A facial burn is a serious injury that is not only physical, but also psychological in nature., because burn marks on the face cannot be hidden from prying eyes. An extensive thermal burn with cicatricial scars will certainly lead to a decrease in the patient’s self-esteem and self-isolation.
Photo 1. Most often, burns on the face occur due to exposure to UV rays. Source: Flickr (Sita McVay)
Types of facial burns
In total, there are 4 types of burns: thermal , chemical , electrical and radiation . External symptoms are usually similar, but subsequent treatment, rehabilitation time and general prognosis depend on the method of injury.
Thermal
A thermal burn occurs under the influence of high temperatures at which cellular protein is destroyed.
- Burns from steam or hot gases . Such an injury usually covers large areas, but does not penetrate deep into the soft tissue, so complete restoration of the skin without scars or scars is possible. However, the gases can cause burns to the upper respiratory tract and eyes.
- Burns from hot or boiling liquids . The most common injury is scalding with boiling water. It is local, but deeper in nature. However, in most cases, such a burn goes away without a trace or with minimal changes to the skin.
- Burns from hot objects . In everyday life, such a burn can be obtained by touching the sole of a working iron or a hot frying pan. The depth of the burn depends on the duration of exposure to temperature and can manifest itself either in slight redness or in a severe 3-4 degree burn with soft tissue necrosis.
- Burn directly by flame . A very dangerous injury, since the action of open fire causes burns not only to the skin of the face, but also injuries to the eyes and mucous membranes of the ENT organs.
Chemical
The cause of such a burn is the effect of chemical agents on the skin of the face. Chemical ingress can occur in domestic conditions (failure to comply with safety precautions when working with household chemicals), during cosmetic procedures, and when working in chemical laboratories.
- Acid burn . When acid gets on the skin, the damaged cells turn into a scab and block further penetration of the aggressive agent deep into the soft tissue. The degree of burn depends on the concentration of the acid: the more concentrated it is, the more layers will be affected.
- Alkali burn . A much more severe injury than an acid burn, since alkali instantly breaks down fats (which are an integral part of human skin) and literally corrodes soft tissue, penetrating deep inside.
- Burn from metal salts . Salt burns are extremely rare, most often in industrial conditions. The injury is usually superficial, resembling an acid burn in appearance.
Electrical
Electrical burns to the face are quite rare , since most electrical injuries occur through direct contact with electricity, and most contact occurs through the hand.
The greatest likelihood of receiving such an injury occurs when caught in an electric arc , and the burn will be of a combined nature:
- electrical burn from electrical discharge,
- thermal burn due to clothes or hair on fire,
- radiation burn due to the light flash of an electrical discharge.
Radiation
Radiation burns to the face are quite common. The most common and simplest is sunburn in the summer.
There are also forms of radiation burns that develop when various radiations (ultraviolet, x-ray, radiation) penetrate deep into soft tissue.
It is important! Symptoms usually appear slowly, and become noticeable only at a time when internal disturbances are already colossal. One of the consequences of radiation burns is skin cancer.
Cautions: how to avoid unpleasant consequences?
The result of burn healing depends on the treatment tactics and behavior of the victims. The face is a sensitive place; any mistake can leave a mark for life, which can worsen the quality of life and cause complexes.
Mistakes to avoid:
- Smearing the burned area with oil is perhaps the most common and dangerous misconception. Oil, even sterile, forms a dense film that will reduce the access of oxygen to the wound and block the outflow of physiological fluid. In the worst case (if you do not use an unrefined product), infection may occur.
- When trying to cool the damaged area during a thermal or radiation burn, blot it with cotton swabs or apply ice and cooled objects. Intense pressure will lead to mechanical damage to tissues, disrupt blood circulation and complicate treatment.
- In case of thermal burns from hot objects, molten metals or plastic, you should never remove them. This action further injures the tissue and can cause bleeding.
- Treating a fresh burn with alcohol-containing substances.
- Cover the burn with a thick cloth, and even more so with an adhesive plaster. The wound must “breathe.”
- Open the resulting blisters yourself. At home, it is impossible to make the process sterile; this will only increase the risk of infection.
- In case of a chemical burn, on the first day, any external actions are prohibited, except for washing with water or special solutions.
Self-medication for deep or extensive burns is strictly prohibited. For chemical burns, this is unacceptable, even if the affected area is small.
Degrees of facial burns
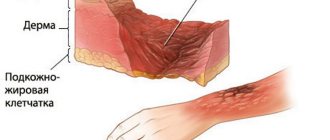
Like any other burns, facial burns have 4 degrees. The only difference is that the layer of soft tissue (up to the bones of the skull) is very small. But there is always a possibility of injury to the eyes and upper respiratory tract.
- First degree burn . Slight redness of the skin, a slight itching sensation, possible swelling. The burned epithelium sloughs off within 3-7 days. There are no traces of injury left.
- Second degree burn . Redness and itching are pronounced. Burn blisters may appear. It takes 2-3 weeks for complete recovery; no traces of the burn remain or they are almost invisible.
- A third degree burn is damage to all layers of the skin, including the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Severe trauma (charring in places), the presence of burn blisters.
- IV degree burn . Death of all layers of skin and deeper tissues: blood vessels, muscles, bones. Most of these burns on the face are incompatible with life, as they penetrate deep into the skull, deprive the patient of vision, burn the mucous membranes of the ENT organs, and can damage the brain.
The more severe the degree of facial burn, the worse the prognosis for full recovery. However, modern medicine and plastic surgery are able to achieve satisfactory results even in very severe cases. An important factor in rehabilitation is the timely start of treatment and strict compliance with all instructions of the attending physician.
Photo 2. The faster and more competently first aid is provided, the greater the patient’s chances of recovery. Source: Flickr (hak kah).
Signs
- Redness of the facial skin from slight pinkness to severe hyperemia.
- Itching or burning sensation, even unbearably painful.
- The appearance of burn blisters with liquid contents (the more severe the burn, the thicker the contents of the blister).
- Presence of charred areas of skin.
- Violation of the integrity of the skin, exposure of more tissue (down to the bone).
- Acute pain in the eyes, with eye burns.
- Acute burning in the nose, mouth, throat or lungs, sore throat, pain when breathing and swallowing due to burns of the ENT organs and upper respiratory tract.
Anti-inflammatory ointments for burns
At the stage of inflammation, the necrotic mass melts. It is necessary to immediately clean the wound, as well as adjacent skin areas, from dirt, decay products and damage.
It is very important to prevent infection. The use of ointments in this category not only relieves inflammation and swelling, but also restores damaged tissue
Advantages
- Ointments for inflammation destroy pathogenic microorganisms. This reduces the likelihood of bacteria and germs multiplying.
- It may take a long time before contacting a medical facility. Therefore, subsequent injury must be prevented.
- To protect the wound from exposure to the external environment, it is enough to apply a bandage soaked in the product.
Flaws
- The drug contains antibacterial components. Therefore, the ointment can cause an allergic reaction in the form of skin hyperemia, burning, and swelling.
- Patients also noted attacks of vomiting and nausea.
- Some ointments, for example, tetracycline, can cause changes in blood composition, damage internal organs, and also increase photosensitivity.
First aid for facial burns
It is important to provide first aid as soon as possible: the faster the agent of injury is eliminated and the burn site is cooled, the greater the likelihood that the burn will not leave a trace in the form of a scar or scar.
To provide assistance with facial burns, it is important to know the cause of the injury so as not to aggravate the patient’s condition.
However, there are several universal recommendations:
- Stop the action of the burn agent : wash off chemicals from the skin, remove a person from an electrical circuit, knock out flames from hair or clothing, pull a person from a fire, remove a hot object. .
- Cool the burned area with running water or something cold. If there is an open wound, you need to cool the skin around it, not inside, to avoid infection.
- Call an ambulance.
- Give the victim plenty of fluids.
- If there are no signs of life, before the ambulance arrives, carry out resuscitation measures: chest compressions and artificial respiration.
Note! Thermal burns should never be lubricated with oil or greasy creams. This way, thermal energy cannot escape and begins to affect the deeper layers of tissue.
- If a hot object sticks to the skin , it is better not to pull it out - this will lead to additional trauma, severe bleeding and promote infection.
- If a person is locked in an electrical circuit , it is necessary to push the victim away using non-conducting materials: wood, rubber, plastic.
- If unknown liquid chemicals with your skin, wash them off only with clean running water. Do not use wet wipes, lotions, etc. If the chemicals are dry (powdery), you will need to sweep up any residue first.
- If the burn is likely caused by acid , it can be treated with soap or soda solution.
- Burns from alkalis are washed with water with the addition of vinegar or citric acid.
What to do first: emergency care
If a burn occurs on the face, first aid must be provided to the victim. This will prevent damage to deep tissue layers and reduce the likelihood of complications.
What to do in these cases? Actions depend on the cause of the burn and can vary significantly:
- In case of thermal burns caused by an open flame, you must first extinguish the flame (cover your face with a thick cloth).
- The next step is to cool the skin. You can place your face (if the integrity of the epidermis is preserved) under a stream of cool water, or wash the skin manually or irrigate it with a spray bottle.
- For chemical burns, it is important to know what exactly caused the tissue damage. Contact of some products (containing aluminum) with water is unacceptable, as the reaction intensifies. If the skin is damaged by acid, it is neutralized within a quarter of an hour with a solution of soap or soda, alkali, table vinegar.
- Examine the victim to ensure the absence or presence of other injuries.
- In case of electric shock, remove the source from your face and check your pulse. If necessary, perform artificial respiration.
- If the burn is small and the person feels relatively well, you should go to the burn department of the nearest hospital as soon as possible. In all other cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance, explain the situation and strictly follow their recommendations.
Deep burns often cause painful shock, when the victim does not experience discomfort, but performs chaotic actions. In this case, he needs to be calmed to prevent mechanical damage to the burned tissues and infection.
During transport to a medical facility, it is recommended to cover the damaged skin with a thin cloth, such as 2-layer gauze.
Treatment options
As with any other burns, in medical practice the most widely used therapeutic method of treatment is indicated for injuries of any origin and any degree of severity.
At the same time , for 3rd-4th degree burns, surgical intervention is often .
Considering the specificity of facial burns (the impossibility of hiding or camouflaging scars), various methods of cosmetology and plastic surgery are often indicated.
Therapeutic treatment of burns
This method involves prescribing medications and treatment procedures that promote rapid regeneration of damaged tissue and are aimed at preventing complications.
Treatment of burns, regardless of the cause of their occurrence, is approximately the same:
- Pain relief with analgesics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In severe cases, narcotic analgesics may be prescribed.
- Drainage of burn blisters. Treatment of wounds, application of antiseptic dressings.
- Infusions to restore various blood balances.
- Preventing wound infections.
- Treatment with drugs that promote wound healing and improve blood circulation (Panthenol, Bepanten, Levosin, Actovegin, vitamins).
- Prevention of scar formation (Contractubex).
- Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment.
Surgical treatment of burns
Surgery for facial burns is performed in cases of extensive or deep tissue damage.
For 3-4 degree burns, skin grafting , plastic reconstruction of the nose, eyelids and lips may be required.
In some very severe cases, it may be necessary to remove eyeballs and bone fragments.
Folk remedies in the treatment of burns
Minor 1st and 2nd degree facial burns can be treated at home. In addition to pharmaceutical products, they relieve swelling well and promote healing:
- cooled decoction of oak bark,
- lingonberry juice,
- cabbage leaf,
- fresh apple puree,
- grated raw potatoes,
- aloe juice,
- compress of chamomile decoction (cooled).
Note! When giving preference to treatment with folk remedies, it is important to follow common sense: do not lubricate burns with oil, do not sprinkle them with sand, and generally avoid any dubious recommendations. If after a week of treatment no positive changes are visible, you should consult a doctor.
The best remedies for healing burns
The active components of products for the treatment of burns, penetrating through the skin, accelerate the synthesis of biologically active substances from the inside. They not only start the healing process of damage, but also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Bepanten - will cure burns and “kill” germs
4.9
★★★★★ editorial assessment
89% of buyers recommend this product
This drug, in composition and principle of action, is very similar to the popular Panthenol. It is produced in the form of ointment, cream and lotion, but the difference between the three medicinal types lies only in the texture and “fat content” of the product.
Bepanten is used for thermal and sunburn, preventing the development of bacterial infection. It is often prescribed to nursing mothers for the prevention and treatment of cracked nipples, and to their children as a remedy for prickly heat and diaper rash.
Plus, the cream helps in the treatment of allergic dermatitis and hemorrhoids, relieves acne and bruises.
Advantages:
- Versatility;
- Cooling effect;
- Rapid healing of shallow injuries;
- Safe for children and pregnant women.
Flaws:
- Sometimes application may be painful;
- Upon contact with mucous membranes it causes a burning sensation.
Many people include Bepanten in their home medicine cabinet. It is truly universal and causes virtually no adverse reactions in either children or adults.
Branolind ointment bandage - a convenient first aid product
4.8
★★★★★ editorial assessment
88% of buyers recommend this product
See review
The name speaks for itself: Branolind is an ordinary cotton bandage soaked in an ointment based on Peruvian balsam.
The package contains 30 sterile breathable wipes that help with burns, bedsores, diabetic and trophic ulcers, and open wounds.
The size of the bandage is 7.5x10 cm, such a patch needs to be changed every 2-3 hours. In addition to the wound-healing effect, Branolind draws out suppuration from the depths of the wound and relieves swelling.
Advantages:
- Prevention of scar formation;
- Ease of use;
- Mild analgesic effect;
- The dressings do not stick to the wound and are easy to change;
- You can cut out appliques of the desired shapes and sizes from napkins;
- Suitable for treating children.
Flaws:
Doesn't stick to the skin at all.
An ointment bandage is suitable as an “ambulance” for the treatment of open wounds and severe burns. But as soon as the condition stabilizes, you need to move on to more serious means.
Rehabilitation and skin care
The skin of the face, even with minor sunburn, requires special care, not to mention severe injuries:
- Avoid exposure to sunlight on the skin,
- mandatory use of creams with a high SPF filter ,
- refusal of solariums,
- refusal to visit baths, saunas, even taking hot baths at home,
- for facial hygiene, use clean water and special medical detergents recommended by a doctor,
- refusal of washing gels, alcohol lotions and decorative cosmetics until the skin is completely healed,
- constant skin hydration,
- if necessary, use absorbable ointments for scars.
When keloid scars form, the victim may be advised to undergo laser scar resurfacing, surgical scar excision, or skin grafting.
The physical consequences of facial burns cause changes in the psychological state: decreased self-esteem and self-isolation, failure to accept one’s new appearance and dysmorphophobia, depression and suicidal thoughts. That is why, with facial burns, like no other, it is important to work with a psychologist during the rehabilitation period.
Possible consequences
Due to anatomy and physiology, burns on the face often provoke various complications:
- loss of sensation;
- damage to the facial nerve;
- impaired visual acuity;
- damage to the respiratory system and, as a result, pneumonia;
- dysfunction of the speech apparatus;
- skin suppuration;
- blood poisoning.
If they occur during therapy, you should contact your doctor.
Deep facial burns may leave scars. If the burned area is small, ointments (Contractubex) and cosmetic procedures (laser resurfacing) will help cope with the problem. If the damage is large-scale and deep, only plastic surgery or skin grafting will help correct the situation.
Neither an adult nor a child is insured against burns. If the face is damaged by any of the aggressive factors, the victim must be immediately assisted. Even minor redness at first can cause serious complications and subsequently leave a scar.
Consequences and complications of burns on the face
The main negative consequence of a facial burn is considered to be a cosmetic defect, however, do not forget about trauma to neighboring organs:
- thermal and chemical burns of the eyes up to loss of vision and the organs themselves;
- burn of the nasal mucosa and upper respiratory tract;
- burn of the mucous membrane of the mouth and esophagus, loss of teeth or even jaw, which has an extremely negative effect on the digestive system and, as a result, the entire body.
Also, open wounds from burns can become infected, and infections, as is known, can spread through the bloodstream to any part of the body.