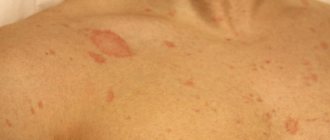
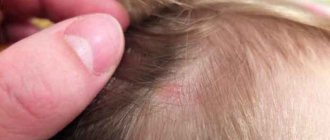
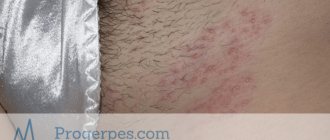
Herpes is considered a common disease, and most people are carriers of it. This disease practically does not lead to serious consequences and is considered relatively safe. But if you don't treat herpes, you may end up with some troubles. Young children are especially sensitive to the disease. In them it manifests itself in the first hours after infection. In the article we will discuss how long the incubation period is and how to detect the disease at the initial stage.
What affects the duration of incubation of herpes
Patients often ask questions about what affects the incubation period of herpes in the intimate area or other areas of the human body.
There are a large number of factors that can either lengthen the reproduction period of viral particles or significantly shorten it.
Doctors usually consider:
- age characteristics - everyone knows that infants and older people have weaker immune systems
- environmental conditions - everything that can contribute to a decrease in immunity (staying in a draft, prolonged exposure to the cold, etc.) can lead to a shortening of the period of time from entering the body to the development of a full-fledged disease
- stress also affects the immune system, which can lead to a shorter period of time
Naturally, adherence to proper nutrition, leading a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits and a number of other recommendations can increase incubation.
Moreover, in some cases, the virus may never lead to the development of a full-fledged disease, remaining dormant in the body.
Traditional methods of treatment
You can cure the disease with your own hands; there are many traditional medicine methods for this.
In order to get rid of unpleasant rashes, you can follow these recommendations:
- Propolis. The beekeeping product has several actions at once - it relieves itching, inflammation, and redness. To treat blisters, you can use propolis tincture.
- Lotions of mint and lemon balm. The products relieve itching and relieve redness. It’s not difficult to prepare the tincture: pour one glass of boiling water over a spoonful of raw materials and let it brew for half an hour. Soak a cotton swab in the warm tincture and apply to the rash for a few minutes.
- Sea buckthorn oil – accelerates regeneration processes. You can treat rashes with oil several times a day.
- Calendula decoction is most often used in the form of lotions. Pour two hundred milliliters of boiling water over one and a half spoons of plant flowers. Infuse for forty minutes, apply lotions several times a day.
- Eucalyptus oil – relieves itching and redness. By applying oil to problem areas, further spread of bacteria can be avoided.
Effective treatment with sea buckthorn oil
As you can see, if herpes develops, its incubation period may vary. Remember that herpes is a highly contagious disease. If you suspect that you are sick, reduce contact with other people and direct all your strength to strengthening your body.
Effect of pregnancy on virus incubation
Often, women who are in the period of bearing a child ask their attending physicians about how the incubation of herpes changes during pregnancy.
It is quite difficult to predict changes in this case.
On the one hand, the body does everything to protect the woman herself, as well as her unborn baby, from negative external influences, including viral particles.
On the other hand, pregnancy is a condition of a woman’s body, accompanied by severe immunosuppression.
Otherwise, bearing a fetus would simply be impossible.
Often it is immunosuppression that prevails in the female body.
As a result, the length of time it takes herpes from entering the body to developing symptoms is significantly shortened. It is also worth considering that herpes is quite capable of penetrating the placenta, leading to infection of the child.
Sometimes it leads to the development of congenital pathologies of varying severity.
Recurrent
If the next stage is present, patients who have survived the first stage can be seen to a greater extent. Depending on the severity of the disease, there are three main forms of relapse of genital herpes:
- Mild (exacerbates no more than three times a year).
- Moderately severe (deterioration occurs 4-6 times a year).
- Severe (manifestations occur monthly).
Also, the course of herpes can be: arrhythmic, monotonous, subsiding. With arrhythmic remission, they last, varying from a couple of weeks to five months. It is worth considering that the longer the period of remission, the more frequent and longer the duration of relapses will be, and vice versa. A monotonous course appears after little changing periods of remission. Menstrual herpes belongs here; it is characterized by a persistent course and a long cure. Less harmless is subsiding herpes. It is characterized by a decrease in relapses and an extension of remissions.
Atypical forms are also distinguished. They look like chronic inflammation of the genital organs, both internal and external (swelled labia, etc.). An accurate diagnosis can be made after passing all the necessary tests. Treatment can only be carried out by a specialist; the sooner you contact him, the easier it will be to cope with the problem, without giving it the opportunity to become severe.
The influence of HIV infection on the incubation period of herpes
Another common question is how the duration of incubation changes during HIV infection.
There is nothing surprising in such a question.
After all, the human immunodeficiency virus is becoming increasingly common in medical practice today.
Much in this case depends on how strongly the patient’s immunity is suppressed.
For example, if a patient regularly takes HIV medications and his lymphocyte levels remain normal, the incubation period may remain within the standard range.
If the patient ignores the doctor’s recommendations and refuses medications, the level of his defense system drops to catastrophic levels.
The result is predictable: the period of time is greatly shortened.
The disease makes itself felt much earlier than if HIV were controlled or completely absent from the body.
Which doctor will help if herpes infection cannot be avoided?
Which doctor should I contact if I still couldn’t avoid a collision with the disease and there is a suspicion of incubation?
This is a very popular question among patients.
This is not surprising, because different types of herpes can be dealt with by different specialists.
If a person has signs of the genital form of the disease, it is worth visiting a venereologist first.
This doctor will be able to prescribe the necessary tests and give recommendations for therapy.
If you suspect infection with the labial form, you can go to a dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, or just a general practitioner.
Any of these doctors will be able to treat the infection using a variety of medications.
Everything is more complicated with the shingles form of the disease.
In this case, it is necessary to contact infectious disease specialists.
They may even decide that the patient needs to be admitted to hospital.
Risk of infection for a child
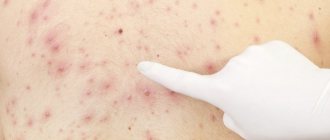
- If the mother has a primary infection and a rash is present at the time of delivery, the risk is 50%. In 70% of cases of neonatal herpes, the mother had no history of genital herpes.
- During vaginal delivery against the background of recurrent genital herpes or asymptomatic viral shedding, the risk of neonatal herpes is 2-8%.
- If a woman has a rash at the time of birth, a cesarean section prevents transmission of the herpes simplex virus to the newborn.
The incubation period is 1-28 days (average 4 days). In most cases, the first symptoms appear after the healthy-looking newborn is discharged.
The prognosis of herpes infection in newborns depends on the course of the disease. In 30% of cases, damage to the central nervous system may be preceded by damage to the skin, eyes and oral cavity.
Breastfeeding is not contraindicated . The child can be with the mother, but must be isolated from other children.
What tests will help detect infection during the incubation period?
Tests during the incubation period, as doctors note, are particularly difficult.
This is due to the fact that viral infections are already difficult to diagnose.
If we are talking about the incubation period, everything becomes even more difficult.
You should immediately forget about such popular and simple methods as microscopy and smear culture.
Of course, seeding is performed in some laboratories with special conditions, but it is more for research purposes.
The most reliable options are ELISA and PCR.
Moreover, as doctors note, PCR usually provides more information, which in itself is more reliable. This is due to the fact that the technique does not detect traces of a pathogenic microorganism in the blood, but detects it itself.
However, it is worth considering that PCR also has limitations.
If at the time of examination there are not enough viral particles in the body (the threshold value is below the detectable value), then the analysis will be false negative.
How common is HSV?
An increasing incidence of HSV infections is observed in both developed and developing countries. Moreover, women get sick more often than men.
The prevalence of the virus varies from country to country:
- At least 20% of all American males and 26% of females are infected with the HSV-2 virus;
- In Russia (data for 205), HSV-2 is present in almost 22% of adults;
- In some European countries, such as Italy and Norway, antibodies indicating infection were found in about 8% of pregnant women.
These numbers are underestimated, since the majority of HSV-infected people do not know about it, and, accordingly, do not consult doctors about this problem.
Risk factors for HSV-2 infection include:
- female;
- ethnic minority status;
- a bad history of genital infections;
- poor economic conditions;
- change of sexual partners.
Features of preventing herpes after infection
Patients who think they are in the incubation period will certainly ask the doctor a question.
What to do to ensure that the disease does not develop fully, but remains in a dormant state.
There really aren't many options.
Firstly, the effectiveness of prevention with Valvir and Valtrex has been proven.
These drugs are taken orally in tablet form and can inhibit the activity of viral particles.
The main thing is to take them according to the doctor-recommended regimen.
However, herpes is a virus that cannot be gotten rid of once and for all.
Today such drugs simply do not exist.
Therefore, for example, the PCR reaction may remain positive during diagnostic examinations.
Doctors additionally note that you should not rely only on medications.
Measures must be taken to increase the overall level of immunity.
To do this, they use immunostimulants, lead a healthy lifestyle, follow a light diet, and engage in physical activity.
Treatment methods
Treatment must be prescribed by the attending physician
Today, there are many methods that can be used to cure herpes infection. This includes many medications, as well as traditional methods. But it is worth noting that all that can be done is to get rid of the symptoms of the disease, but not to completely remove the virus from the body.
Below are several effective methods for treatment:
- Antiviral therapy . Medicines are prescribed in several forms - ointments, injections and tablets. For the treatment of mild forms, it is recommended to use local remedies. To eliminate the severe consequences of the disease - tablets. The most commonly prescribed medications are Zovirax, Famvir, and Acyclovir.
- Restoring immunity . Immunotherapy should be carried out during remission. Interferons and immunoglobulins are prescribed to strengthen the immune system. The dosage regimen is selected by the doctor, the instructions must be followed without fail.
- During the acute period, bed rest. During the period when body temperature rises, it is recommended to adhere to bed rest. This way you can avoid complications and speed up the healing process.
- Complete nutrition . Due to the long course of the disease, physical exhaustion occurs; to compensate for this condition, you need to eat well.
- Taking vitamin complexes . In order to get rid of the consequences of viral intoxication, it is necessary to saturate the body with useful minerals and vitamins.
- Drink plenty of fluids . Such an event helps remove all toxins from the body. As drinks, it is better to give preference to compotes and fruit drinks.
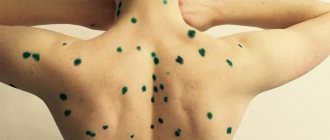
- If chickenpox develops, quarantine must be observed . The disease is considered contagious, so during its development, do not leave the house and do not contact household members.
The main treatment is with medications
An important component of treatment is strengthening the immune system. Eat right, strengthen your body, and get plenty of rest. Remember that any stress can cause mental or physical exhaustion.
What to do if herpes incubation takes a very long time
Doctors have long noticed that not all patients develop herpes according to the standard pattern.
This fact further complicates treatment during the incubation period.
It is worth keeping in mind: if the patient has a strong body, an active immune system, symptoms of the disease may not appear for a very, very long time.
Do you need to worry if there are no symptoms of the disease, although they should be, since infection has definitely occurred?
Until rashes begin to appear, the patient can be calm about his health.
Herpes is not an infection that undermines the body unnoticed.
Its symptoms are quite vivid and difficult to ignore.
If there are no symptoms, then the virus is dormant and does not pose a threat to the body.
Since it is completely impossible to remove a pathogenic microorganism from the body, all that remains is to make efforts to prevent it from becoming more active.
Routes of infection and types of herpes infection
According to the WHO, herpes is one of the most common infections in the world. Up to 90% of people are infected with herpesvirus and are carriers of the pathogen throughout their lives.
A person with a strong immune system may not even be aware of the presence of the herpes virus.
There are 8 known types of pathogens, of which 6 pathogens are the most common.
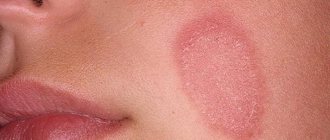
- Type 1 – herpes labialis virus. Affects the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, the skin of the lips and nasolabial triangle. Infection occurs through contact with a sick person or a virus carrier (through kissing, dirty hands), through sneezing and coughing with drops of saliva, through household items and toys. Infection occurs in early childhood (3-6 years). The most common representative of herpes viruses.
- Type 2 – genital herpes virus. It affects the mucous membranes of the urethra and vagina, the skin of the external genitalia, perineum, and inner thighs. Infection occurs during sexual intercourse without the use of barrier contraception. Infection with herpes infection occurs at the age of onset of sexual activity.
- Type 3 – varicella zoster virus in children and herpes zoster virus in adults. Primary infection is typical in childhood (3-7 years) by airborne droplets or contact and causes chickenpox. Once infected, the virus can take 10 to 40 years to reactivate and lead to shingles.
- Type 4 – Epstein-Barr virus. Primary infection occurs between the ages of 3 and 18 years. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, contact, blood transfusion (blood transfusion), and transplantation (organ transplantation). The pathogen manifests itself in the form of infectious mononucleosis, and less commonly causes nasopharyngeal carcinoma and herpangina.
- Type 5 – cytomegalovirus. Primary infection occurs in childhood (3-15 years) by contact (usually through kissing) or by airborne droplets, during organ transplantation and contaminated blood transfusion. The pathogen leads to the development of mononucleosopod syndrome.
- Type 6 is a virus that causes sudden (infantile) exanthema. Infection is typical for children aged 2-5 years. Infection occurs by contact and airborne droplets.
The herpes virus is transmitted vertically - during childbirth from a mother in an active form of the disease to the child. In such cases, infection of a newborn causes severe damage to internal organs, the nervous system, and the organ of vision.