.
- Kidney itching. UVB therapy (12 courses) will help soothe itching in kidney diseases. For longer-term treatment, the following are prescribed: Activated carbon, Thalidomide, Naltrexone, Ondansetron, antihistamines (Tavegil), and Capsaicin cream for topical use.
- Endocrine diseases. If the functions of the thyroid gland are impaired, the course of treatment is usually based on hormonal medications (“L-Thyroxine”). For diabetes mellitus, insulin medications are prescribed. After a course of replacement therapy, the itching goes away on its own.
- Blood diseases. Treatment of blood cancer is very complex; in severe stages it includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and blood stem cell transplantation. For iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements are prescribed in the form of injections or orally (Sorbifer Durules, Totema).
- Immunodeficiency states. . Local treatment in the course of therapy for HIV infection consists of moisturizing and nourishing the skin to eliminate dryness. To do this, use fatty creams that create a protective film on the skin (“Silicone”).
- Diseases of the nervous system. To normalize the patient’s condition, doctors prescribe sedatives (“Adaptol”, “Akatinol Memantine”, “Actovegin”). To relieve itching, use ointments and creams with a soothing effect, for example, Nezulin cream-gel.
- Avitaminosis. If there is a lack of vitamins A and B, take vitamin complexes (“Alphabet”, “Revit”, “Vitrum”). Radevit cream has nutritional properties.
- Intestinal helminths. You can cope with an unpleasant symptom (itching) only by eliminating the cause. To get rid of helminths, take “Vormil”, “Vermox”, “Pyrantel”. Creams “Bepanten” and “Actovegin” will help reduce skin itching.
- Periarteritis nodosa. Treatment of the disease is complex, including immunosuppressive cytostatic drugs “Azathioprine”, “Cyclophosphamide”, drugs against hyperthrombosis “Heparin”, “Pentoxifylline”. For external use, hormonal ointments “Prednisolone”, “Hydrocortisone”, “Akriderm-GK” are recommended.
Important! Be very careful when treating itching in the presence of internal diseases and allergies. Hormonal and antihistamine drugs have many side effects!
Prevention of physiological itching
If skin itching is not associated with the presence of dermatological diseases or pathologies of internal organs, preventive measures will help reduce discomfort:
- Ventilate the room and make sure the air remains moist.
- For sleep, use light clothing made from natural fabrics. Avoid synthetic items.
- Drink less coffee and alcohol: they promote blood flow to the skin.
- Do not use cosmetics until the cause of the itching has been determined.
- Take baths in warm, not hot, water.
- Don't use detergents too often.
- Avoid alkaline soap.
- Wash and iron clothes and bedding regularly, especially if the cause of itching is skin parasites.
- Lubricate areas of skin that are too dry with moisturizing ointments and creams (“Baby cream”, “Silicone”).
Non-pathological causes of dry and itchy skin
Among people who consulted dermatologists about dry skin, only 40% were found to have any pathologies that led to the development of xerosis. In other cases, doctors dealt with healthy individuals who had problems with skin care. Among these factors, the most common are:
- Frequent baths. It has been noticed that dry skin and itching all over the body are especially disturbing immediately after taking a hot bath with abundant use of gels and scrubs.
- Swimming in the sea. Salts dissolved in water remain on the dermis, “pulling” it.
- Excessive insolation. A long stay on the beach or in the solarium dries out the skin.
- The influence of cold. Areas of the skin not protected by clothing may lose moisture from exposure to cold wind and frost.
- Dry indoor air. Air conditioners and heating devices dry out the air in the room, which necessarily affects the dermis.
- Natural age-related changes. In old age, xerosis is detected in 75% of people.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods help reduce the symptoms of itching, but do not cope with severe diseases. For serious pathologies, they are used only as part of complex therapy.
Sunflower oil ointment
Ingredients:
- Sunflower oil – 1 tbsp.
- Onions – 6 pcs.
- Wax – 1 tbsp.
How to prepare: Boil oil and add chopped onions to it. When the onion darkens, strain the mixture and add crushed wax. Boil for another 5 minutes, cool.
How to use: Apply to the affected area of skin for 15-20 minutes 2-3 times a day.
Result: The ointment relieves itching and moisturizes the skin.
Boric acid mash
Ingredients:
- Black tea – 50 g.
- Boric acid – 5-7 drops.
- Medical alcohol – 7 drops.
How to prepare: Boil 0.5 liters of water and brew tea. Add alcohol and boric acid to the cooled and strained liquid.
How to use: Lubricate the affected areas of the skin 2-3 times a day.
Result: The skin is disinfected and itching goes away.
Mint tincture
Ingredients:
- Mint or lemon balm leaves – 10 g.
- Vodka – 50 ml.
How to prepare: Pour mint leaves with vodka and infuse the mixture for a week.
How to use: Wipe the affected areas with the tincture 2-3 times a day.
Result: Peppermint essential oils soothe the skin, itching goes away.
Question answer
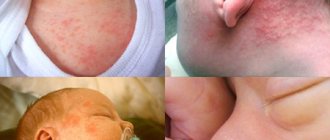
What childhood diseases can be accompanied by itchy skin?
When you have chickenpox, your skin will itch and watery blisters will appear on your body. To treat the disease, antiviral drugs are prescribed (“Viferon”, “Cycloferon”). Lubricate the rash with a solution of brilliant green (zelenka). The solution helps reduce itching and disinfects wounds. Sometimes the skin itches with rubella, and the rash is bright pink and occurs against a background of fever, cough, and runny nose.
Is it possible to cure senile itch?
As you age, your skin becomes drier. The reason is a general slowdown in metabolic processes in the body. It is impossible to completely cope with age-related skin itching. To reduce discomfort, use fatty creams to nourish and moisturize the skin (Belita, Green Mama).
How to relieve itching during pregnancy?
If a pregnant woman does not suffer from any of the diseases listed above, the cause of itchy skin during pregnancy is hormonal changes and stretching of the skin. Since most drugs for pregnant women are prohibited, use folk remedies: make lotions from oatmeal soaked in milk, wash the skin with decoctions of string, calendula, chamomile. Follow the drinking regime (at least 1.5 liters of clean water per day) and preventive measures.
Hives
Urticaria is considered the most common allergic disease. It is distinguished by a number of features that make it easy to diagnose among other typical diseases. On the skin, urticaria appears as blisters and red swellings that appear consistent with nettle lesions. To get advice on its treatment, you need to contact an allergist and immunologist, which is due to the dual nature of the formation that this skin itch has. Allergies in this case are not always easy to treat, since the rapid progression of urticaria can lead to eczema, bronchial asthma and even anaphylactic shock, which is fatal.
Itching with urticaria is the first and most reliable symptom of the disease, but satisfying the need to relieve pain by scratching the affected areas is strictly prohibited. The best method of overcoming this disease is considered to be medication. Drugs that quickly eliminate urticaria include: calcium gluconate and calcium chloride solution (used orally), solutions of salicylic acid and calendula (for rubbing the affected areas).