A boil on the chest is a purulent-inflammatory infiltrate that develops due to the proliferation of staphylococci inside the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. The formation is accompanied by intense pain, swelling of the surrounding tissues, and redness of the skin. The chest boil tends to open on its own. Drug therapy facilitates the inflammatory process.
Reasons for the formation of a boil on the chest and its code according to ICD 10
A boil on the chest (code L02.2 according to ICD-10) is formed as a result of the active reproduction of opportunistic microflora in the structures of the skin. A number of factors contribute to the development of the pathological process:
- A weakened body provides a favorable environment for the life of microorganisms.
- People with endocrine diseases (diabetics, thyroid pathologies) suffer from boils localized on the chest.
- Bad habits are provoking factors for the appearance of abscesses. Smoking and drinking alcohol lead to a weakening of the body's defenses. The chain reaction ends with staphylococci entering the hair follicle and sebaceous gland on the chest.
- Lack of sleep, constant nervous tension, lack of vitamins and minerals increase the risk of viral and bacterial diseases due to weakened immunity.
- Hormonal disorders can provoke activation of pathogenic microflora of the boil.
- Dirty skin becomes a haven for many bacteria that get inside the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and cause abscesses. The situation is typical for the warm season. A person sweats a lot and rarely takes a shower, which causes breast formation.
- The culprit for the development of boils in nursing women may be their child. During feeding, he injures the nipples with his teeth, damage to them becomes an entry point for infection.
- Prescribing cytostatics and glucocorticoids for a long time can cause the development of staphylococcus.
A boil on the mammary gland will not appear in people who do not have a history of the listed risk factors.
To control the situation on the mammary glands, you need to properly care for them and properly treat acquired pathologies in a timely manner.
Effective methods of treating and preventing pathology
Treatment of boils on the chest involves the use of:
- Local therapy.
- Systemic medications.
- Physiotherapy.
- Surgical intervention.
During the initial visit, the patient is also given a number of recommendations:
- frequent change of underwear;
- restriction of water procedures on the affected area;
- elimination of overheating;
- a diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables.
If an abscess appears in a nursing mother, then the following is indicated:
- temporarily stopping the baby from attaching to the affected breast;
- regular pumping;
- wearing a loose bra.
Local therapy is the main way to influence boils. Recommended for these purposes:
- Pulling ointments – Levomekol, Ichthyol.
- Disinfecting solutions – Fukortsin, Diamond green.
- Antiseptics: Hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine.
- Drugs that improve the discharge of the purulent core - Himopsin.
- Antibacterial ointments – Lincomycin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin.
- Products that improve tissue regeneration – Solcoseryl gel.
The use of these drugs is permitted during lactation due to the low amount of active substances entering the blood. They are allowed to be used independently at home before consulting a specialist. However, it is not worth treating boils on the chest with local remedies during lactation in order to avoid negative consequences for the child.
General treatment is always carried out when the disease is detected in women. Purpose shown:
- antimicrobial drugs;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamins;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (for severe pain, fever).
Pregnant and lactating women can use:
- Antibiotics: Amoxicillin, Ceftriaxone.
- To increase immunity - suppositories Genferon, Viferon.
- Among the antipyretics and painkillers – Ibuprofen.
There is no need to stop breastfeeding completely. This is due to the fact that the listed products are approved for use from the first days of a child’s life. However, you should not choose your own treatment regimen at home. Only a doctor can assess the risks of using drugs for the fetus/child.
Surgical treatment is indicated for large abscesses. The procedure is performed by a surgeon in a sterile operating room on an outpatient basis. Afterwards, local and general therapy is definitely recommended. Management tactics, medications, and duration of treatment are selected individually by the doctor. The average course is 7-10 days.
Prevention of boils is important for all people, but it is especially necessary for pregnant and lactating women, as well as people with weakened immune systems. It is worth saying that specific methods for preventing the disease have not been developed. For these purposes it is recommended:
- proper organization of breastfeeding;
- prevention of cracked nipples;
- “air” breast baths;
- personal hygiene;
- wearing special bras.
The appearance of boils on the chest is a reason to consult a doctor. The high risk of developing purulent complications, including amputation of the mammary gland, indicates the seriousness of the pathology, so self-medication is extremely undesirable.
Localization of boils on the chest in women and their danger
The boil appears in areas with hair and sebaceous glands. The breast has both conditions for the formation of an abscess. Pregnant and lactating women are at high risk of development. Their weakened immunity and sensitive mammary glands become a trigger for the proliferation of staphylococci.
Boils on the chest have a variety of localizations:
- A boil never occurs on a nipple where there is no hair. The formations are located on the areola. This area has rich innervation. A characteristic symptom of damage to the areola is shooting pain. It is combined with the release of pathological fluid and enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes. With a prolonged course of the pathology, the nipple becomes deformed.
- A boil appears under the breast in women with large mammary glands. Increased sweating and poor hygiene provoke the appearance of abscesses. The educational clinic is characterized by constant pain and low-grade body temperature. The location is dangerous. It is difficult to provide therapeutic care for abscesses in this area. The inflammatory process may be delayed with the development of complications.
- Localization on the mammary gland and between the breasts is accompanied by mild pain, aggravated by wearing a tight bra.
The danger of locating a purulent abscess on a sensitive area of the chest threatens the following consequences:
- The spread of bacterial infection deep into the mammary gland leads to the formation of mastitis.
- An untreated condition can become a source of blood poisoning. The entry of staphylococci from a boil into the vascular bed threatens the development of bacteremia and breast sepsis.
- A bacterial infection easily penetrates the brain through the lymph and blood flow. The situation ends with meningitis and encephalitis.
To prevent complications of breast pathology, you need to promptly seek qualified help. The following conditions require mandatory medical consultation:
- The inflammatory process of the boil has captured the surrounding cells and tissues.
- High temperature is difficult to correct and lasts for more than 3 days.
- Due to the disease, the lymph nodes became enlarged.
- Mastitis developed.
- There is furunculosis on the chest, an abscess or phlegmon.
Early treatment of the condition guarantees successful recovery and prevents unpleasant complications.
Effective methods of treating the problem
Treatment of the disease largely depends on the condition and stage of its progression. Today, the following are used to treat boils:
- Traditional medicine methods.
- Folk remedies.
Good results are achieved using physiotherapeutic procedures:
The patient should be under the supervision of a doctor until complete recovery.
Drug therapy
Among the medications used to treat pathology are:
- Ointments with a pulling effect (Vishnevsky, Ichthyol, Levomikol).
- Disinfecting liquids (Fukortsin).
- Antiseptics (Chlorhexidine).
- Medicines that improve the output of the abscess core (Chymopsin).
- Antibacterial ointments (Tetracycline).
- Medicines that enhance tissue repair (Solcoseryl).
- Antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Amoxicillin).
They can be used at home before seeking medical help. However, experts emphasize that it is not necessary to treat abscesses on the mammary glands with topical medications if a woman is pregnant or breastfeeding. Such carelessness can harm the baby.
Regarding general treatment, the following are recommended:
- Antimicrobial drugs.
- Immunostimulating agents.
- Vitamins.
- Anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications (for severe pain and fever).
Surgery
Surgical assistance is required in cases where the abscess has become alarmingly large and the abscess affects a large area.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis and is almost painless using local anesthesia. The total procedure time is 30-40 minutes.
The doctor will make an entrance hole (a small incision in the tissue) and open the boil. Using a special sterile instrument, all pus will be cleaned out and the necrotic core in the form of a dead hair follicle will be removed.
Next, the specialist will treat the wound with an antiseptic solution (for example, furatsilin or hydrogen peroxide), inject an antibacterial drug and make a bandage. After surgery, local and general treatment is indicated.
ethnoscience
Medicines have a number of side effects, so in some cases it is advisable to use alternative medicine recipes, this is especially important during pregnancy and lactation. The onion is baked in the oven, cooled slightly, then cut into two parts and applied to the sore spot.
The compress is changed 3 times a day
The onion is baked in the oven, cooled slightly, then cut into two parts and applied to the sore spot. The compress is changed 3 times a day.
If the boil is located on the nipple, you need to be careful. Before using the medicine, the skin around the abscess is treated with vegetable oil, then covered with a thin cotton cloth, and then onions are applied
Potato
The root vegetable is thoroughly washed, peeled and grated on a fine grater. The resulting pulp is wrapped in gauze and applied to the affected area overnight.
Nail and honey
This folk method can help cure an abscess. They take a rusty nail, heat it red-hot and dip it in linden honey. After some time, a dark mass resembling tar appears around the nail, which is used to smear the boil.
A small aloe leaf is cut in half and the cut side is applied to the affected area. A bandage or wide bandage is applied on top. The compress is changed every 2-3 hours, adding a fresh leaf of the plant.
Herbal compress
To draw out a boil, healing compresses based on ficus, plantain or tradescantia leaves are often used.
The selected plant is ground into a homogeneous paste, wrapped in one layer of gauze or bandage and applied to the affected area in the evening. The next morning the compress is removed.
Egg treatment
Boil a dozen or more eggs. The yolks are separated from the whites and transferred to a strainer and kept over the fire. After a while, liquid appears from them, which is carefully collected and lubricated with it on the affected area.
Features of the formation of a boil on the chest of a man
According to statistics, men are susceptible to boils 10 times more often than representatives of the opposite sex. Painful breast lump goes through three main clinical stages:
- The infiltrative phase is characterized by the appearance of an inflammatory infiltrate. The formation is accompanied by painful sensations such as tingling. The redness area gradually expands.
- After 4 days, the stage of suppuration begins. It is accompanied by a temperature reaction of the body and the formation of a purulent-necrotic core. After a couple of days, the boil, localized on the chest, opens. The patient's temperature and general well-being are normalized.
- In the third stage, the skin defect heals with the formation of a scar on the chest.
In men, the formation of an inflammatory seal is associated with insufficient hygiene, increased sweating, frequent hypothermia, and bad habits.
Symptoms
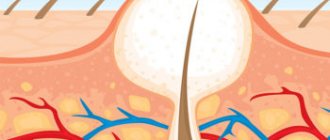
The main symptom of the disease is a painful cone-shaped lump, which goes through several stages of development:
| Stage of development of soft tissue infiltrate | There is a slight swelling, the skin turns red, and a formation resembling a pimple appears. |
| Stage of suppuration of the hair follicle/tissue necrosis | The boil thickens, the skin on it shines, and a white dot appears in the middle. This is the necrotic core, which indicates suppuration of the hair follicle and necrosis of surrounding tissues. The body suffers from general intoxication. |
| Necrotic core exit/healing | The pus presses on the walls of the boil, as a result of which it “opens”, releasing a purulent core. If the wound is well cleaned, the breakthrough site will heal quickly enough, filling with granulation tissue. |
Every patient can tell about the accompanying symptoms of the “ripening” of a boil, since they are often individual in nature:
- moderate/severe pain (depending on the location of the boil);
- decreased ability to work;
- temperature increase;
- weakness/malaise;
- headache.
How to treat a mass on the sternum
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Treatment of a boil on the female breast is carried out in two ways: medication and surgery. The choice of method of influence depends on three factors: the stage of formation, the severity of the process, and medical restrictions on the use of the proposed therapy.
Drug treatment can reduce the unpleasant manifestations of the disease, speed up the release of pus, and wound healing. Effective means of combating boils on the chest include:
- Local preparations with drawing properties make it possible to remove pus from the necrotic area and promote the activation of reparative processes. Compresses are made with them, which are changed 2-3 times a day. Local preparations with a pulling effect include Vishnevsky's liniment, Ichthyol ointment and Levomekol.
- When applying a compress to a boil, it is important not to introduce a new infection into the inflammation site and to reduce the number of microorganisms inside the formation. Disinfecting liquids such as Fukortsin, Chlorhexidine, and hydrogen peroxide cope with this function. The listed means are used to treat the inflamed area and surrounding breast tissue before applying antibacterial, wound-healing drugs.
- In the second phase, it is necessary to speed up and facilitate the exit of the pustular rod. Doctors advise using Himopsin.
- Staphylococci are the main cause of breast boil formation. To achieve recovery of the patient, they resort to the use of antibiotics locally and systemically. Penicillins, Macrolides, and Cephalosporins in tablets, powders, and ointments are used for treatment.
- In order to restore tissues damaged by pathology, Solcoseryl gel is used.
Surgical treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- The patient developed complications of the disease.
- The breast boil does not break out for a long time.
- There were signs of systemic damage.
- There are several boils in one place.
Surgical intervention is carried out as follows:
- The pathology site is treated with antiseptic drugs (iodine, Betadine, Miramistin).
- The breast boil is injected with local painkillers such as Lidocaine, Novocaine.
- When the anesthesia takes effect, they begin to open the boil.
- The surgeon cuts the abscess and removes the pathological contents.
- Then he places a drainage and bandages the postoperative area.
- Discusses the dressing days with the patient and gives recommendations on wound care.
To prevent the recurrence of breast boils, doctors advise taking preventive measures:
- Purchase your own hygiene items. They should not be given to anyone.
- Daily bath procedures are the key to beauty and health. Microbes will not be able to resist the local immunity of well-groomed skin.
- Skin lesions of varying depths must be promptly treated with antiseptic drugs.
- A balanced, fortified diet will help strengthen the body's protective functions.
Timely treatment of furunculosis and proper skin care provide a favorable prognosis for the pathology.
Prohibitions: what you absolutely cannot do
Incorrect treatment tactics and independent manipulation can lead to serious complications.
What not to do with boils on the chest:
- Squeeze out the abscesses, otherwise the infection will spread to adjacent healthy tissues.
- Use compresses, create conditions for the surface of the skin to become wet. If the boil does not dry out, the pus will accumulate inside and will not be able to break out.
- Engage in self-treatment when new boils or other signs of complications appear.
- Use medications for a long time that do not lead to positive dynamics on days 3-5. The infection can be mixed, and the remedy does not act on all possible pathogens of the purulent process. Then there will be no effect from the treatment.
What not to do if an abscess forms on the chest
At home, when treating a breast boil, the following actions are prohibited:
- Do not try to squeeze out the pus. During mechanical impact, the pathological focus may become infected for the second time. Squeezing the boil leads to the spread of its contents into the deep layers of the epidermis.
- Massage movements of the chest will have a similar result with mechanical action.
- The boil should not be wetted, nor should wet compresses be applied to it. A moist environment will become a breeding ground for new bacteria.
- During the treatment of pathology, one should not overdo it with drugs and folk remedies. Getting rid of the formation should be discussed with your doctor.
A breast furuncle is an intradermal focus of inflammation caused by the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. With the right approach to treatment, a person can be cured within a week. Adequate prevention of the disease will prevent relapses.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Causes
The appearance of purulent cavities in the mammary glands in women is provoked by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, which contribute to the necrosis of healthy cells and melting of the tissue.
Associated factors provoke the development of inflammation of the mammary gland with the formation of an abscess:
- mastitis – when breast milk stagnates, the infection spreads quickly;
- traumatic lesion - bruises, scratches, open wounds, abrasions, especially with the formation of a hematoma, which suppurates with encapsulation of pus inside;
- an abscess can form in the presence of cysts; when the ducts are compressed and blocked, the risk of secondary microflora joining increases;
- cracked nipples are an entry point for infection, especially if the areola is constantly injured during feeding;
- inflammation of the milk ducts not related to lactation - occurs due to various reasons, most often due to an incorrectly selected bra, bruise, compression during sleep;
- an abscess is provoked by hormonal disorders due to endocrine pathologies, disruption of the monthly cycle, and diseases of the reproductive system;
- the presence of formations on the body - boil, carbuncle, phlegmon, lymphadenitis, which, when spread through the bloodstream, provoke the formation of a purulent infiltrate in the chest;
- reduced immunity due to pregnancy, chronic diseases, positive HIV status.
Classification of mammary gland abscesses:
- by localization - subcutaneous, subareolar, intramammary, retromammary;
- the vastness of the process - one-sided or both are involved;
- by quantitative indicator - single, multiple abscesses.
The main cause of breast abscess in 90% of cases is cracked nipples, which are observed during breastfeeding. This manifests itself already early after birth, when the baby begins to latch on to the breast. A nipple that does not undergo the treatment procedure is taken through cracks through which a microbe (infection) penetrates.
Cleaning your nipples with soap and water is not recommended for the first 2 weeks as this can cause dry breast skin. And this may lead to the baby refusing to breastfeed due to dryness.
In addition to cracks, irritation may occur during feeding. The resulting cracks are covered with crusts. Some of the wounds may bleed, through which the infection will penetrate directly into the milk ducts.
The microbe can penetrate through such cracks in the nipples due to dirty hands. If a woman wears dirty clothes, touches her breasts with dirty hands, or uses eau de toilette or perfume, then the infection can enter the mammary glands through such pathways.
Other mistakes made by nursing women include the following factors that provoke the development of breast abscess:
- Stagnation of milk.
- Untimely pumping. Especially when the child drinks little mother's milk.
- Refusal of breastfeeding.
- The desire to “save” milk in the breast until the next feeding.
- A large volume of the gland when its lower parts descend, which leads to poor milk excretion.
The disease develops when pathogenic flora penetrates into the breast tissue,
mastitis is a pathological process associated with the development of stagnation of milk in the mammary gland and accompanied by the active proliferation of bacterial flora, which leads to the development of a cavity filled with purulent contents;
galactophoritis is a disease manifested by inflammatory damage to the milk ducts, which occurs against the background of injuries to the mammary gland and is related to non-lactation mastitis;
a cyst or benign neoplasm causes compression of the breast tissue and blockage of the milk ducts, as a result of which a secondary infection occurs and the development of abscess formation.
In addition, the development of an inflammatory-purulent focus can be observed with hormonal disorders, lymph stagnation, and purulent-inflammatory lesions already present in the body.
The development of the disease is facilitated by cracked nipples, decreased immunity, lactostasis, smoking, endocrine disorders and invasive medical procedures.
Complications
Single suppurations do not pose a threat if the doctor’s treatment recommendations are followed. But multiple boils are more dangerous because the infection from them can penetrate into the lymph nodes in the neighborhood and develop lymphadenitis. In extreme cases, death can occur due to blood poisoning, which contains pathogenic microorganisms from pus. In nursing women, after successful treatment and recovery, the development of mastitis is possible.