Causes of allergic reactions
Patients suffering from allergies usually associate the onset of symptoms with animal fur or hair. However, the main reason for such allergic reactions lies in the substances secreted by the glands of the animal.
Allergy-causing agents are found in fur, saliva and dander, as well as in animal excrement, so the causes of allergic reactions may include:
- improper care of the animal;
- somatic diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- diseases of the digestive system.
In some cases, an allergy to animal fur occurs as a concomitant pathology in patients suffering from other somatic disorders.
Factors that most often provoke an allergic reaction:
- bird feather;
- sheep's wool;
- clothing and other products based on camel wool;
- waste products of rodents;
- cat and dog saliva;
- animal hair and dander.
As practice shows, children suffer from this disease much more often, so you need to approach the issue of choosing a pet carefully . In order to minimize the risk of allergic reactions to cat fur, experts recommend giving preference to the so-called hypoallergenic breeds, including the Sphinx, Balinese and Oriental cats, Devon and Cornish Rex, as well as Allerka. Allergies to dog fur occur less frequently when keeping Terriers, Miniature Spitz, Bichon Frize, Chinese Crested and Poodle at home.
What contributes to its development
Allergies to animals most often occur in people with weakened immune systems and hereditary predisposition. You can suspect the development of a reaction to a cat or dog in a person suffering from:
- atopic dermatitis;
- any chronic diseases of the nose, including runny nose;
- conjunctivitis;
- bronchial asthma.
In addition, the development of sensitization to animal allergens can be facilitated by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver, lack of vitamins, taking immunostimulants without a good reason, as well as infection with worms.
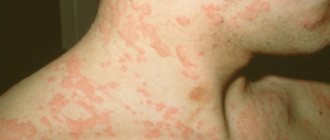
Symptoms of a wool allergy
Symptoms in adults do not differ significantly from the signs accompanying allergic reactions in pediatric patients, and are presented:
- congestion of the nasal passages;
- frequent sneezing;
- copious mucous discharge from the nose;
- redness of the eyes;
- itchy feeling on the conjunctiva;
- profuse lacrimation;
- causeless shortness of breath;
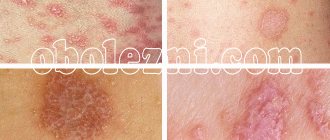
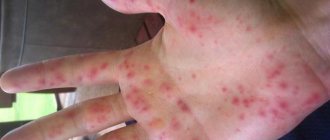
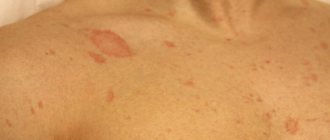
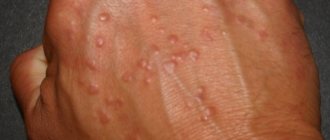
- rash of different localization;
- intense skin itching;
- Quincke's edema in conditions of high concentration of allergens.
In patients of early age and with a weakened immune system, tachycardia and rapid breathing, dizziness and digestive disorders, including abdominal pain and colic, nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea, are noted.
Symptoms of the disease
An unpleasant feature of allergic manifestations to animal fur is addiction to the allergen (sensitization). For example, a patient who has been living with a pet for a long time suddenly experiences an allergic attack, which can neutralize on its own. However, the disappearance of acute symptoms does not mean that the allergy has receded. For its complete cure, the help of highly qualified specialists is required.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to wool are characterized by the following manifestations:
- frequent sneezing, mucus from the nose and watery eyes;
- hyperemia in the eye area, unbearable itching;
- wheezing and difficulty breathing;
- cough and severe shortness of breath, which can sometimes be accompanied by suffocation;
- the appearance of pinpoint rash and tissue swelling.
In severe cases of allergies, dangerous complications such as Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock are possible. Both of these conditions require immediate action, as they threaten the patient’s life, especially in childhood, when symptoms can increase rapidly and the immune system, due to its immaturity, is unable to cope with them.
Cat hair is an allergen
An allergy to cat fur occurs when the body is exposed to special proteins contained in the animal’s saliva, urine and excrement. The microscopic size of the protein retains its allergic properties even after drying, and its presence on the coat is due to the cat’s habit of actively licking itself. Symptoms of an allergy to cat hair:
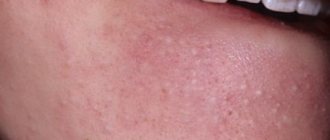
- itching sensation on the body;
- swelling on the face;
- difficulty breathing;
- severe tearfulness;
- the appearance of a sore throat;
- hoarseness of voice;
- frequent and dry cough;
- urticaria of varying degrees of intensity;
- asthmatic attacks;
- Quincke's edema.
Hairless cat breeds cause fewer symptoms, but cannot be a panacea for fur allergies.
Manifestation of allergies in childhood
Negative symptoms in children may appear within 10 minutes of the start of contact with an animal or objects containing allergens. Children under five years of age suffer from wool allergies much more often.
Symptoms of an acute allergic attack are as follows:
- first the skin turns red and a pinpoint rash appears;
- swelling of the mucous membranes is noted;
- lacrimation and discharge of contents from the nose;
- spasmodic cough and shortness of breath;
- body temperature rises;
- lethargy or, conversely, increased excitability may be observed;
- The baby cries and refuses to eat.
In newborns, an allergic reaction can manifest itself in the form of atopic dermatitis. If such symptoms develop, immediate medical attention is required. Otherwise, severe consequences, including death, are possible.
Allergic reactions to dog fur
The coat of a dog is less allergenic compared to the fur of representatives of the cat family. In this case, the allergy manifests itself in the form of:
- hives;
- neurodermatitis;
- eczema;
- hyperemia on the skin;
- discomfort and severe itching;
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- swelling in the eyelid area;
- tearfulness;
- small focal rashes;
- allergic rhinitis;
- shortness of breath and attacks of suffocation.
A severe form may develop, accompanied by bronchial asthma. The Can-F1 allergen that provokes the development of the disease is contained in the dog’s skin, so the pet is provided with complete and competent care, including systematic hygiene procedures.
Animal allergies in adults
Allergens are found in the skin, epithelium, dander, saliva, urine and feces of animals. The most common reaction in adults is caused by cat allergens, and half as often by dog allergens. At the same time, pet owners should be aware that there are no hypoallergenic breeds; any breed, even a hairless one, can cause a runny nose, itching or more serious symptoms.
Less common is increased sensitivity (sensitization) to waste products in other pets - hamsters, birds, mice, etc. When people have a reaction to a cat, they are often cross-allergic to other members of the cat family, as well as to dogs and horses.
Cross-reaction between pork and beef is also possible. There have been cases of choking and severe swelling as a result of exercise after consuming these products.
Please note that animal allergens can cause very serious reactions, including death. Therefore, if an allergy to a pet is confirmed, it is better to give it to family or friends. In severe cases, call an ambulance.
Medical aspects of therapy
Treatment is prescribed after the diagnosis has been established, based on the collected medical history, clinical and special studies, and visual examination of the patient. The only effective treatment option for allergic reactions caused by animal fur is to avoid keeping pets at home. Any other treatment methods fall into the category of “half measures”, and only help to reduce the frequency and severity of regularly occurring exacerbations.
Mild allergic reactions can be treated with nasal aerosols supplemented with antihistamines:
- “Diphenhydramine”, “Diazolin”, “Suprastin”, “Tavegil” and “Fenkarol”;
- "Claridol", "Clarisens", "Clarotadine", "Lomilan", "Lora-Hexal", "Claritin", "Rupafin" and "Kestin";
- "Gismanal", "Trexil", "Telfast" and "Zyrtec";
- "Cetirizine", "Desloratadine", "Fenspiride", "Fexofenadine", "Loratadine", "Azelastine", "Xyzal" and "Ebastine".
"Desloratadine" belongs to the group of the most popular antihistamines designed for patients of all age groups. The product is one of the safest, without many contraindications or unwanted effects. Allegra-D and Sudafed are prescribed as decongestants.
Treatment of strong and severe allergic manifestations requires consultation with an allergist and the prescription of corticosteroid tablets:
- "Prednisolone";
- "Metypreda";
- "Kenaloga";
- "Celeston"
- "Florinefa";
- "Triamcinolone";
- "Medrola";
- "Lemoda";
- "Kenacorta".
Corticosteroid ointments and gels are prescribed for topical use:
- "Elokom";
- "Akriderm";
- "Triderm";
- "Advantan";
- "Gistan-N";
- "Sinaflan";
- "Hydrocortisone ointment";
- "Flucourt";
- "Lokoid";
- "Prednisolone ointment";
- "Pimafukort";
- "Lorinden-S";
- "Oxycort";
- "Nistaform";
- "Sibikort";
- "Dermozolon".
Contraindications for use include pregnancy, childhood, lactation, arterial hypertension, severe renal pathologies, liver diseases and peptic ulcers.
Today, a highly effective treatment for wool allergies is immunotherapy, which consists of long-term hyposensitization and subcutaneous administration of gradually increasing small doses of provoking allergens. Stimulation of immune defense is accompanied by the production of appropriate antibodies that prevent allergic symptoms.
Diagnosis of allergies
Diagnosis is primarily based on medical history, visual examination and examination of the patient’s premises.
At the first appointment, the doctor finds out the patient’s allergic status (genetic tendency to develop various types of allergies). Then information about the animal that is present in the house is specified (feeding, maintenance, care, etc.).
Allergic diagnosis is carried out using a blood test to determine the content of group E immunoglobulins. In addition, if necessary, a skin test is prescribed to determine the dangerous allergen. Based on the diagnostic results, adequate treatment is prescribed.
Reliable folk remedies
Treatment with medications is complemented by folk remedies that eliminate unpleasant symptoms and discomfort. Such effective remedies include freshly squeezed celery juice, infusion of dandelion roots and claspberry. The following have proven high efficiency:
- an infusion based on a string, used as a lotion for the skin;
- dry tea, which replaces coffee and other traditional drinks;
- a decoction of oak bark and ivy used to treat rashes;
- infusion or decoction of yarrow, consumed 70 ml three times a day.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to substitute folk remedies for medications prescribed by the attending physician.
Medicinal therapeutic measures
Many patients quite often ask questions when visiting an allergist about how to get rid of allergies with the help of medications?
For mild allergies, simply limiting contact with allergens is sufficient. If symptoms are clearly expressed, the doctor selects individual treatment tactics:
- as a rule, antihistamines (Zodak, Erius, Loratadine tablets, etc.) are prescribed to relieve swelling, itching and redness of the skin;
- To relieve rhinitis, nasal sprays are prescribed (Nazol, Azmacort, etc.);
- to remove toxic substances, enterosorbents are prescribed (Lactafiltrum, Enterosgel, etc.);
- in severe cases, treatment with glucocorticosteroid drugs (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, etc.), which have a strong antiallergic effect, is recommended. However, it should be remembered that steroid drugs can only be used under the supervision of a physician. Drugs in this group have powerful side effects.
With the development of primary symptoms that characterize an allergy to animal fur, it is necessary to begin therapy, especially in young children, since it is impossible to predict the development of symptoms in them (it can be delayed, or a sharp and rapid increase in symptoms is possible).
The most dangerous emergency conditions are those that must be dealt with immediately. If the patient is suffocating and his face swells right in front of others, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, since delay threatens the patient’s life.
Preventive actions
Treatment of an allergic reaction to animal fur with traditional means will not be as effective as possible in the absence of effective preventive measures:
- regular cleaning of floors;
- daily removal of dust and animal hair from surfaces;
- eliminating all sources of allergens;
- removing all woolen items;
- compliance with hygiene measures;
- frequent washing of pets' bedding;
- high-quality home ventilation;
- performing quartz treatment of the room using a special lamp;
- systematic use of antihistamines.
For preventive purposes, it is very important to stabilize the functioning of the stomach and intestinal tract and properly strengthen the immune system using well-proven folk remedies or medicinal analogues. In the first case, chicory, Kalanchoe juice, nutritional yeast, infusions based on Eleutherococcus, Chinese lemongrass and ginseng, as well as vitamin and mineral complexes are used. Any pharmaceutical medications should be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Allergies to animals in children
In general, allergy symptoms in children are the same as in adults: sneezing, red eyes, dry cough, redness on the skin, etc. But in addition to the usual routes - through the respiratory tract and skin - allergens can reach children through food. Children under 3 years of age, who like to put everything in their mouths, especially often swallow particles of wool and skin that settle on household items. In this case, an allergy to animals can manifest itself in the form of vomiting, upset stool, and abdominal pain.
However, you should not immediately blame your pet for a rash on your baby’s body. They may have been caused by components of the food, litter tray, or shampoo you use to wash your animal. And if your pet goes outside, the reaction may be caused by pollen or fluff carried on the animal’s fur.