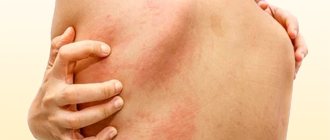
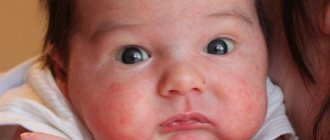
Skin and allergic rashes appear after contact of the dermis with an external irritant or consumption of certain foods. The histamine reaction is accompanied by redness, swelling of the tissues, severe itching and the formation of small blisters.
Treatment of the disease is carried out with ointments for external use, antihistamines and healing agents. How many days it takes for an allergic rash to go away depends on the degree of skin damage, the presence of complications and the duration of contact with the irritant.
How long does it take for food allergy pimples to go away?
Most often, this type of disease affects young children, this is due to a hereditary predisposition, an unformed immune system and insufficiency of the digestive tract.
Rashes form on the face, mouth, or throughout the body. The mucous membranes swell greatly, turn red, cause pain and burning. To alleviate the condition, patients need to take antihistamines; this will help quickly reduce swelling and relieve spasm of soft tissues.
The blisters will go away in 3-5 days if you eliminate the allergen from your diet. During this period, the irritating component will be completely eliminated from the body. Enterosorbents and antioxidants help speed up the process and reduce rashes.
Recovery is delayed if there are concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, when scratching pimples, inflammation and suppuration of soft tissues. In such cases, the use of anti-inflammatory ointments is required; regeneration lasts up to 2–4 weeks.
How many days does it take for allergies to go away, causes and symptoms of allergies – On the skin
22.11.2019
Skin and allergic rashes appear after contact of the dermis with an external irritant or consumption of certain foods. The histamine reaction is accompanied by redness, swelling of the tissues, severe itching and the formation of small blisters.
Treatment of the disease is carried out with ointments for external use, antihistamines and healing agents. How many days it takes for an allergic rash to go away depends on the degree of skin damage, the presence of complications and the duration of contact with the irritant.
How long does it take for food allergy pimples to go away?
Most often, this type of disease affects young children, this is due to a hereditary predisposition, an unformed immune system and insufficiency of the digestive tract.
Rashes form on the face, mouth, or throughout the body. The mucous membranes swell greatly, turn red, cause pain and burning. To alleviate the condition, patients need to take antihistamines; this will help quickly reduce swelling and relieve spasm of soft tissues.
The blisters will go away in 3-5 days if you eliminate the allergen from your diet. During this period, the irritating component will be completely eliminated from the body. Enterosorbents and antioxidants help speed up the process and reduce rashes.
Recovery is delayed if there are concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, when scratching pimples, inflammation and suppuration of soft tissues. In such cases, the use of anti-inflammatory ointments is required; regeneration lasts up to 2–4 weeks.
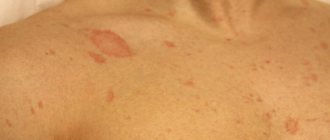
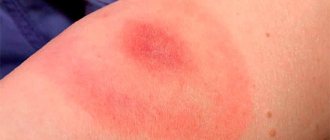
Skin rashes due to urticaria
The pathology occurs in acute or chronic form, which determines how long the clinical manifestations of the disease persist.
In acute cases, the rash appears immediately after contact with the allergen and lasts for 2–48 hours. In rare cases, signs of pathology are observed for up to 6 weeks.
The use of medications accelerates recovery, redness and swelling subsides within 1 day, the skin clears up in 14 days.
How long does it take for chronic urticaria to go away in children and adults? Symptoms of the recurrent form of the disease persist longer than 1.5 months. With proper treatment, the rash begins to disappear within the first week of antihistamine therapy. However, repeated rash and resumption of the acute course in the presence of unfavorable factors cannot be ruled out.
Cold and heat urticaria develops under the influence of temperature stimuli.
The disease is characterized by seasonal exacerbations; a skin rash appears after exposure to sunlight or frosty air.
It is impossible to get rid of allergies; protective creams, medicinal ointments, and moisturizing gels help reduce the manifestations of pathology. Therefore, the duration of the rash directly depends on compliance with preventive measures and the ambient air temperature.
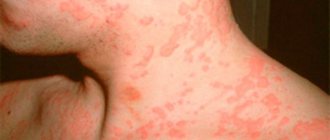
Duration of treatment for contact dermatitis
The cause of contact dermatitis is the direct impact of allergens on the skin. The affected area exhibits redness, swelling, and the formation of weeping, itchy blisters. Treatment begins with the exclusion of external irritants, taking antihistamines, and applying ointments with corticosteroids.
How quickly does a rash with contact dermatitis go away in a child and an adult? The use of hormonal drugs speeds up recovery. Skin manifestations can last for several hours or 1–2 weeks, after which they begin to dry out and form crusts.
Intense itching of the skin can lead to scratching and bacterial infection. Such complications are often diagnosed in a child due to weak immunity or poor hygiene. Pustules take longer to heal and can turn into erosions and ulcers. Children are prescribed antibiotics, vitamins, and immunomodulators. The rash completely disappears within 1 month.
Allergic eczema
How long does it take for inflamed skin eczema to go away? Since the cause of the formation of pathology is not only an external factor, but also a disruption of the nervous system, treatment is carried out with antihistamines and sedatives.
Eczema lasts for quite a long time, skin cleansing occurs only after 30–40 days.
In children, pathology against the background of atopic dermatitis can persist constantly, proceed in waves and pass with the onset of puberty. Treatment only temporarily relieves the symptoms of the disease.
Therapy for microbial eczema lasts at least 1 month and includes antibiotics, desensitizing agents, antihistamines, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, hormonal ointments, and antiseptics for external use.
Seborrheic eczema develops against the background of concomitant diseases, so the duration of treatment will depend on how quickly the underlying disease can be eliminated and the body’s immune defense can be increased.
Skin rash due to inhalant allergy
A person can inhale allergens along with the air, the irritant being dust, mold, animal hair or pollen from flowering plants. The components enter the lungs, then are absorbed into the systemic bloodstream, causing the development of a histamine reaction, the formation of an itchy rash, rhinitis, lacrimation, dry cough and sneezing.
Inhalation allergies are most often seasonal, so skin manifestations usually persist until the flowering period passes or the person changes their place of residence to an area with cleaner air. In case of a severe reaction to particles of pet hair, you should not keep pets in the apartment or have close contact with them.
To make the blisters go away faster, patients drink antiallergic drugs, use nasal drops, healing, antipruritic ointments, and sprays for irrigating the larynx.
Prevention of allergic rashes
It is possible to prevent the appearance of skin rashes in people suffering from allergies by completely eliminating contact with the allergen. If the disease worsens after eating certain foods, you should carefully monitor your diet and adhere to a special diet.
In cases where a person does not know the true cause of the development of a histamine reaction, laboratory tests are prescribed to determine the allergen. It is possible to vaccinate during the period of remission so that exacerbations are mild or the pathology goes away completely.
To prevent the elements of the rash from becoming inflamed and festering, you should not scratch the pimples. It is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations, hygiene rules, use prescribed medications, lead a healthy lifestyle and strengthen the immune system.
How quickly do the symptoms of an allergic rash go away?
Skin and allergic rashes appear after contact of the dermis with an external irritant or consumption of certain foods. The histamine reaction is accompanied by redness, swelling of the tissues, severe itching and the formation of small blisters.
Source:
How long does it take for allergies to go away after symptoms appear?
string(10) "error stat"string(10) "error stat"
string(10) "error stat"
You can find out which types of the disease are most common and how long the allergy lasts in this article.
Features of allergies
- When faced with allergies for the first time, many people do not understand what this disease is, what manifestations it is characterized by, and how long its symptoms last.
- Allergy is a consequence of a hypersensitive reaction of the immune system to an allergen entering the body from outside.
- In general, the main task of the immune system is to protect the body from viruses and bacteria by producing antibodies to fight them.
In an allergic reaction, the immune system begins to fight substances that are generally harmless to most people, such as dust mites, pollen or medications.
As a result, allergy symptoms appear, such as urticaria, itching and swelling of the eyelids, rhinitis (runny nose), difficulty breathing, nausea, Quincke's edema, etc.
An allergic reaction does not occur after initial contact with the allergen, since in this case the body only recognizes the substance.
For example, the first time after a bee sting, a person may experience only pain, redness and slight swelling of the skin.
But if the bee stings again, you may experience hives or breathing problems. This is due to the reaction of the immune system.
A significant number of people (and even very young infants) experience allergic reactions to some irritant at least once in their lives. Symptoms that occur with allergic reactions range from mild to severe and life-threatening.
Most allergic reactions are mild, and home treatment can relieve many symptoms. An allergic reaction is more serious when there is angioedema, which makes breathing difficult, or anaphylaxis, which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Types and duration of allergies
Let's look at the most common types of allergies and the average duration of symptoms.
♦ Food allergies are most common in people who have a hereditary tendency to develop allergic diseases. It is worth noting that food allergies are more common in children than in adults. As a rule, the following symptoms appear: itchy skin, urticaria, diathesis, allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis, frequent sneezing, itching of the eyelids, Quincke's edema.
Will food allergies go away? In some cases, the child manages to outgrow the allergy, that is, it goes away with age. This is due to the formation in the intestines of enzymes necessary for the normal functioning of the body and the digestive system, including.
♦ Medicinal. Many pharmaceutical drugs, such as antibiotics, can cause an allergic reaction. The severity of symptoms varies depending on the drug taken and its dosage.
♦ Insect (for insect poison). An allergic reaction to an insect bite or sting occurs when the immune system reacts to venom and toxins that penetrate the skin. As a result, swelling, redness, pain, itching at the bite site and more severe manifestations, including anaphylactic shock, may occur.
♦ Animal allergies are more often expressed by respiratory symptoms than by skin manifestations. As a result, in some cases a person cannot determine the cause of deterioration in health on his own for a long time. It should be noted that the reaction does not occur to the fur itself, but to the epidermis (dander) and animal excrement.
♦ Allergy to latex. Some people develop allergic reactions after prolonged contact with latex. Allergic reactions to latex gloves are especially common.
♦ Allergy to mold. The disease is widespread, as molds can be found almost everywhere: from bathroom walls to logging sites.
♦ Seasonal allergies appear annually during the flowering season of trees, meadows and weeds. Hay fever is the most common disease resulting from the negative effects of pollen.
Can hay fever go away? It is impossible to cure the disease forever, but it is quite possible to get rid of symptoms for several years. To do this, it is worth taking a course of allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT). You can find out more about this treatment method in this article.
Duration of symptoms
How quickly does the allergy go away?
Respiratory symptoms. If mild symptoms occur, such as sneezing and itchy nose, the allergy goes away 30 minutes after taking the antihistamine.
More severe symptoms: rhinitis (runny nose), cough, suffocation, wheezing in the lungs may disappear several days or even months after identifying and eliminating the allergen, depending on the type of allergy.
For example, allergens from a pet, even after the pet is moved from an apartment, can remain indoors for up to 4 months.
Skin manifestations. For example, diathesis, urticaria, dermatoses, redness of the skin, blisters, and swelling can last from several hours to several weeks or more.
It all depends on whether the rashes are the result of an immediate allergic reaction or have a chronic form.
It is worth starting from these factors in order to answer the question “In how many days will the symptoms go away?”
Prevention
Avoid contact with the allergen.
In order for food allergies to go away and no longer bother you, follow an elimination (hypoallergenic diet); in case of seasonal manifestations associated with plant dust, take protective measures to protect the mucous membranes: put on sunglasses and wear a protective mask; in case of contact allergies, avoid contact skin with an allergen, etc.
- Carry out wet cleaning of the apartment at least once a week, and also try to ventilate the room more often and maintain an optimal humidity level.
- As for infants, doctors recommend maintaining breastfeeding for as long as possible, or selecting a hypoallergenic formula in accordance with the age of the child.
Source:
Skin rashes due to urticaria
The pathology occurs in acute or chronic form, which determines how long the clinical manifestations of the disease persist. In acute cases, the rash appears immediately after contact with the allergen and lasts for 2–48 hours. In rare cases, signs of pathology are observed for up to 6 weeks. The use of medications accelerates recovery, redness and swelling subsides within 1 day, the skin clears up in 14 days.
How long does it take for chronic urticaria to go away in children and adults? Symptoms of the recurrent form of the disease persist longer than 1.5 months. With proper treatment, the rash begins to disappear within the first week of antihistamine therapy. However, repeated rash and resumption of the acute course in the presence of unfavorable factors cannot be ruled out.
Cold and heat urticaria develops under the influence of temperature stimuli. The disease is characterized by seasonal exacerbations; a skin rash appears after exposure to sunlight or frosty air. It is impossible to get rid of allergies; protective creams, medicinal ointments, and moisturizing gels help reduce the manifestations of pathology. Therefore, the duration of the rash directly depends on compliance with preventive measures and the ambient air temperature.
Duration
Although the duration of the reaction depends on many factors, there are average values. The numbers are correct for an adult who uses medications, and the symptoms are moderate:
- Hives can last from one day to a week and go away without leaving any traces;
- The rash, like urticaria, goes away within a few days, but after it there is peeling of the skin for another 2-3 days;
- The papules disappear within 3–4 days, sometimes peeling remains;
- If the allergy was manifested only by itching, then it all depends on how damaged the skin was - if it is not damaged, then the itching disappears within a few minutes after applying the medicine, but if the patient scratched the skin and it is damaged, then healing occurs from one to several days ;
- Respiratory symptoms disappear a few hours after the allergen is eliminated, when the mucous membranes return to normal.
A child's allergies go away even faster. But it can be more severe.
Duration of treatment for contact dermatitis
The cause of contact dermatitis is the direct impact of allergens on the skin. The affected area exhibits redness, swelling, and the formation of weeping, itchy blisters. Treatment begins with the exclusion of external irritants, taking antihistamines, and applying ointments with corticosteroids.
How quickly does a rash with contact dermatitis go away in a child and an adult? The use of hormonal drugs speeds up recovery. Skin manifestations can last for several hours or 1–2 weeks, after which they begin to dry out and form crusts.
Intense itching of the skin can lead to scratching and bacterial infection. Such complications are often diagnosed in a child due to weak immunity or poor hygiene. Pustules take longer to heal and can turn into erosions and ulcers. Children are prescribed antibiotics, vitamins, and immunomodulators. The rash completely disappears within 1 month.
How long does a skin allergy last? What determines the duration?
When itchy redness appears on the skin, naturally there is a desire to find out when it will all stop and whether it is possible to speed up the process of getting rid of unpleasant symptoms.
Today we will talk about how long skin allergies last, what affects the course of the disease, and also talk about special types of reactions to irritants.
Types and forms of allergic reactions
Allergy occurs as a result of an immune response to an external irritant in the form of acute inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes. The reason for such a response can be any external object: an animal, dust, food, a chemical with which there has been contact at least once before.
The fact is that the mechanism of development of the immune response is such that upon initial acquaintance with the allergen, our body, having identified it as dangerous, prepares certain combat tactics so that when we encounter it again, we can apply it as quickly as possible.
This explains the fact that when interacting with a new irritant for the first time, no allergic reaction occurs, but when we encounter it again, our body can react sharply and fearfully. And the more of these fateful encounters occur, the sooner and more severely the allergy sufferer’s immunity will respond.
Therefore, in the treatment of this disease, it is extremely important to establish that from the patient’s environment his immunity regards him as an enemy to health.
Allergies have three forms, which can be combined and complement each other.
- Hives. A general nosological group that combines types of allergic reactions to the skin.
- Quincke's edema (angineurotic). It is characterized by rapid swelling of the soft tissues of a certain part of the body, most often the face or limb. It is dangerous because it can develop on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, which leads to suffocation. It can occur simultaneously with urticaria, however, unlike the latter, it affects the tissue deeper. This condition requires emergency care and hospitalization.
- Anaphylactic shock. Instant reaction to an allergen. Usually occurs on drugs, food factors (eg, peanuts). It is characterized by the rapid development of symptoms: severe pain, increasing laryngo- and bronchospasm, acrocyanosis. When this form of immune response appears, a spasm of the peripheral circulation and vascular collapse develop, therefore it is accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, and without emergency medical assistance leads to death.
If you have a tendency to allergic reactions, you should remember that any contact with a potential irritant can have an unpredictable outcome and any form of manifestation.
Types of skin allergies in adults and children
An allergic reaction has several types of manifestations on the skin, which differ in symptoms and represent different diagnoses.
- Atopic dermatitis. Referred to as a type of hereditary allergies. This form can develop in infants almost from the moment of birth (5-7 days of life). The disease can be secretive and appear in adolescence or adulthood. Foci of atopic dermatitis are localized in places of folds: elbow, popliteal, cervical, as well as on the lips and in the corners of the mouth. Characteristic signs: the formation of areas of redness on the skin, which during the period of exacerbation become crusty, tend to merge and itch unbearably. The latent phase of the disease makes itself felt by excessive dryness of the dermis and a tendency to form cracks and wounds. The disease progresses in waves, alternating remission with relapses. The main provoking factor is considered to be food allergens and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Contact dermatitis. It develops most often with prolonged skin contact with an allergen. This includes chemicals, cosmetics, hygiene products, medications for external use, and plants. Characterized by the appearance of rashes and papules at the sites of interaction with the reagent. The skin in these places becomes hyperemic, swollen, may be painful, and itching is certainly present. The duration of contact dermatitis can vary from several days to two weeks. If the influence of the allergen is not eliminated in time, the condition will worsen. For children, the triggering mechanism is incorrectly selected care products and items washed with aggressive surfactants.
- Hives. It occurs on any part of the body, occupying quite large areas. In terms of sensations and external symptoms, this form of allergy resembles a nettle burn. It is characterized by the sudden appearance of small blisters filled with fluid, which disappear spontaneously. This is all accompanied by itching and burning, tissue swelling, redness, destruction of the epithelial membrane and the appearance of wounds are also present. The reaction can be fleeting, lasting for several hours, but in general the duration of the process takes from 7 to 14 days.
- Eczema. A disease very similar to atopic dermatitis, which is also characterized by the formation of extensive foci of inflammation on the skin. It often likes to appear on the face and in places of physiological folds. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by an acute course and dry nature of problem areas; eczema is accompanied by the development of weeping ulcers that do not heal for a long time.
- Neurodermatitis is a special category of skin reactions and for the most part refers to idiopathic (unexplained etiology) diseases. In terms of symptoms, it has similar features to the above skin lesions, is characterized by difficulty in eliminating symptoms and various variations of the rash: nodules, papules, vesicles, urticarial changes. With neurodermatitis, it is customary to take into account not only the immune, but the neurological nature of development. It is characterized by a chronic course.
- Photodermatitis. This is a special skin reaction that occurs when the response to an allergen is triggered by exposure to sunlight. This effect can be produced by some drugs that have a photosensitizing effect: fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin) and tetracycline, as well as plants and essential oils. Taking these antibiotics may be accompanied by the appearance of a rash and serious damage to the skin (burns) after contact with ultraviolet radiation. With regard to photodermatitis, you should always be especially vigilant, since they can be a sign of not only an allergic reaction, but also signal the start of more severe autoimmune diseases, for example, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Dear readers, due to the fact that the classification of skin allergies has very similar symptoms and causes of occurrence, making an independent or remote diagnosis (for example, from a photo) is absolutely impossible.
Due to the high probability of worsening symptoms upon repeated contact with the allergen, treatment and observation should be carried out only under the supervision of a physician. To make a final diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination, perform skin tests and examine immunoglobulins .
Allergy to hair dye in adults: features
Each manufacturer of a hair coloring product indicates in the instructions a mandatory recommendation for conducting a skin sensitivity test before use. The fact is that the chemical components contained in the product can not only cause an immune response, but also provoke a chemical burn of the scalp.
Also, inhalation of vapors can lead to toxic damage to the respiratory tract, swelling, and suffocation. If you are prone to allergies, do not neglect the recommendations to conduct a preliminary test on the elbow.
Allergy to hair dye in adults has a long course, since chemical irritants penetrate deep into the tissue and structure of the hair, which ensures their prolonged effect on the skin.
Differences in effects from nicotinic acid: physiology, overdose, allergies.
The use of nicotinic acid preparations (nicotinamide, vitamin B3, vitamin PP), both parenterally and orally, is accompanied by specific side effects that are difficult to differentiate from signs of allergy or overdose.
When using the drug, especially at the beginning of the course, as a rule, the following symptoms develop, which under certain conditions do not pose a threat and are a variant of the norm:
- burning sensation, tingling sensation on the skin;
- feeling of a rush of blood to the head;
- intense redness of the upper body, especially the face and hands.
With normal tolerability of the drug, these phenomena disappear on their own, on average, within an hour. And with subsequent repeated use, they may not occur at all.
Exceeding the permissible dose of the drug may be indicated by:
- difficulty salivating, thirst;
- nausea and vomiting;
- clouding of consciousness;
- dizziness,
Allergic symptoms arising from nicotinic acid are characterized by persistent manifestation of persistent and increasing side effects, respiratory disorders, the appearance of edema, even angioedema, and the development of signs of anaphylaxis.
Therefore, when treating with this drug, monitoring of the patient’s condition by a medical professional is required. The difficulty of providing assistance lies in the blurred boundaries of the condition between a physiological and an allergic reaction.
Please note that even external use of nicotinamide solution in the form of masks to improve hair growth can lead to serious consequences if you are allergic to this substance.
An allergic reaction to antibiotics can take any of the known forms. There are two options for the appearance of the process:
- Instant reaction when symptoms increase immediately or within 72 hours.
- Deferred. It may occur on days 5-7 of taking the drug or at the end of the course.
Allergies to medications in this group can develop in people of any age, but are especially severe in children. The duration of symptoms is explained by the fact that the drug is not eliminated from the body immediately, but continues to persist in the blood plasma and organs for 10 days.
Therefore, when treating skin allergies that arose during treatment with representatives of this group, in addition to the use of local ointments and creams for allergies and allergies, oral (in severe cases, injection) treatment with antihistamines and enterosorbents should be carried out in order to reduce the toxic effect.
Also, in rare cases, an allergy to antibiotics can take severe, atypical forms:
- Steven-Johnson syndrome: rashes appear not only on the epidermis, but also affect the mucous membranes. Accompanied by severe fever.
- Lyell's syndrome - detachment of large areas of skin, with the appearance of blisters and weeping ulcers, similar to a burn.
- serum sickness: an allergic reaction accompanied by increased permeability of blood vessels and cell membranes, the appearance of a rash and damage to the blood vessels of internal organs: kidneys, heart, lungs.
- drug fever.
Any manifestation of a negative immune response to antibiotic therapy requires immediate discontinuation of the drug and specific measures to reduce sensitization.
Due to the unpredictability of the body's reaction to antibiotic treatment, these drugs are not allowed for self-treatment; only a doctor can prescribe them, based on the severity of the underlying disease.
If there is a history of hypersensitivity to drugs, before starting treatment, it is advisable to conduct skin tests using the scratch method or intradermal injection of small doses of the substance.
What determines the duration of allergy treatment?
The rate of occurrence of an allergic rash, as well as the area of skin surface damage, directly depends on the individual characteristics of the immune system.
The following factors play a special role in the development of the disease:
- age;
- type of activity (specific working conditions create higher risks);
- whether this reaction is primary or appeared earlier;
- neurological status;
- chronic diseases: skin, digestive organs.
If contact with the allergen has already occurred more than once, then the reaction will accordingly intensify each time. It is noteworthy that it is impossible to reliably predict what type of allergic symptoms will develop upon repeated encounter with the irritant. An alternation or combination of urticaria and angioedema is possible, and anaphylaxis may occur.
During a skin allergic reaction, it is customary to distinguish two forms:
- Spicy. Affects only the superficial layers of the skin, can last only a few hours and even goes away without the use of medications. The maximum duration should not exceed two weeks. This form is characteristic of contact dermatitis and urticaria. May be accompanied by minor conjunctival irritation and sneezing.
- Chronic. The duration can be more than six weeks, it responds poorly to therapy, and tends to intensify and be supplemented by new reactions to other stimuli. Often, concomitant symptoms include a dry cough, shortness of breath, and soft tissue swelling. Such skin allergies are often accompanied by the addition of a microbial or fungal infection, leading to changes in the epidermis (its thickening) and affecting the functioning of the nervous, digestive and respiratory systems. Chronic allergies require careful selection of therapeutic methods, and if there is no improvement, inpatient treatment, consultation with an immunologist, allergist and pulmonologist.
Of course, the duration of the course and the effectiveness of recovery are influenced by:
- timely identification and elimination of the allergen;
- degree of severity (the more symptoms, the more difficult the treatment);
- adequate therapy;
- the nature of the allergic factor (the rate of its elimination from the body).
- psycho-emotional state.
Dear readers, every year the number of officially confirmed allergic reactions among people around the world reaches an alarming level.
This complex and formidable disease has not yet been fully studied, so even minor skin manifestations can serve as a signal that the immune system is not working properly. You should not ignore this disease and let the development of the disease take its course.
And in order to determine with a certain accuracy how long a skin allergy lasts, you must always take into account the type and nature of the symptoms and the specifics of the irritant.
Source: https://lavida-live.ru/dermatologiya/allergija/skolko-dlitsja-allergija-na-kozhe.html
Allergic eczema
How long does it take for inflamed skin eczema to go away? Since the cause of the formation of pathology is not only an external factor, but also a disruption of the nervous system, treatment is carried out with antihistamines and sedatives.
Eczema lasts for quite a long time, skin cleansing occurs only after 30–40 days.
In children, pathology against the background of atopic dermatitis can persist constantly, proceed in waves and pass with the onset of puberty. Treatment only temporarily relieves the symptoms of the disease.
Therapy for microbial eczema lasts at least 1 month and includes antibiotics, desensitizing agents, antihistamines, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, hormonal ointments, and antiseptics for external use.
Seborrheic eczema develops against the background of concomitant diseases, so the duration of treatment will depend on how quickly the underlying disease can be eliminated and the body’s immune defense can be increased.
Skin rash due to inhalant allergy
A person can inhale allergens along with the air, the irritant being dust, mold, animal hair or pollen from flowering plants. The components enter the lungs, then are absorbed into the systemic bloodstream, causing the development of a histamine reaction, the formation of an itchy rash, rhinitis, lacrimation, dry cough and sneezing.
Inhalation allergies are most often seasonal, so skin manifestations usually persist until the flowering period passes or the person changes their place of residence to an area with cleaner air. In case of a severe reaction to particles of pet hair, you should not keep pets in the apartment or have close contact with them.
To make the blisters go away faster, patients drink antiallergic drugs, use nasal drops, healing, antipruritic ointments, and sprays for irrigating the larynx.
Prevention of allergic rashes
It is possible to prevent the appearance of skin rashes in people suffering from allergies by completely eliminating contact with the allergen. If the disease worsens after eating certain foods, you should carefully monitor your diet and adhere to a special diet.
In cases where a person does not know the true cause of the development of a histamine reaction, laboratory tests are prescribed to determine the allergen. It is possible to vaccinate during the period of remission so that exacerbations are mild or the pathology goes away completely.
To prevent the elements of the rash from becoming inflamed and festering, you should not scratch the pimples. It is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations, hygiene rules, use prescribed medications, lead a healthy lifestyle and strengthen the immune system.