- The most common diseases and their causes
- Diagnosis of diseases
- Treatment of skin diseases on the hands
- Additional recommendations during the treatment of skin diseases
- The use of traditional methods of treating dermatitis and mycoses
- Disease prevention measures
The skin is a very important system of the human body. It performs many functions: from removing toxins to shock absorption. Therefore, any skin diseases on the hands are evidence of serious disorders of the body.
Causes of dermatitis
Skin diseases on the hands can occur for many reasons. The following main factors provoking the development of dermatitis are identified:
- Biological - allergenic vegetables and fruits, some plants (euphorbia, nettle, etc.); exposure to viruses, fungi and other harmful microorganisms.
- Physical - solar radiation, friction and pressure of clothing, thermal effects.
- Chemical – household chemicals, paints and varnishes, acids, industrial chemicals, cosmetics, perfumes.
Also, skin diseases on the hands often appear as a result of dysfunction of internal organs, which are responsible for metabolism and removal of various toxins from the body (kidneys, liver, lymphatic system, etc.). Sometimes inflammation is associated with stress, nervousness, and depression, which provoke hormonal imbalances.
In most cases, dermatitis develops for internal reasons, as well as due to the entry of certain allergens into the body.
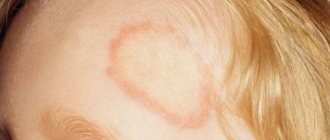
Candidiasis
Candidiasis also refers to fungal diseases. Sores on the hands (photo below) appear due to manifestations of a fungus of the genus Candida.
It is generally accepted that these fungi are conditionally found in the body of every person. They can become painful due to the following diseases: thrush, stomatitis, fungal skin infections.
Symptoms of candidiasis:
Typically, candidiasis begins to manifest itself in the form of harmless itching at night.
A scraping is taken as a diagnostic tool. Treatment is local, and in advanced stages of candidiasis, the doctor may prescribe hospitalization. It is recommended to use antifungal drugs as treatment. For prevention purposes, you must carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
How to identify skin diseases
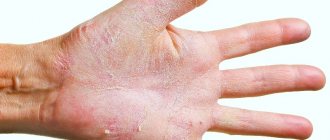
Depending on the cause of inflammation, its external manifestations may differ slightly. In acute forms of dermatitis, intense redness, severe burning, itching and pain are observed. These are typical symptoms that describe skin diseases on the hands. Bubbles, erosions and swelling appear in complex inflammation and can have varying degrees of severity. For example, when damaged by a chemical agent, blisters filled with liquid form, which gradually burst, and in their place weeping erosions remain. After drying, dry crusts form on the affected area.
In the chronic form of dermatitis, swelling of the skin can persist for a long time. The top layer of skin thickens noticeably, the hand turns blue, and its surface becomes dry and flaky. If left untreated, the disease threatens atrophy of the epidermis.
If dermatitis on the hands is caused by mechanical damage, then traces of abrasion remain on the affected areas. Sometimes swelling and blisters filled with serous fluid occur.
Skin diseases on the palms of the hands can take the form of calluses. With further exposure to the irritating factor, yellow-brown plaques form. This part of the skin is more sensitive.
Skin diseases on the fingers very often occur after prolonged exposure to the cold and are expressed in itching, burning and bluish-red swelling.
Classification
It is quite difficult to divide dermatitis into separate types. So far, there is no unambiguous classification of pathology. The disease is divided into types, taking into account the following characteristics:
- localization of lesions (face, limbs, folds);
- area of influence of negative factors (contact, atopic);
- the contact form of pathology is divided into simple and allergic;
- cause of the disease (allergic, toxic-allergic, inflammatory, infectious, fungal, stagnant);
- duration of course (chronic form and acute stage);
- type of rash (erythematous, vesicular, bullous, scaly);
- the nature of the symptoms (dry, weeping, itchy, purulent).
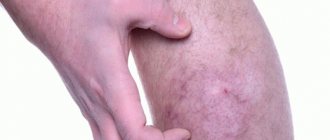
Venous
This form of the disease develops against the background of venous insufficiency of the lower extremities. The disease occurs in people suffering from varicose veins . The following are formed on the skin:
- hyperemic areas;
- dryness;
- seal locations;
- scales.
In severe cases of varicose dermatitis, ulcers form on the feet, legs and other parts of the legs. Treatment is aimed at eliminating varicose veins.
Allergic
When the body is exposed to an irritant, an allergic form of dermatitis develops. External signs of the disease are as follows:
- redness of the affected areas;
- small rash;
- itching and burning.
Increased intoxication leads to the formation of cracks and papules filled with liquid.
Doctors use tests to determine the allergen and eliminate contact with it. Symptomatic therapy will not give positive results if the impact of the irritant is not eliminated.
Cold
The reaction of skin vessels to low temperature is expressed by the development of cold dermatitis. There are 2 reasons for the occurrence of the disease:
- Capillaries spasm when exposed to cold, resulting in impaired blood flow.
- Due to the cold, skin proteins are transformed, which provokes an allergic reaction.
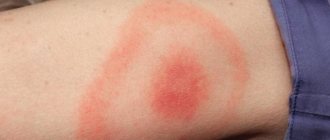
Infectious
This type of dermatitis is caused by various infectious diseases (measles, chickenpox, syphilis) . However, this form of the disease can develop as an independent pathology. The appearance of the disease is provoked by various pathogens:
Dermatitis disappears after suppression of the primary infectious disease.
Stagnant
This form is considered a type of venous dermatitis. Pathological damage to the feet and other parts of the legs occurs if the outflow of blood and lymph is impaired . Appear on the skin:
In the stagnant form of the disease, the skin is very itchy. Epithelial cells do not receive enough nutrients. Secondary damage occurs on the integument, which is infectious and allergic in nature.
Types of skin diseases of the hands
Depending on the cause of development, all skin ailments of the upper extremities are divided into the following groups:
- Contact dermatitis. They are caused by the direct influence of an irritating factor on the skin and are divided into simple (temperature, radiation, chemical burns and mechanical damage) and allergic, which manifest themselves when the body is prone to rashes, as well as when the functions of the immune system are impaired. The main difference between contact dermatitis is the limited influence of the irritant and the rapid recovery of the affected skin after the provoking factor is eliminated.
- Toxidermy. This type of disease occurs as a result of the penetration of a harmful substance into the body, which is manifested by a skin rash. This group of diseases includes neurodermatitis, atopic and dry dermatitis. Their main feature is that the irritant enters the body through airborne droplets and through food.
- Secondary dermatitis is a skin disease that occurs as a result of other ailments of the body, hormonal disorders, etc. Some of them affect the nail plates and the tissues closest to them.
Sores on the hands: photos, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Human skin protects the body from the environment, serving as a barrier between the body and external influences.
Therefore, the skin often suffers from various bacteria and negative factors that cause dermatological diseases. Sores on the hands can indicate either a minor illness or a serious illness.
It is important to consult a specialist in time and get treatment in a timely manner. How do various ailments on the hands manifest themselves? Let's take a closer look.
The causes of skin inflammation are within us
If the sore on the arm does not heal, then perhaps an inflammatory process is occurring inside the body. Thus, changes in the epidermis are affected by the following internal pathologies in the body:
- hormonal changes (usually during puberty);
- nervous tension, stress;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic dysfunction;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
The individual characteristics of the human body are important, since hereditary predisposition and allergic manifestations most often cause changes in the epidermal layer.
Fungal dermatitis
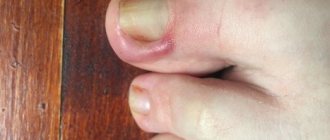
The most common contact dermatitis is fungal diseases on the fingers. You can become infected with them almost anywhere: in public transport, in the gym, in the swimming pool, sauna, etc. Women are most susceptible to the disease during manicures.
Fungal diseases on the hands develop gradually. The nail plate is affected first. Nails acquire a yellowish tint, become brittle and look unkempt. Then the disease affects the folds between the fingers. Fungus on the skin appears as characteristic spots that may become wet or peel. The affected areas may vary in size and range in color from pale pink to blue. Sometimes the folds of the skin dry out and crack.
Most often, this type of dermatitis affects people with weak immunity, diabetes mellitus and endocrine system disorders.
Often, under the influence of physical factors, non-fungal diseases of the fingernails develop. Thus, with frequent hand injuries, onycholysis can develop, in which the nails turn white and separate from the nail bed. This group of diseases also includes grooves, hangnails, and splitting of nails.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease. Pink plaques, spots and peeling appear as external signs. A characteristic symptom is severe itching. Popularly, this disease is better known as a red sore on the arm.
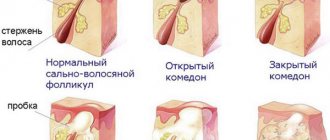
The cause of psoriasis: epidermal cells divide faster than necessary. This leads to the fact that the skin does not have time to develop, so most of the epidermis dies and then peels off. The immune system intervenes in this process. It acts against its own cells. This causes inflamed formations to appear on the skin.
There are several types of psoriasis:
Each type is characterized by its own intensity of development and nature of its course. Most often, plaque and drop-shaped types appear on the skin of the hands.
Psoriasis is characterized by seasonality. The disease may worsen in spring and autumn.
Why psoriasis appears is still unknown. There are many negative factors that provoke the disease:
Treatment of psoriasis should be comprehensive: relief of itching, elimination of external manifestations. In addition to external medications, you need to undergo a course of general therapy.
Psoriasis is not a contagious disease. It is not transmitted in everyday life or through contact with the skin of a patient. It is important not to neglect preventive therapy, since the disappearance of plaques does not mean the absence of the disease. You should periodically consult a dermatologist.
Diagnosis of skin diseases
If you suspect the presence of skin diseases, you should definitely consult a dermatologist or allergist. During the examination, you may also need to consult a neurologist, endocrinologist and gastroenterologist.
Common skin diseases on the hands are diagnosed based on an external examination of the patient and a survey about the possible causes of the disease. If allergic manifestations are suspected, the allergen must be identified. In this case, special skin tests, general and biochemical blood tests, stool tests are carried out, and the performance of the endocrine and immune systems is also determined.
To determine more complex types of dermatitis, additional diagnostic methods can be used: microscopic examination of tissues taken for analysis or bacteriological culture of skin scrapings.
Scabies
Are the sores on your hands itchy? Perhaps this is a manifestation of scabies. A fairly common disease, which is provoked by the active work of the scabies mite.
Dermatologists classify scabies into the following subspecies:
Main symptoms: the formation of a watery red rash on the skin of the hands between the fingers and on the sides of the palms. Severe itching is an additional symptom that worsens during sleep. It is at this time of day that tick activity is observed.
Sores on a child’s hands most often appear in the form of rashes, which are located in pairs. This external manifestation is precisely characteristic of scabies.
This is a contagious disease that is transmitted through contact with the patient's skin or personal belongings. The incubation period of the disease lasts from 7 to 10 days.
If treatment is not timely, the following complications may occur: a purulent infection develops in the form of a rash. Treatment requires the use of sedatives to control severe itching. Scabies can be treated externally and internally.
Treatment of dermatitis
The method of dealing with skin diseases of the hands depends on the cause of their occurrence. For contact, atopic and neurodermatitis, systemic therapy is prescribed, which includes the use of antihistamines, sedatives and vitamins A, B and E. In the case of infectious dermatitis, antibacterial and antifungal treatment is used.
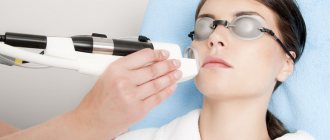
Physiotherapy procedures are often used in combination with drug therapy: laser treatment and sanatorium-resort treatment.
There are some skin diseases on the hands that can only be treated with ointments. As a rule, these are uncomplicated dermatitis with minor symptoms.
In addition to basic treatment, you need to follow recommendations that are important for all types of dermatitis. So, it follows:
- Eliminate exposure to the irritating factor.
- Provide care with nourishing and restorative products.
- Limit water treatments.
- Carry out parallel treatment of other diseases that affect the skin.
- Stick to a diet: during treatment you need to exclude salty, fried, spicy foods, sweets and baked goods, as well as foods that cause allergies (citrus fruits, honey, fruits, mushrooms, etc.).
Prevention of skin diseases
To prevent dermatitis, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid contact with allergens.
- Do not be nervous.
- Take care of dry skin.
- Avoid hand sanitizers.
- Use hypoallergenic powders and rinse clothes thoroughly after washing.
Following these simple rules is not difficult at all. They will help not only prevent unpleasant skin diseases on the hands, but will also help preserve their youth and health for a long time.