Causes
A small lump on the clitoris may turn out to be a common pimple. Such skin defects can also appear in the intimate area. There are several main reasons for the formation of pimples on the external genitalia, namely:
- Skin irritation after depilation;
- Failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules;
- Excessive hypothermia of the external genitalia;
- Wearing low-quality synthetic underwear;
- Poor nutrition, abuse of alcohol, fatty and fried foods;
- Stressful situations, emotional stress;
- Long-term treatment with potent medications;
- Hormonal disorder.
Most acne and skin rashes are not dangerous to the patient's health. A dense white plug on the clitoris may turn out to be an ordinary wen or an ingrown hair follicle. The depilation method must be selected carefully, taking into account the characteristics of your epidermis. If this procedure is carried out incorrectly, the hairs will begin to grow in, and white bumps will appear on the pubic skin in the clitoral area.
Often, a lump on the clitoris occurs due to any hormonal imbalances in the female body or allergies to medications. Such problems are not dangerous and often go away on their own, without additional treatment.
Pathological
A clitoral cyst is a serious disease that is accompanied by the appearance of a lump and lump in an intimate area. The sebaceous glands are closed by the skin, as a result of which they become blocked, and white lumps appear in the groin area. The fatty cyst is removed surgically.
If the Bartholin gland becomes infected or inflamed, a lump may also appear on the clitoris. The progression of this disease leads to inflammation of the labia, pain and discomfort while walking or touching clothing to the formation. This disease must be treated under medical supervision.
A lump near the clitoris is a common symptom of sexually transmitted and infectious diseases. You should definitely consult a doctor and undergo an examination if the appearance of such a lump is accompanied by additional alarming symptoms - burning, itching, fever.
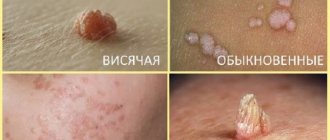
Ball on the labia: photo, possible diseases, removal
Any minor lumps in the female genital area should not be ignored.
The ball on the labia can be small or large, painful or not cause discomfort, located deep in the tissue or directly under the skin.
There are many causes of tumors, one of which may well be oncology. To determine the origin of the ball, additional research is needed (biopsy, histological analysis of a tissue sample).
Although such bumps do not pose a mortal danger, they can cause serious complications. These include:
- Atheroma. An epidermal cyst is characterized by a ball on the labia under the skin, filled with a mass of sebaceous gland secretion. The contents accumulate due to blockage of the excretory duct. The tubercle may have a round or oval shape. But the main difference between atheroma is the black dot in the center of the compaction. The situation becomes dangerous when bacteria penetrate into the clogged airless cavity, causing inflammation and tissue necrosis. The lesion swells, becomes hot, and hurts. The woman’s body temperature rises, and an unpleasant-smelling liquid is released from the cone.
- Lipoma. This is the most common wen, formed from adipocyte adipose tissue cells. The contents are hidden in a soft, movable capsule, which upon palpation resembles a small nodule. Lipoma formation can be triggered by naturally oily skin, increased sweating, hormonal imbalance, bad habits, and neglect of hygiene rules. The wen inside the labia produces mucus and is located directly under the epithelium. It does not cause discomfort, but tends to grow rapidly and often becomes inflamed. Therefore, it is more correct to remove it in a medical facility.
- Myoma. A lump is formed from muscle tissue and is located in the thickness of the labia majora. Its consistency is elastic and elastic, growth is slow, treatment is surgical.
- Fibroma. A pea-sized ball on the labia appears in the submucosal layer of the vagina. It consists of connective cells and collagen fibers, can be soft or hard, has a smooth texture and an oval shape. The growth of fibroma is unhurried, but some of its varieties are prone to malignancy. Treatment of the disease is exclusively surgical.
- Hidradenoma. This seal is formed from elements of the sweat glands and occurs more often in young girls under 20 years of age. These are multiple nodules, not exceeding 10 mm in diameter, pink, yellow or brown. Although hidradenomas do not acquire oncogenic properties, they never disappear on their own. They can be removed through a simple operation.
- Lymphangioma. Cones of lymphatic vessels are localized on the labia majora closer to the inguinal folds. The tubercles of a heterogeneous shape with a bluish tint tend to merge with each other. The swelling is painful on palpation, soft, but with hard inclusions. Lymphangioma grows slowly, but can become infected, so it is better to remove it.
- Myxoma. It is formed from the remains of embryonic connective tissue in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the labia majora. It is diagnosed mainly in older women and requires surgical intervention.
All of the listed pathologies do not pose a threat to life; timely consultation with a doctor will help solve the problem as soon as possible.
Ball on half lips photo
Cancer rarely develops in women under 50 years of age. Due to the inability to independently examine the external genitalia, it is often detected too late. Moreover, in the initial stages there are no alarming symptoms. Then a slight itching appears, intensifying at night, swelling of the vulva occurs, and minor lumps form.
When the tumor reaches a large size, foul-smelling discharge mixed with blood appears. Violation of the general condition (fever, weakness, loss of strength, nausea, drowsiness) occurs even when treatment is ineffective.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland
With bartholinitis, the ball on the labia is most often found on one side, but the bumps can also be symmetrical.
A dense capsule filled with purulent contents forms on the surface of the gland. The woman experiences severe pain, which makes it difficult to move.
The culprits of the disease are various pathogenic microbes that penetrate both from inside the body and from outside. The reasons may be:
- advanced thrush;
- sexually transmitted infections (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, herpes);
- the presence of foci of bacterial flora (streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli and others).
There are acute and chronic (recurrent) forms of the disease. In the first case, an abscess occurs. False if the external duct of the gland becomes inflamed and clogged with secretion. Or true, when purulent exudate causes inflammation of not only the gland, but also the tissues surrounding it.
If the acute process is not treated, then after spontaneous opening of the purulent capsule, chronic bartholinitis develops. The pathological process periodically subsides and resumes, a Bartholin gland cyst is formed.
Inflammation of hair follicles
Folliculitis occurs after injury to the hair root and infection. This is preceded by careless hair removal or shaving, ingrown hairs. A white or yellow lump with a red, inflamed edge forms on the outer labia. A twisted hair is visible inside. A large pimple is filled with pus and is very painful.
Squeezing it out is extremely dangerous, otherwise harmful bacteria can enter the bloodstream and cause blood poisoning. Treatment consists of wiping the affected area with local antiseptics. To absorb the pus, make compresses with Vishnevsky ointment at night.
Fortunately, almost all diseases, the symptom of which is a ball on the half lips, can be treated. If you see a doctor in time, you can even defeat cancer.
Source: https://venerologiya.com/sharik-na-polovyih-gubah.html
Bartholinitis
Have you discovered that the lump on your clitoris is itchy and painful? Then consult your doctor immediately. These symptoms may indicate the development of bartholinitis.
Bartholinite glands are paired organs that are located in the labia area. They produce a lubricant that moisturizes the vagina during intercourse. When a woman experiences sexual arousal, the Bartholinite glands begin to actively produce secretions.
During adolescence, this organ is not yet fully developed, which is why small bumps may appear on the clitoris. Inflammation of the bartholinite glands is called bartholinitis. This disease can be of two types:
- Spicy. The seal hurts when touched, severe inflammation develops, which can be accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
- Chronic. The ball on the clitoris increases from time to time and then disappears without any treatment. The disease periodically worsens and does not go away for a long time.
Chronic bartholinitis is accompanied by complete or partial blockage of the glands and the formation of characteristic compactions. The secretion does not come out and gradually accumulates under the skin. At first, the patient may not notice any alarming symptoms, but gradually inflammation and pain appear.
A ball on the labia - a dangerous symptom or a natural process?
The external genitalia of a woman have a thin folded structure. This is due to the protective mechanisms necessary to prevent infection.
However, there are situations in which one or more lumps are found on the labia or surrounding tissues. There can be many reasons for this, and not all of them are harmless.
Almost all pathologies are accompanied by burning, itching, pain, swelling and heat (due to the inflammatory process). Here it is better not to wait for complications to develop and seek help from a surgeon.
Inflamed hair follicle
The appearance of a ball on a woman’s labia may be associated with the occurrence of a boil (inflammation of the hair follicle). The intimate area has a large number of hairs. Wearing uncomfortable underwear, damaging the protective layer of the skin during depilation and hair removal, and discharge from the genital tract create a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms inside the follicle.
As a result, a ball with whitish contents and a purulent core is formed. The disease is characterized by painful compaction, a red edging around the affected area, and absence of itching.
Treatment should begin immediately by treating the affected area with an antiseptic and applying an antibacterial ointment (for example, Levomekol).
If symptoms increase and swelling of the surrounding tissues develops, you should consult a surgeon to open the abscess surgically.
Thrush
A disease caused by pathological reproduction of the fungus of the genus Candida. Infection occurs through sexual contact, although transmission of the pathogen from mother to child can also occur. The acute course is manifested by copious curdled discharge, a white coating and pronounced itching.
In the absence of adequate treatment, over time it can become chronic, which is characterized by the appearance of small swollen whitish tubercles on the mucous membrane of the perineum and a rash on the labia.
Treatment of the disease should be carried out comprehensively, including the following points:
- antifungal therapy to combat the causative agent of the disease;
- measures aimed at increasing the body's immune defense;
- normalization of vaginal microflora (lacto- and bifidobacteria, lactic acid).
A timely visit to a doctor will help get rid of thrush in 5-10 days.
Herpes genital
The disease is caused by herpes virus type 2 (the second name is genital). The resulting balls are of soft consistency and small in size.
Often grouped together and filled with watery contents. They cause significant discomfort and can manifest as severe, unbearable vaginal itching.
When scratching the affected area, small ulcers form, and the infection spreads to adjacent tissues.
The rashes disappear about a month after the first blisters appear. Even with adequate treatment, the pathology can recur, causing serious discomfort to the woman. It is transmitted sexually, so treatment of both partners is considered mandatory.
Syphilitic chancre
Syphilitic chancre is the primary sign of the development of syphilis. Infection occurs through sexual contact, although contact also occurs. Initially, chancre looks like an area of redness on the skin or mucous membrane.
As it develops, it is separated from healthy tissues by compaction along the periphery with the formation of a hard bottom. It may appear as a pea-sized ball on the labia.
Its size most often does not exceed 1 cm, but in rare cases two-centimeter chancres are also found.
It does not cause discomfort to the woman and proceeds without itching, burning or pain. This is often the reason for the detection of the disease in late stages, when a number of other symptoms are added. The disease is treated at the first or second stage with antibacterial therapy for three weeks; it rarely becomes chronic.
Benign neoplasms
Benign diseases are not seriously life-threatening, but can cause serious discomfort. Possible causes of a ball on the clitoris, labia and perineum include:
- Lipoma. Neoplasm from adipose tissue. It has a capsule that separates it from surrounding tissues. It can be felt as a soft, moving ball on the labia majora (less often the labia minora). The main reason for the development is the increased tendency of the skin to secrete fat in combination with hormonal imbalance.
- Atheroma. It is a cyst of epidermal tissue, the cavity of which is filled with fatty secretion. Develops when the main duct of the sebaceous gland is blocked. A characteristic feature is a black dot in the middle of the compaction.
- Fibroma. A tumor from the submucosal layer of the vagina, consisting of collagen fibers. The consistency ranges from soft to very dense formation.
- Myoma. A tumor of muscle tissue located in the labia majora. Characterized by slow growth.
- Hemangioma. A neoplasm developing from vascular tissue. It is characterized by the most aggressive growth among all benign tumors. It is more common in childhood and manifests itself as a hard ball on the labia minora.
- Hidradenoma. Tumor of sweat glands. It has small sizes (up to 1 cm) and a low growth rate. Color can vary from light yellow to bright pink.
All benign tumors are surgically removed and sent for histological examination. Its purpose is to determine the tissue identity of the tumor and exclude a malignant process.
Complications
Any lump on the clitoris, even an ordinary harmless pimple, requires special attention. Under no circumstances should the surface of the cone be damaged. If you try to squeeze a pimple, it can lead to infection and further infection of the skin in the intimate area.
Ignoring the problem can have serious consequences - profuse painful rashes will appear in intimate places. If a tumor on the clitoris causes you discomfort, gradually increases in size or is filled with pus, you should definitely visit a doctor to determine the exact cause of its appearance.
Any delay may lead to aggravation of the patient’s condition. Often the development of the inflammatory process spreads to the skin around the seal, causing severe pain.
You can diagnose bartholinitis in an intimate area yourself. A woman develops a lump on her clitoris or labia, which feels quite hard to the touch and resembles a grape.
At the very beginning, the new growth is red or pink, but gradually it acquires a bluish tint. At this stage, heat and increased body temperature may occur in the labia area. As the tumor develops, the patient loses a lot of strength, which becomes the main reason for the feeling of fatigue and general fatigue.
During diagnosis, the gynecologist will conduct a thorough examination of the labia, and especially the seal, and take a smear from the vagina to detect genital infections. When the examination results are ready, the doctor will determine the exact cause of the lump and prescribe the most effective therapy.
Vulvar neoplasms
Vulvar neoplasms are tumor diseases of the external genitalia. The formation of foreign bodies may be asymptomatic.
If the tumor develops rapidly, it increases in size, the woman feels discomfort and pain. Accompanied by bloody or purulent discharge from the perineum. Causes itching and irritation of the vulva.
Diagnosed during examination by a gynecologist. Various studies are being carried out. Vulvar neoplasms are recognized by smears and biopsies.
The type of tumor is determined and treatment is prescribed. Benign ones are excised or enucleated. Special technologies and individual therapy are used to treat malignant tumors.
The collection of external female genitalia is called the vulva. This includes the pubis, clitoris, labia, and vestibule of the vagina. The organs serve as a protective barrier for the genitourinary system. The hymen is the boundary between the reproductive system and the vulva. The vulva has a sensitive function.
Her external organs are responsible for arousal during sexual intercourse. The signal is transmitted to the secretion of the glands, thereby moisturizing the vaginal slit. Congenital defects of the vulva include a violation of the development of any organ, for example, hermaphroditism. A visual examination of the vulva can be performed by a gynecologist.
You can do this yourself with the help of a mirror or a sexual partner.
Damage to the organs of the vulva is possible during childbirth and injury. The process is accompanied by pain, swelling, and wounds. Bleeding is observed, the area of the clitoris and vestibule suffers.
The vulva is subject to a number of inflammatory diseases, such as gonorrhea, vulvovaginitis, vulvitis, trichomoniasis, and candidiasis. There are growths: papilloma, condyloma, kraurosis, leukoplakia.
These diseases are frequent precursors to cancer. Treatment includes surgical radiation or medication.
Vulvar neoplasms are found in the following places:
- Pubic area.
- Labia majora and labia minora.
- Cliteral part.
- Perineum and posterior commissure.
- The opening of the urethra.
Benign neoplasms
Frequently encountered benign formations are fibroma, papilloma, and fibroids. Benign tumors are not dangerous. They differ in the following characteristics:
§ slow growth;
§ do not damage other organs with metastases;
§ germination into neighboring organs is not observed;
§ the large size of the growth can compress nearby organs;
§ have clear boundaries.
The danger of neoplasms is that they continue to develop even after all provoking factors have been eliminated. There are several types of benign neoplasms in gynecology:
Myoma. This neoplasm, consisting of muscle fiber, is divided into 2 subtypes: rhabdomyoma and leiomyoma. One is caused by transverse, and the other by smooth muscle fibers. The main characteristics are mobility, dense consistency, independent existence without connection with neighboring tissues. Fibroids are most often diagnosed on the surface of the labia majora.
Fibroma. Consists of connective tissue processes. It consists of bundles of collagen fibrils. Has no adhesions with nearby tissues. It has a leg and a main body. Differs in slow growth. The density of the consistency depends on the degree of compaction of the cytoplasm and collagen fibrils. Location deep in the muscle tissue of the labia. Sometimes found in front of the vaginal opening.
Vulvar fibroids. This neoplasm is found in the large ligamentous muscles. Has combined characteristics of previous types.
Papilloma (condyloma). The formation consists of an epithelial cover. Associated with human papillomavirus. It has a multi-layer structure and rich pigmentation. Mostly brown, sometimes white. External growth.
Spreads singly and multiple times. The leg can be wide or thin. Externally it resembles a papillary shape. Localized on the labia majora and in the vestibule of the vagina. A dangerous type of neoplasm.
After contact with the vaginal mucosa, there is a high risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Lipoma. Fatty structure interspersed with connective tissue. This is a capsule that has a round shape. The consistency is soft. The neoplasm has little mobility. Location: lips or pubis.
Lymphagioma. Consists of lymphatic fibers. There are many cavity grooves on the surface. Visually it resembles a bluish nodule. The consistency is soft. Contains compactions and protein accumulations. Localized in the labia majora.
Myxoma. The tumor is located on the skin of the labia or pubis. It is diagnosed more often in older women. On microscopic examination it has a round shape. The capsule is filled with a light yellow color. The consistency is jelly-like.
Hemangioma. Located on the labia. These are small nodules of a reddish or bluish tint that hang over the skin or mucous membrane. Hemangioma has a capillary structure. It grows quickly. Intensively affects the vaginal tissues, and also enters the uterus and cervix.
Benign tumors, if they do not cause harm to health, can be under medical supervision. Non-progressive and asymptomatic neoplasms are not dangerous. Surgical intervention is used in case of malignancy, exacerbation of symptoms, causing discomfort, acceleration of growth.
If the neoplasm has a stalk, then excision of the base is performed. The tumor is removed from the tissue, and the bed is sutured. If the location is near the urethra, the operation is performed extremely carefully, with the involvement of a urologist. When exposed to a tumor, the urethra can be damaged.
When removing any type of formation, various treatment methods and surgical operations are used. Typically, small tumors do not cause symptoms. Muscle, fibroid and fatty tumors protrude to the surface due to rapid growth. This causes the sensation of a vaginal foreign body.
In the perineal area, a woman feels discomfort, restriction of movement and sexual intercourse. If the integrity of certain types of neoplasms is violated, bleeding occurs. If the tumor affects the bladder, urination is impaired. When pressure is placed on capillaries and vessels, necrosis and hemorrhage appear.
Swelling and pain appear in the vulva area. Swelling changes the color of tissues.
Diagnostic procedures
The vulva is examined during a pelvic examination. A gynecologist performs vaginal examinations. A transvaginal ultrasound is prescribed. If necessary, vulvoscopy and colposcopy. A bacterial smear is examined to exclude infectious diseases. Clarification of the nature of the neoplasm using histological examination. For biological analysis, scrapings and punctures of tumors are taken.
Removing the tumor often causes a new growth to appear. Removing papillomas requires long-term treatment. Surgeries and the postoperative period may occur with complications. Hematomas may form, the urinary system may be disrupted, and severe bleeding may occur.
Types of surgery
Based on the characteristics of the tumor, its treatment is prescribed. Surgical interventions to eliminate this disease:
- Cryodisruption. Nitrogen exposure is carried out. Freezing tissue stops cell development. During the operation, low-temperature liquid nitrogen is applied to the condyloma. The operation is performed without anesthetic. Not painful. The operation was well tolerated. Removing tumors with liquid nitrogen is a special technology; not every clinic performs these manipulations. The operation has minimal complications. There may be a small scar or burn.
- Radio wave excision. A directed flow of low frequencies dissects the tumor. Radio wave is the most gentle method in relation to neighboring tissues. There is no pain. There is no risk of scarring, bleeding, suppuration, or necrosis. Healing occurs in the shortest possible time.
- Laser. A directed laser evaporates the tufted growths. Laser ablation is used to excise resistant condylomas. The skin is not injured, and under the influence of the laser, epithelial cells grow. The depth of laser exposure is controlled. Does not leave scars. No contact with tissue occurs.
- Electrical coagulation. Electric current is used to cauterize the damaged area. The removed material is sent for histological analysis. The process has a number of contraindications. For example, herpes, oncology, hemostasis, inflammation of neoplasms. There are cases of relapse. There may be a small scar on the surface of the vulva.
- Chemical exposure. The destruction method involves applying a special drug to the affected area. A special composition with organic and inorganic acids, nitrates causes burning and death of condyloma cells. It is not accompanied by pain and is used without anesthesia.
- Plasma coagulation. An arc discharge containing gas penetrates the tissue and vaporizes areas with growths. Cauterizes blood vessels. The method has a high level of efficiency. Thermal damage to tissue occurs at a minimum depth, which promotes rapid healing. No scars are formed and pain is minimal.
Malignant neoplasms
The external part of the female genital organs is susceptible to cancer. Young women are diagnosed with papilloma, which most often develops into a malignant neoplasm. Penetrating to the cellular level, the pathogen causes gene changes. This leads to abnormal protein release and accelerated cell proliferation.
Various factors for the development of vulvar cancer are known:
1. Age-related changes. More than half of women over 70 years of age have this diagnosis.
2. Bad habits. Smoking has a detrimental effect on blood vessels. Increases the risk of developing cancer.
3. HIV. The infection weakens the woman's immunodeficiency. The risk of contracting papillomavirus increases.
4. Vulvar neoplasia. Precancerous condition. An abnormal number of epithelial cells are found in the subcutaneous layers, then transform into cancer.
5. Cervical cancer. Oncology spreads to the vulva.
The appearance of malignant tumors is caused by the occurrence of adenoma-carcinomas. They are located in the thickness of the labia. Tumors are mistakenly confused with cysts.
Adenocarcinoma can arise in the Bartholin glands and sweat gland cells of the vulva. Basal cell carcinoma sometimes occurs in this area. Melanomas arise from cells that produce melanin.
It most often occurs in areas of the skin exposed to sunlight.
Vulvar cancer is divided into 4 stages:
1. The first stage of the tumor is caused by tumor growth within the vulva. It does not affect the lymph nodes and neighboring organs.
2. The second stage tumor grows into nearby organs. This can be the vagina, anus and urethra.
3. Neoplasms at the third stage affect the lymph nodes.
4. The last stage is characterized by damage to the lymph, vagina, bladder, and pelvic bones. Metastases penetrate to distant areas.
The stage of the tumor determines the further prognosis of the patient’s life activity and treatment. The growth of the tumor deeper causes manifestations; before this, no prerequisites may appear.
The color of the skin differs significantly from healthy tissues; a pink or red tint predominates. A skin lump appears; it could be a wart, papilloma, or ulcer.
The occurrence of pain, burning and itching.
Many women experience bloody discharge outside the menstrual cycle. These symptoms indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm of the vulva. Adenocarcinoma is located deep in the labia majora and can be palpated, creating the sensation of a foreign body.
Diagnostics
Cancer is diagnosed using a biopsy. High accuracy of the study helps to distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one. A gynecologist examines a woman using a colposcope. The skin is treated with a special solution, which makes the lesions appear more pronounced. If the tumor spreads beyond the vulva, perform the following steps:
- Research of the genitourinary system and rectum.
- Detection of tumor growth and penetration into lymph nodes and organs using CT or MRI.
- Search for metastases using radiography.
Treatment
Without prior consultation with a gynecologist, you do not need to independently treat a lump in the intimate area. If a doctor examines you and diagnoses bartholinitis, you will be prescribed special therapy. Most often, medications are used to treat this disease. Therapy may consist of several main stages, namely:
- If pus begins to accumulate in the seal on the clitoris, it must be opened under sterile conditions, all excess fluid must be pumped out and disinfected.
- To destroy the infection and eliminate the possibility of complications, be sure to take the antibiotics prescribed by your doctor.
- Additionally, you can take baths with antibacterial infusions from time to time.
- Be sure to use special gels for intimate hygiene, and dry only with your own clean towel.
Folk
You can cure a small lump on the clitoris yourself at home. However, this can only be done when you are completely sure that such a compaction is not dangerous. Let's look at some simple home therapy methods.
- Lotions with fresh aloe juice. To make a healing lotion, cut a small leaf of a medicinal plant lengthwise, apply the wet side to the pimple, and then secure it with a band-aid. It is better to apply this lotion in the evening and change it in the morning. Aloe is good at drawing pus out of the bump, relieving pain and reducing inflammation.
- Treating the seal with iodine. This product helps to quickly dry the pimple, disinfect it, and also accelerates its maturation.
- Lubricating the seal with hydrogen peroxide. This treatment will quickly dry out the pimple and avoid infection.
- Compress made from Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment or Levomekol. Such medications for external use relieve inflammation, disinfect, and draw pus from the abscess.
Never try to squeeze out a pimple on your clitoris yourself. It is very painful, and you also run the risk of infection in the wound. The consequences of such actions can be sad - the appearance of bruises, the spread of inflammation, the appearance of new rashes in the intimate area.
Prevention
Bartholinitis and the formation of seals in the intimate area can be prevented. To do this, it is enough to follow the recommendations of the experts presented below.
- Always maintain intimate hygiene. You need to wash your face in the morning and evening, with warm water with the addition of a small amount of intimate hygiene gel. If you have already started an inflammatory process on your skin, use a decoction of medicinal chamomile to wash off.
- If you change sexual partners quite often, be sure to use a condom during intercourse. This way you will protect yourself from dangerous bacteria and sexually transmitted infections.
- Monitor your body's thermal balance, especially in the intimate area. In winter, dress warmly to prevent hypothermia.
- Avoid stress and emotional overstrain. Remember that the state of your immunity largely depends on your emotional state.
Every woman should remember that she needs to visit a gynecologist at least once a year, even if you do not have any complaints. This way you can prevent the development of many dangerous gynecological diseases. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and giving up bad habits is the best prevention of bartholinitis. Try to eat right and pay due attention to physical activity.
Share: