General information
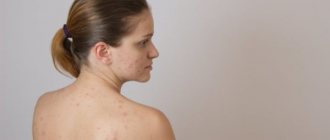
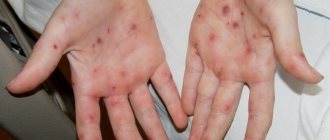
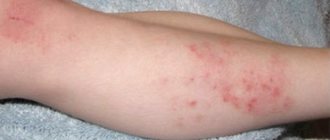
Purulent blisters are skin rashes that can vary in size; their distinguishing feature is the presence of a greenish secretion inside.
They can form anywhere on the body, be it the mucous membrane of an organ or the skin. An abscess is considered a subtype of abscess. The shape of the rash can be cone-shaped, round or flat. Often the diameter of one pimple does not exceed 10 mm. Purulent sores form in the upper layer of the skin, but sometimes penetrate deeper into the dermis. If they are not treated promptly, they may heal.
Causes of pustular rash
Among the most common reasons that contribute to the formation of rashes containing pus are the following:
- Infection in an open wound when picking out pimples;
- Failure to comply with basic personal hygiene standards;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Inflammatory processes in the body;
- Appendicitis.
In addition, ulcers can be symptoms of the following diseases: herpes, scabies, acne and psoriasis.
Factors that contribute to skin rashes include:
- Vitamin deficiency;
- Hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2;
- Diseases of the central nervous system;
- Allergy;
- Disturbances in the production of skin secretions.
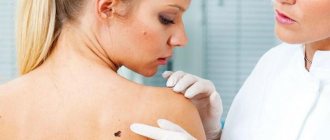
Patient examination plan
Diagnostic measures are aimed at identifying the causative agent and excluding non-pustular skin diseases. The following studies are required:
- dermatoscopy;
- bacteriological culture of rash discharge;
- general blood analysis;
- analysis for the presence of fungi;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- biochemical blood test.
Most purulent diseases can be recognized by their clinical picture. Anamnesis is of great value. During the survey, the dermatologist identifies the patient’s main complaints, the time and conditions of the appearance of the first symptoms, and also establishes possible risk factors for the development of pyoderma. It is necessary to exclude diseases such as anthrax, acne, pityriasis rosea, syphilis and toxicoderma.
Skin damage due to abscess
An abscess is a pathological condition in which inflammation appears in the soft tissues and a cavity forms. It contains pus. Most often, this pathology manifests itself in the neck, head, upper and lower extremities.
The development of an abscess occurs due to a fungal infection. It can become a complication as a result of untreated pharyngitis, osteomyelitis, paraproctitis or damage by pubic lice.
Signs of an abscess:
- Local pain;
- Redness of the skin;
- Painful sensations caused by touch;
- Swelling;
- Feeling depressions in the skin or protruding bumps;
- Increased body temperature;
- Tachycardia.
Other pustular diseases
Impetigo vulgaris is considered mixed pyoderma; it is contagious. The process extends to the skin and its appendages. First, the appearance of hyperemia is observed, later in its place bubbles filled with serous contents appear - phlyctenas. Over time, the contents become purulent and dry out, forming crusts. One of the common areas of localization of pyoderma is the face.
Abscess
Ulcers on the skin can appear as an abscess. It is characterized by the formation of an inflammation process and a cavity that fills with pus. It is most often localized on the limbs, neck, head, and in women - in the axillary area. Women often complain that they have ulcers after sugaring. This can occur if the rules for disinfecting the instruments used are not followed, as well as due to ingrown hairs.
This pathological condition occurs as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skin and the penetration of bacteria. The clinical picture appears:
- pain in the affected area,
- hyperemia,
- fluctuation,
- rapid heartbeat,
- swelling,
- temperature rise,
- tubercles, depressions on the skin.
First, the appearance of redness is observed, which subsequently turns into an infiltrate and an abscess with leukocytes, living and dead microorganisms. The pathological condition is dangerous because it can cause the spread of infection.
READ ALSO: 15 best facial peels - Rating 2020
Features of folliculitis
Folliculitis gets its name due to the fact that this pathology concerns the hair follicles. Caused by a staphylococcal pathogen that has penetrated the tissue through breaks in the skin, folliculitis can cause hair loss.
Among the features of the manifestation of the disease are characteristic:
- Formation of pustules;
- Multiple rashes;
- Localization on the head and groin;
- Soreness;
- Itching;
- The rash is riddled with hairs;
- After the rash disappears, ulcers and crusts remain.
Course of furunculosis
Damage to the hair follicles simultaneously with the sebaceous glands is called furunculosis. This disease is more common in men.
Most often, boils appear in the neck, nose, pelvis, armpits and face.
Stages of furunculosis:
- The formation of an infiltrate, accompanied by redness of the skin around, the appearance of swelling and thickening.
- Formation of a nodule, which over time transforms into an abscess. This stage is characterized by pain on palpation, increase in size, accumulation of pus and formation of a rod.
- The healing stage begins with the opening of the pustules. Next, the general symptoms of the disease subside and the patient’s condition improves.
Clinical picture of furunculosis:
- Fever;
- Painful sensations on palpation;
- General weakness;
- Headache.
Furunculosis can be complicated by meningitis or sepsis
Pyoderma in adults and children
Pustular skin diseases are primary and secondary.
Pustular skin diseases are a large group of diseases caused by staphylococci, streptococci or mixed flora.
The prevalence of this pathology is very high.
Almost every person experiences pyoderma during their lifetime. The following structures are affected:
- epidermis;
- dermis;
- nails;
- hair;
- sebaceous glands;
- sweat glands.
The infection can spread to joints and bones. In severe cases, microbes enter the bloodstream and disrupt the function of internal organs.
Pyoderma in children and adults can be primary or secondary. In the first case, it develops independently. The secondary form can be a complication of other diseases: scabies, diabetes, eczema.
There are staphyloderma, streptoderma and streptostaphyloderma.
Infection may spread to joints and bones
The most common pustular diseases are:
- furuncle;
- furunculosis;
- carbuncle;
- folliculitis;
- vesiculopustulosis;
- hidradenitis;
- sycosis;
- ostiofolliculitis;
- pseudofurunculosis;
- streptococcal impetigo;
- lichen simplex;
- jam;
- ecthyma;
- cellulite;
- paronychia;
- erysipelas;
- mixed form of impetigo;
- ulcerative-vegetative chronic pyoderma;
- cicatricial folliculitis.
The greatest danger is posed by deep pyoderma.
Causative agents of pustular diseases
In children and adults, pyoderma is caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are representatives of the natural human microflora. Their habitat is the skin. Most staphylococci and streptococci belong to opportunistic microflora, but some of them are pathogenic.
Staphylococci produce toxins
Staphylococci play a major role in the development of pyoderma. These bacteria have the following distinctive features:
- are normal inhabitants of the skin;
- found in large quantities under the nails and in the folds of the skin;
- represented by 20 species;
- unable to move;
- spherical shape;
- undemanding to the nutrient medium;
- can cause allergic reactions;
- have different pathogenicity factors.
Staphylococci produce toxins (sphingomyelinase, alpha toxin and exfoliative toxin). Other pathogenicity factors of these bacteria are adhesins, protein A, enzymes and capsule. All of them help microbes maintain their numbers, penetrate the skin and survive under unfavorable environmental conditions.
Streptococci in children and adults have a spherical shape. They are arranged in the form of chains. Streptococci produce toxins, enzymes and protein M. These bacteria are isolated in every tenth patient with pyoderma. They are very stable in the environment. Streptococci can withstand low temperatures.
Causes of pustular diseases
Abscesses on the body in children and adults form for various reasons. The following predisposing factors are of greatest importance:
- presence of scabies;
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- viral diseases;
- overwork;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- chronic kidney and heart diseases;
- foci of chronic infection;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- skin microtraumas;
- malignant tumors;
- radiation or chemotherapy;
- autoimmune diseases;
- cachexia;
- hypovitaminosis;
- overheating;
- obesity.
Microbes begin to manifest their properties when the body’s resistance decreases. Immunity impairment can be local or general. In the first case, the barrier (protective) function of the skin decreases. This makes it easier for bacteria to penetrate the skin.
Risk factors for the development of pyoderma are overwork, poor nutrition, childhood, skin contact with various chemicals and irritants, environmental pollution and sweating. Children under 4 years of age often get sick.
Hidradenitis as a type of pyoderma
Adults may develop a pathology such as hidradenitis. This is a purulent disease characterized by damage to the sweat glands. The causative agents of infection are staphylococci. Hidradenitis does not develop in childhood and old age, since during these periods the sweat glands practically do not function.
Predisposing factors are puberty, menopause, changes in skin pH, hyperhidrosis, obesity, diabetes mellitus, impaired thermoregulation, diaper rash and skin maceration.
Hidradenitis is characterized by damage to the sweat glands
The following areas are most often involved in the process:
- armpits;
- crotch;
- scrotum;
- labia majora;
- breast halos;
- scalp.
In most patients, the axillary area is affected.
The inflammation is unilateral. The following symptoms are observed:
- itching;
- dense nodules;
- paired blackheads;
- change in skin color over the node;
- soreness;
- edema;
- pain;
- sleep disturbance;
- fever;
- headache;
- weakness.
Initially, a node up to 2 cm in size appears. After a few days, it suppurates.
If treatment is not carried out, there is a risk of developing sepsis
Black dots appear near the node, resembling blackheads or purulent pimples on the face. The color of the skin in the area of suppuration becomes red-blue. Swelling occurs. It is caused by stagnation of interstitial fluid. Multiple nodes can merge with each other.
In this case, a large infiltrate is formed. The sweat gland tissue is destroyed. A cavity forms and fills with pus. At first the knot is tight, but then it softens. The symptom of fluctuation is characteristic.
A necrotic core does not form in hidradenitis. The abscess opens. During this period, the general condition of the person improves.
An ulcer appears at the site of the node, which leaves behind a scar. If treatment is not carried out, then there is a risk of developing phlegmon, sepsis and lymphadenitis. Frequent relapses are possible. Sometimes this pustular disease becomes chronic. The total duration of hidradenitis is about 2 weeks.
Formation of boils on the skin
A purulent pathology such as a boil can occur in children and adults. In everyday life it is called boil. This is a form of staphyloderma, characterized by purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and involvement of surrounding tissues in the process. This disease should not be confused with carbuncle. In the latter case, several hair follicles are affected at once.
The boil has 3 stages of development. It all starts with the appearance of an infiltration zone. The affected area of the skin turns red, swells and becomes dense. The diameter of the infiltrate reaches 2-3 cm. The skin becomes painful.
The hair is located in the middle. Most often, boils appear where the skin is most dirty and subject to friction.
This could be the neck, back, chest, groin area and buttocks. Sometimes the lips, cheeks and eyelids are affected. In the second stage, suppuration occurs. A rod is formed. This happens within 3-4 days. Signs of intoxication of the body appear. The necrotic core ends in a pustule. Pus is represented by dead tissue and lymphocytes. After opening the boil, the general symptoms disappear. Stage 3 is characterized by skin healing. A scar forms, which then fades and disappears.
Vesiculopustulosis in newborns
In young children, a disease such as vesiculopustulosis is diagnosed. This pathology is most often caused by staphylococci. Otherwise, this disease is called bullous impetigo. The terminal sections of the baby's sweat glands are involved in the process. This is the most common dermatological disease of newborns. In most cases, the first symptoms appear 5-7 days after birth.
Vesiculopustulosis is most often caused by staphylococci
The risk group includes premature babies. The most common pathogen is Staphylococcus aureus. The pathogenesis is based on damage to the skin. In babies they are thinner, more tender and vulnerable.
Predisposing factors are improper child care, high or low air temperature, artificial feeding, infection with the human immunodeficiency virus, excessive sweating, the presence of pustular diseases in the mother and improper swaddling.
The following symptoms are observed with this skin disease:
- pink rash;
- fever;
- tearfulness;
- dry mucous membranes;
- decreased appetite;
- restlessness.
Exanthema may be the only sign.
Exanthema may be the only sign of the disease
It is formed by vesicles (bubbles). These morphological elements have the following features:
- up to 5 mm in diameter;
- have a red corolla;
- Pink colour;
- contain serous secretion;
- single or multiple;
- prone to fusion;
- quickly spread throughout the body.
After some time, pustules appear. They are represented by pustules. There is purulent exudate inside. Pustules open and erosions form.
Forming crusts fall off and do not leave behind scars. Complete healing occurs. Initially, the rash is localized in the head, upper back, buttocks and folds.
If treatment is carried out late, complications such as sepsis, abscesses and phlegmon are possible.
Development of sycosis in adults
Pustular diseases of the scalp include sycosis. The development of this pathology is based on a violation of the sensitivity of hair follicles. Predisposing factors are:
- chronic rhinitis;
- cuts while shaving;
- microtraumas;
- chronic conjunctivitis;
- plucking nose hair with tweezers.
Sycosis often causes hair loss
With this form of pyoderma, the scalp of the face is affected. Most often, pustular rashes appear in the area of the mustache, beard, wings of the nose, eyebrows and the edge of the eyelids.
Sometimes the axillary areas and pubic area are involved in the process. Men are most often affected. Initially, folliculitis develops.
Many small pustules (pustules) appear on the skin. They open up and dry out. The skin of sick people becomes covered with yellowish crusts. Additional symptoms include redness and swelling.
With sycosis, the morphological elements of the rash have a dense base. They are bright red in color and are found in groups.
There is pain when touching the skin. Itching and burning are rare. The general condition does not change. Regional lymph nodes do not enlarge. In the parasitic form of sycosis, the symptoms of inflammation are less pronounced. This pathology has an acute course.
Relapses are not observed. Lupoid sycosis often causes hair loss.
Erysipelas of the skin
The group of streptoderma includes erysipelas. The process involves mucous membranes and skin. This is one of the most common bacterial diseases. Erysipelas is found everywhere. The incidence rate reaches 20 cases per 100,000 people. Symptoms most often appear in summer and autumn.
Erysipelas is included in the group of streptoderma
Women get sick more often than men. The risk group includes people with chronic tonsillitis, damage to the teeth and pharynx. Erysipelas is a contagious disease.
Transmission of microbes is possible by contact and aerogenic mechanisms.
Predisposing factors are:
- rare hand washing;
- injuries to the skin and mucous membranes;
- venous insufficiency;
- violation of lymph outflow;
- mycoses;
- disruption of tissue trophism;
- overweight;
- presence of diabetes mellitus.
The incubation period reaches 5 days. The disease begins acutely with fever, chills, pain in the head and muscles. Sometimes there is impaired consciousness and vomiting. After some time, itchy skin appears in a certain area.
Symptoms of erysipelas most often appear in summer and autumn
This area thickens and becomes painful. There may be a burning sensation. Later swelling and redness occur.
Areas of hyperemia have clear boundaries and uneven edges. They are bright red, sometimes with a brown tint. When pressed, the hyperemia disappears for a few seconds. Local temperatures rise. Bubbles with serous or purulent secretion appear. Sometimes hemorrhages occur.
The skin most often affected is the cheeks, corners of the mouth, nose, forearm, legs and scalp. Fever may persist for more than a week.
A characteristic sign of erysipelas is lymphadenopathy. After the red spots disappear, slight peeling of the skin is observed. If treatment is carried out incorrectly, abscess, phlegmon, thrombophlebitis, sepsis and pneumonia develop.
Formation of pus in sycosis
Neuroendocrine disorders often lead to sycosis. This pathology more often affects representatives of the stronger sex and develops against the background of rhinitis or conjunctivitis, which are chronic.
The following are more often affected than usual:
- Nasal mucosa;
- Skin of the nose;
- Eyebrow arches;
- Eyelids;
- Skin around the mouth and chin;
- Pubic area.
Sycosis begins with redness of the skin. Then pustules begin to form in this place. They fill with pus and become disc-like. Groups of ulcers may disappear for some time and then appear again. Folliculitis becomes more and more deep.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- The appearance of edema;
- Skin hyperemia;
- Increased sensitivity of affected areas;
- Soreness.
After opening the abscess, a yellowish crust forms in its place.
Other diseases accompanied by a pustular rash
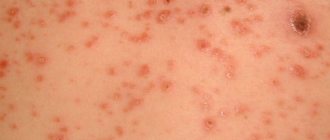
Vulgar impetigo is a type of pyoderma that has a mixed etiology.
This pathology is contagious to others. There is a high probability of damage to internal organ systems. The pathological process affects the skin and its appendages. The primary symptom of the disease is redness of the skin. At this site, over time, vesicular-type rashes with serous content begin to form.
After a certain period, pus forms inside. The development of the disease is acute. In place of the blisters, crusts appear after the pus flows out.
The disease is characterized by two features: children are more susceptible to the disease than others, and the localization of the rash occurs on the face. Sometimes the disease can become chronic.
Often there is the formation of carbuncles - ulcers that simultaneously affect several follicles.
Characteristic features:
- The disease usually manifests itself in the summer;
- Affects the face, but may affect the area between the shoulder blades, gluteal area and neck;
- The size of the carbuncle is several centimeters;
- Ripening occurs within 7-10 days;
- Accompanied by fever and pain;
- After opening the pustule, a scar remains;
- Often requires surgical intervention.
What to do and how to treat?
Traditional methods
Therapy is prescribed only after the cause of the appearance of ulcers on the skin has been determined. It is possible to cope with the problem through medications of various effects. Ointments and other local medications are effective for purulent acne. In advanced cases, tablet forms of medications are prescribed. Eliminate ulcers with the medications indicated in the table.
| Medication group | Name |
| Antibacterial drugs | "Unidox Solutab" |
| "Erythromycin" | |
| "Azithromycin" | |
| "Doxycycline" | |
| Tetracycline ointment | |
| Medicines that suppress the activity of the sebaceous glands | "Tretinoin" |
| "Adapalene" | |
| "Isotretinoin" | |
| Sorbents and dietary supplements containing lactobacilli | "Polysorb" |
| Activated carbon | |
| "Linex" | |
| "Lactofiltrum" | |
| Topical medications | Zinc ointment |
| "Levomekol" | |
| Salicylic acid |
When treating ulcers, it is necessary to adjust the daily diet. The patient needs to exclude all harmful products that negatively affect the condition of the epidermis and the function of the sebaceous glands. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also recommended. It is possible to cope with purulent acne using ultrasonic waves. It is especially important during this period to monitor the hygiene of the entire body, especially the area affected by ulcers.
READ ALSO: Acne - causes, signs, symptoms and treatment
Treatment with folk remedies
If a pustular rash has formed on the skin, you can use natural substances. Since such acne is dangerous, such treatment must be combined with traditional methods. When ulcers appear, you can remove them using the following recipes:
- Agave juice. This medicine is aimed at drawing out purulent fluid. To stop the pathological process, you need to apply an aloe leaf, cut in half, to the pimple.
- Calendula. A plant-based tincture is used to wipe the affected areas. It is recommended to treat ulcers with the addition of honey and apply medicinal lotions.
- Healing mixture. To prepare the solution you will need to mix birch and nettle leaves, dandelion and burdock roots. At 2 tbsp. l. medicines use half a liter of boiling water. Place on the fire for a quarter of an hour, strain and cool. Take orally 3 times a day.
- Onion applications. To eliminate the abscess, use a vegetable, which is baked and fixed on the affected area with a plaster. It is recommended to carry out the manipulation before going to bed.
Return to contents
Treatment of suppurations
When the question arises of how to treat pustular formations on the skin, they usually resort to the following groups of drugs:
- Local gels and ointments are designed to act directly on the lesions;
- Systemic medications with antibiotic action – affect the patient’s body as a whole;
- Bacteriophages;
- Toxoids or vaccines;
- Immunostimulants and immunomodulators.
Therapy will depend on the severity of the disease, other pathological processes occurring in parallel with the underlying disease, as well as on the patient’s immune system.
The skin is treated with antiseptic agents. These are:
- Fukortsin,
- Chlohexidine C,
- Betadine.
In addition, the use of a weak solution of potassium permanganate and brilliant green has a good effect.
Systemic antibiotics are prescribed if the skin condition is too advanced and cannot be treated with topical agents. In this case, penicillin, tetracycline or aminoglycoside drugs may be prescribed.
Systemic therapy involves the following stages:
- Relief of exacerbations from internal organs.
- Therapeutic diet. It is recommended to exclude fatty, hot, spicy and canned foods from the diet, and increase the consumption of vegetable fats and clean water.
- If a patient has a tendency to allergies, he is prescribed antihistamines and a hypoallergenic therapeutic diet.
- If the rash is differentiated as a boil or carbuncle, surgical intervention may often be necessary. Then the preparatory stage begins with taking steroid and antiallergic drugs. And after opening the pustules, the wound is washed with hydrogen peroxide, and compresses with ointments are applied to kill bacteria.
- Antibacterial drugs can be prescribed only after a culture test of the discharge has been performed. When will the degree of sensitivity to antibiotics be determined?
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. This is usually electrophoresis using antibacterial drugs or ultraviolet irradiation.
We recommend reading:
List of the best ointments that draw out pus from wounds;Ointments for wound healing;
The best acne remedies are.
Common causes of ulcers and ways to eliminate them
Abscesses on the body, or pustules , can appear on various parts of the body. It is not always possible to predict their appearance. The diameter of the pustules reaches 3-5 mm, their head is pointed, like a cone, or convex, in the shape of a hemisphere.
Pus forms inside the pustules, which comes out when the membrane breaks through. In place of the abscess, an open wound remains, which can take a long time to heal, and the skin around it turns red.
Doctors name several common reasons for the formation of purulent acne on the body. These include:
- individual characteristics of the skin (tendency to hyperkeratosis, when the upper cells of the dermis become denser and drier, and after complete keratinization exfoliate, sebum is distributed unevenly over the surface of the skin, thereby creating favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms);
- excess production of sebum (as a result of long-term use of steroids and other drugs, or as a result of diseases of internal organs);
- premenstrual period;
- conceiving a child;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules (sweat that accumulates on the surface of the skin mixes with sebum, thereby provoking the proliferation of harmful bacteria);
- nervous exhaustion, depression, stress;
- a sharp weakening of the immune system (after suffering from a cold, etc.).
With hyperkeratosis, the skin of the body requires special care, including timely exfoliation and softening.
All other common causes are easy to eliminate: take a shower regularly, choose the right bath gels and foams, as well as a sponge (loofah), pay attention to the condition of the skin before menstruation, strengthen the immune system, etc.
In addition to the general ones, there are also specific reasons for the appearance of ulcers on the body. Here a lot depends on their location.
What should you not do if a rash with pus occurs?
First of all, as with the manifestations of any other disease, you cannot self-medicate.
If you start using absorbable ointments without a doctor’s prescription, you can provoke the spread of pathological formations to neighboring areas of tissue. As a result of independently prescribing a course of treatment, complications such as abscess, phlegmon, sepsis, damage to internal organ systems can occur, and in the worst case, death is possible.
In addition, it is not recommended to squeeze or open pustular pimples. This can be especially dangerous during the period of maturation of the formation, since the contact of microbes with the surrounding healthy area of the epidermis causes the spread of the rash and an increase in the lesion. The treatment process may be delayed, and the disease may become chronic.
Important! The area of the nasolabial triangle is called the “triangle of death.” Squeezing pus out of pimples that appear on this area of the skin can cause serious complications, including encephalitis, meningitis and inflammation of the nerves in the brain.