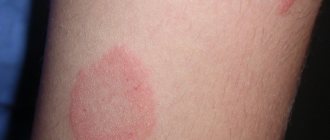
Ringworm is a fungal skin lesion that appears as spots on the body.
The disease is also called sun fungus or pityriasis versicolor. The skin suffers from the parasite and bothers a person only with characteristic spots, and not with itching, as with other types of fungi.
The risk group includes men and women with reduced immunity and a predisposition to the disease.
Problem Definition
A dermatologist diagnoses lichen versicolor based on the characteristics of the spots.
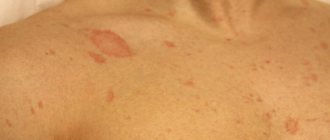
It looks different : formations can be located on any part of the body, but most often they are localized on the sides of the torso, chest and shoulders. The duration of treatment may be delayed due to the ability of fungi to form protection against the medications used.
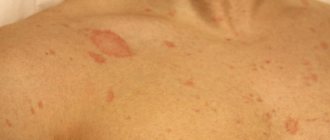
Ringworm on the body
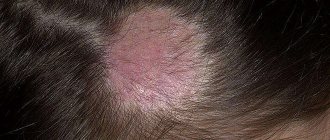
In rare cases, tinea versicolor appears on the face. You can detect the presence of tinea versicolor in the scalp using a special device.
The contagiousness of the disease is minimal , cases of infection between people are quite rare.
The fungus can only live on human skin, so you cannot get infected from animals or using other people’s things.
Fungus prevention (expert recommendations)
Despite the fact that this type of lichen is considered practically non-contagious, all members of the patient’s family are subject to examination by a dermatologist. This also applies to those persons who were in close contact with the patient.
Diagnostics are carried out using a special fluorescent lamp (see types of diagnostics above).
To prevent the appearance of sun fungus on the skin, it is recommended to wear clothes only made of natural hygroscopic fabric (especially underwear). Do not forget about careful hygiene of the epidermal integument; you need to take frequent baths with soap and a hard washcloth.
Once every 7 days, you can also lubricate the skin with regular pharmaceutical salicylic alcohol. When the first signs of increased sweating, and in some cases itching, appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Below are some tips to prevent fungal infections:
- Avoid unkempt, dirty beaches.
- If you visit public pools, ponds, saunas, baths, then do not forget to thoroughly wash your skin with a washcloth and soap while swimming.
- After swimming, let your skin dry before starting to tan in the sun.
- Be sure to use sunscreen for your face and body. Moreover, it is better to buy them in trusted pharmacies.
- Do not let anyone use your personal hygiene items - bath towel, face and foot towels. Wash these items frequently. Also, do not use other people’s equipment yourself.
- After playing sports or being active in nature, take a hygienic shower or bath.
Strengthening the body's immune defense is also considered a good method of prevention. Start to harden yourself, take baths with sea salt and periodically lubricate your skin with solutions of salicylic alcohol or vinegar.
Tinea versicolor: causes
To date, the exact cause of lichen colorus has not been established by dermatologists, as well as the question of whether it is contagious or not. Only factors influencing the activity of the disease are known.
The main causes and diseases that provoke the appearance of colored spots:
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- tuberculosis;
- seborrhea;
- chronic lung diseases;
- diabetes.
Since lichen spottedeum provokes severe sweating, it is often found in people suffering from hyperhidrosis. In this case, the spots are located in areas of active sweat production.
A person’s individual predisposition to a fungus of the genus Pityrpsporum orbiculare, combined with the peculiarities of the body’s functioning, can provoke the occurrence of lichen. The disease is promoted by the special chemical composition of sweat, disruption of the functioning of epidermal cells, and general weakening of the body by various problems and neuroses.
Additional factors leading to the development of pityriasis versicolor:
- chronic fatigue, lack of sleep; pityriasis versicolor
- prolonged stress;
- climate change;
- lack of vitamins;
- unsystematic use of personal hygiene products;
- synthetic clothing;
- use of synthetic bedding;
- ionizing radiation;
- long-term use of corticosteroids.
In case of contact infection, the incubation period of the disease can last from two weeks to six months.
What is pityriasis versicolor and how can you get it?
Pityriasis versicolor is a harmless fungal disease that affects the skin. The causative agent of the disease is a yeast-like fungus. It is called Pityrosporum and has three forms:
- rounded;
- mycelial;
- oval.
In humans, round and oval-shaped mushrooms are found on the skin, but this does not necessarily result in lichen. Characteristic rashes on the surface of the epidermis will appear when these forms are transformed into mycelial.
Medical statistics indicate that the male part of the population is more susceptible to the disease. Most often, pityriasis versicolor is diagnosed in young people living in regions with humid and hot climatic conditions.
This chronic and often recurrent disease develops in people under the influence of the following external and internal factors:
- suffered stress;
- diabetes and other endocrine diseases;
- increased sweating;
- pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- immunodeficiency (during cancer and HIV therapy);
- decreased immunity;
- excess body weight;
- heredity.
Signs of the disease (symptoms)
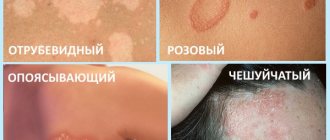
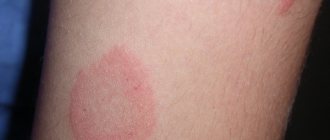
The presence of fungus can only be determined by a specialist. However, the appearance of a fungal infection can be assumed by the presence of pink, brown or yellowish spots on the skin. The formations have uneven edges and an asymmetrical shape.
For each individual patient, the location, volume of the lesion, and color of the spots will be different. The size of the spots in the initial stage can be up to one centimeter in diameter. As the disease spreads, the spots begin to increase in size and merge into one.
The shape of the spots also changes : it becomes oval or diamond-shaped, with active peeling in the center.
Most often, spots are located on the chest, shoulders, neck and abdomen. In adolescents, lichen florida can be found on the legs and arms.
With tinea versicolor, spots appear on the body in a chaotic manner. In order not to confuse sunburn spots with pink lichen, the diagnosis should be carried out by a specialist. Often these types of fungal infections are similar due to the same symptoms - in some cases, the spots of tinea versicolor have a pink tint.
What does tinea versicolor look like: photo
To accurately determine the type of disease, a specialist applies a five percent iodine tincture to healthy and infected areas of the body. Fungi of the genus Pityposporum are stained more strongly than in the healthy zone.
This diagnosis is called the Balzer test and helps doctors make a diagnosis without scraping.
There is no itching or pain in the lesions of tinea versicolor . Ringworm can be identified by the peeling of the skin on the affected areas after wetting them with water.
To further check, a dermatologist may examine the spots under a special lamp. Under the light of a Wood's lamp, the tinea versicolor spots will have a yellowish tint.
Wood's lamp in action when detecting lichen
The most effective way to determine the disease is by scraping.
To do this, skin flakes are scraped off at the spots where the spots are located, which are then sent for microscopic examination. Once a person's symptoms are confirmed, treatment begins immediately .
Additional symptoms of ringworm:
- increased sweating is observed in the affected area;
- due to disruption of melanin synthesis, areas with spots do not tan;
- peeling changes intensity from weak to strong;
- spots lighten under ultraviolet light and darken during the cold season;
- Lichen formations merge with the skin, rarely protruding above the surface.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of lichen on the hands are the following:
- itching, discomfort and burning in areas of future lesions;
- the appearance of weeping watery blisters of various shapes;
- peeling of the skin;
- changes in the structure of the skin due to the appearance of plaques on it.
Consequences of the disease
The presence of tinea versicolor does not lead to dangerous complications and does not harm health.
Other types of fungus can affect and negatively affect human internal organs and systems. The only trouble that can be caused by lichen is that scratching the spots can cause inflammation and suppuration of the skin.
If you constantly touch the spots, wet them with water or damage the skin in the inflamed area, this can cause seborrheic eczema and other similar diseases of the epidermis.
After the patient has managed to cure tinea versicolor, white pigment spots remain on the skin for a long time. They are gradually compared to the skin tone under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
Video:
In addition to disrupting the aesthetic appearance of the skin, tinea versicolor can lead to social problems. Stress and fear of appearing in public places lead to neuroses, insomnia, and loss of ability to work. If you don't think about how to treat lichen, it can cause a relapse.
Effect on pregnancy
Pregnant women, when this pathology is identified, are interested in the question of whether pityriasis versicolor poses a threat to the health of her unborn child. For a baby, lichen is not dangerous. It is important that fungi do not penetrate the placenta and are not dangerous to the fetus. Pityriasis versicolor does not change the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth. The main thing is to identify the problem in a timely manner and competently begin to eliminate it.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor in pregnant women involves the use of antifungal and antiviral drugs.
Methods for treating ringworm
Treatment of formations is carried out at home.
Exceptions are rare cases of complications when a bacterial infection is associated with the fungus. A set of measures aimed at combating tinea versicolor includes local and systemic medications (ointments and tablets). One ointment for lichen will not be fully effective, since the external agent cannot penetrate deep into the skin and destroy the main causative agent of the disease.
In addition to taking medications and treating the infected area of skin, to destroy the fungus you need:
- follow a diet that excludes the consumption of fried and fatty foods, alcoholic beverages, yeast bread, sweet dishes and kvass;
- sunbathing (provided that the treatment takes place in the warm season);
- carefully observe body hygiene;
- disinfect the patient’s apartment, clothes, bed linen and household items.
For tinea versicolor of moderate severity, the doctor prescribes systemic antimycotics that prevent relapse and shorten the treatment period as much as possible. The drugs need to be taken for several days.
These medications include:
- Lamisil;
- Fluconazole;
- Clotrimazole;
- Terbinafine and others.
The advanced form of the disease is difficult to treat and often provokes relapse. Therefore, measures in this case will be more stringent; you will need the medicine Neotigason, which normalizes the functioning of epidermal cells.
If the spots affect a large area of the skin, severe pigmentation cannot be avoided. In this case, after the basic course of treatment, the dermatologist will prescribe a drug that will regulate the synthesis of skin pigments and restore color.
Since in most cases, fungal infection is caused by a decrease in immunity, in parallel with the main treatment, the doctor may prescribe drugs to increase the body's resistance. This is echinacea tincture, Immunal, Leuzea and various complexes of vitamins and minerals.
External treatment of the affected areas is carried out regularly for two to three weeks.:
- wiping and applying the area with fungus with salicylic alcohol;
- covering areas with sulfur ointment;
- treating the area affected by lichen with antifungal agents in the form of solutions, lotions, sprays;
- replacing regular shampoo during treatment with Nizoral shampoo for body hygiene.
External use of the products is indicated until the elements of lichen completely disappear.
Description of the drug
The pharmaceutical drug "Clotrimazole" is a popular and well-known product based on an imidazole derivative. Actively used to combat lichen of fungal etiology, applied externally. It is characterized by a predictable therapeutic and therapeutic effect when applied in doses.
The spectrum of action of the drug extends to the following mushrooms:
- moldy;
- actinomycytes (mainly Nocardia);
- parasites of dimorphic type;
- dermatophytes;
- blastomycosis.
A synthetic antimycotic agent is used externally (with local treatment of the affected areas) and intravaginally.
Clinical and pharmacological group
Clotrimazole is a representative of a large group of synthetic antibacterial drugs. Also applies to antifungal agents. The effect of the medication covers most of the bacteria that cause infectious diseases in the human body. Medicines of this type have a mainly fungistatic effect.
Activity is manifested against invasive mycoses and superficial pathogens. Repeated fungal resistance is extremely rare. With prolonged therapy, pathogenic microorganisms may develop resistance to azoles.
pharmachologic effect
Clotrimazole has a simple mechanism of pharmacological action (directed primarily against fungi). The main component of the drug is an imidazole derivative.
The principle of action of this substance is as follows:
- azole interferes with the normal synthesis of ergosterol (a key component of membranes in fungal cells);
- the permeability of the shell of pathogenic microflora increases significantly;
- the structure of the cytoplasm is corrected.
In fact, we are talking about violating the integrity of pathogenic fungi by destroying their membrane structure. As a result, microorganisms die very quickly.
Release form and composition
The antifungal agent is produced by several companies located in Russia, Ukraine, Poland and India. The pharmaceutical drug is available in the following dosage forms:
The drug Clotrimazole is available in several forms
- vaginal tablets – cardboard packs with 1, 3 or 6 tablets, equipped with an applicator;
- solution - a 15 ml glass bottle, supplemented with a small dropper for administering the composition;
- cream (1%) - available in aluminum tubes of 20 and 30 g;
- ointment (1%) - supplied in aluminum tubes of 15, 25, 30 and 40 g, packed in cardboard boxes with instructions for use.
Ointments and creams are considered universal forms of release of the drug in question. The main active ingredient is imidazole derivatives (1%). Auxiliary components are nipagin, propylene glycol, polyethylene oxides.
Traditional methods of treatment
Additionally, treatment with proven folk remedies can be used:
- Boric acid in the amount of 10 g is mixed with a glass of boiling water. After the solution has cooled, they need to treat the skin several times a day using a cotton swab. Boric acid
- Celandine decoction : a tablespoon of crushed plant stems is added to two glasses of boiling water. You need to infuse the product for 15-20 minutes. The cooled mass is applied to fungal spots twice a day.
- A mixture of string and eucalyptus - in the amount of two tablespoons, is poured with boiling water and infused for half an hour in a water bath. This combination solution is used before bedtime.
Strictly following the doctor’s instructions will help you quickly get rid of spots on your body and forget about tinea versicolor forever. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to use medicated anti-fungal shampoos or lotions once a week. To preventive measures it is worth adding sweating control and timely body hygiene.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of pityriasis versicolor (lichen versicolor) is carried out by a dermatologist. You should not get carried away with self-medication, since most relapses of the disease occur precisely because of improper treatment. Only a qualified specialist can make a correct diagnosis and determine how to treat pityriasis versicolor.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the characteristic appearance of the spots, as well as several tests that make it possible to distinguish the disease from others similar to it in clinical manifestations, such as:
- vitiligo,
- white or pink lichen,
- psoriasis,
- seborrheic dermatitis,
- eczema,
- cutaneous syphilis.
The symptoms of the pathology are quite specific. Additional diagnostics of pityriasis versicolor includes the following methods:
- examination of skin flakes under a microscope, during which a fungus is detected;
- examination under a Wood's fluorescent lamp, during which a peculiar yellow or brown glow is found;
- Balzer test, revealing hidden peeling.