With various diseases not only of the lower extremities, but also of systemic damage to the body, trophic ulcers can develop on the legs. The main problem is identifying them in the initial stage, since the initial prognosis of the disease depends on how early treatment is started. Progressing over time, trophic ulcers on the legs lead to serious impairments in the patient’s quality of life.
Why do leg ulcers appear?
This pathology occurs as a result of a long-term increase in sugar, so it is so important to follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Being in high concentration, glucose begins to crystallize, and the crystals damage blood vessels and nerves. Damage to blood vessels is called diabetic angiopathy. Small blood vessels are primarily affected; they become thinner, become fragile and lose their elasticity. Later, large vessels also suffer, and atherosclerotic plaques form in them.
Nerve damage is called diabetic neuropathy. They are damaged for two reasons:
- The affected capillaries do not perform their function well enough, as a result the nerves are poorly supplied with blood and experience oxygen starvation.
- With constantly elevated sugar, a large number of ketone bodies and other toxic substances are formed, they directly damage the nerve trunks.
The affected vessels and nerves cannot cope with their work, and as a result, tissue nutrition suffers. The skin loses elasticity, atrophies, dries, flakes, swells and itches. This is a signal that you urgently need treatment, otherwise ulcers will begin to appear.
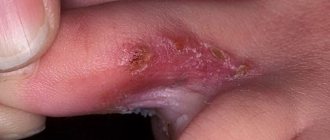
Purulent leg wound, its signs
A purulent wound is a damage to the skin with the penetration of bacteria (usually staphylococci and streptococci) that form the microflora. As a result of the activity of microorganisms, pus, particles of dead tissue, and bacterial bodies accumulate in the wound.
Signs of wound suppuration:
- The appearance of a purulent wound is accompanied by hyperemia around the injury and edema.
- An infected wound becomes hot to the touch, and a dull, throbbing pain is felt inside.
- In some cases, if the situation is left to chance and treatment is not carried out, signs of intoxication appear: a person begins to feel fever, weakness, and thirst.
Suppuration of a leg wound can have serious consequences for a person - sepsis, abscess, and phlegmon are noted.
Wound suppuration
An unpleasant type of purulent wounds is suppuration on the toe, causing the toe to become red and very swollen. The phenomenon occurs on the back of the leg and begins with redness on the toe, often near the nail. Then a blister gradually forms at the site of the lesion, where gray-yellow pus accumulates, in rare cases mixed with blood. If the abscess on the finger becomes larger, there are reasons to immediately seek medical help. Possible inflammation under the nail.
Purulent wounds on the finger or under the nail often require the provision of qualified medical care to the patient; if the process is advanced, treatment is expected to be difficult, and there is a risk of finger amputation. Such injuries must be treated under the strict supervision of a doctor!
There is a specific recommendation for expectant mothers: it is recommended to avoid any infections, including purulent processes under the nail or on the toe, this can harm the unborn child. You should refrain from attending various pedicure procedures; there is a risk of tissue infection from poorly processed instruments.
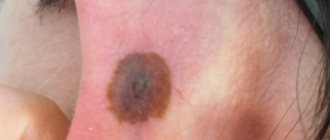
What does an ulcer look like?
An ulcer is a skin defect. Since in diabetes mellitus they are formed as a result of tissue nutritional disturbances, they are called trophic. With this disease, they are most often localized on the lower extremities, in the area of the legs and feet.
Ulcer
Before a defect appears, the skin begins to shine and thin, becomes covered with pigmentation spots, and later a round painful ulcer forms in their place, which gradually increases in size without treatment.
It is very important to immediately contact a specialist if you experience unusual sensations in a limb, such as pins and needles, numbness, or changes in the appearance of the skin. This will help prevent the development of ulcers in diabetes at a very early stage.
The most common complication of diabetes is diabetic foot syndrome. This is a combination of damage to the skin, soft tissues, bones and joints. Ulcers form on the feet and joints become deformed. The danger lies in the fact that with diabetes, the sensitivity of the skin is impaired, so patients may not notice that their shoes are rubbing or there are damages. In simple terms, a diabetic may miss the onset of the disease, which can lead to a more severe course of the disease with the development of gangrene and amputation.
Significantly complicates the course of infection, which often accompanies ulcers. When the defect becomes infected, the skin around it turns red and swells, purulent contents ooze from the wound, the body temperature may rise and the leg practically loses its supporting function. A festering ulcer requires urgent medical attention, otherwise you may lose a limb.
Trophic ulcers in diabetes mellitus have a peculiarity - they are very difficult to treat and heal poorly. This is due to the fact that skin defects are formed under the influence of many factors and in order to promote healing, it is necessary to act on all these causes. But it is almost impossible to restore full blood flow and damaged nerves, so it is much easier to prevent the formation of ulcers than to treat them.
Visualization
In the initial stage, an ulcer on the skin of the leg is a small rounded skin defect with limited damage to the subcutaneous layer to a depth of no more than 2 mm. But at the same time, all the signs of a trophic ulcer can be traced: impaired local circulation, clear boundaries of the defect, dryness of the underlying tissues, weak granulations in the wound area.
Even in the initial stage, ulceration poses a serious problem, since due to trophic disorders, scarring occurs at an extremely slow pace, and treatment of the disease is delayed. First of all, eliminate the causes:
- Varicose veins.
- Impaired lymphatic drainage from the leg.
- Thrombophlebitis.
- Atherosclerotic damage to the arteries of the legs.
- Skin diseases - eczema, dermatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Mechanical or thermal effects at the initial stage - injury, burn.
- Systemic connective tissue diseases that provoke trophic disorders - lupus, dermatomyositis.
The main mechanism for the formation of the initial stage of a trophic ulcer is local microtrauma with damage to the skin, and then subsequent disruption of blood circulation in this area. The lack of a sufficient amount of active anti-inflammatory factors due to poor blood flow causes the formation of an ulcer.
Complications of trophic ulcers
Ulcers that are left unattended can lead to serious consequences that can lead to the loss of a limb and even life.
Infectious complications: erysipelas, phlegmon, cellulitis, thrombophlebitis, anaerobic infection, osteomyelitis, arthritis and others. Without treatment, this pathology can lead to sepsis and ultimately death.
Malignancy, that is, an ulcerative defect can transform into a malignant tumor.
If a large vessel passes near the ulcer, life-threatening bleeding may develop. This primarily applies to deep wounds.
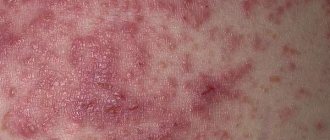
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms that may occur with ulcers and blisters depends on the cause of their occurrence. They may be accompanied by itching and pain, and may also appear before, during, or after the sores.
- Dryness
- Small, fluid-filled blisters
- Leg pain, itching or tingling
- Spread of ulcers in case of infections
- Difficulty walking and wearing socks or shoes
- Bleeding may occur in moderate to severe conditions
- Redness of the skin, swelling, especially before the appearance of ulcers
- Peeling, cracking, or flaking of the skin on the soles of your feet.
In situations where sores are associated with medical conditions and diseases, some symptoms may be life-threatening or lead to complications. Therefore, it is recommended to treat any of the above symptoms in the early stages.
Prevention of the formation of trophic ulcers
Every patient should know how to prevent the development of complications; this guarantees an easier course of diabetes and a full life.
- Glucometer
First of all, you need to strictly monitor your glucose levels. To do this, every diabetic is required to purchase a glucometer. If your sugar levels rise, you should contact your endocrinologist to adjust your treatment. - You must strictly adhere to nutritional rules; when adding a new product to your diet, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
- Do not self-medicate and be sure to take prescribed medications.
- Undergo regular medical examination, including ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities.
- Monitor the condition of your skin and consult a doctor when the first signs of damage appear.
- Taking daily walks in the fresh air will improve blood flow to the legs and saturate the tissues with oxygen. Gymnastics and massage of the lower extremities will be useful.
- Wear comfortable clothes and shoes made of natural, breathable fabric. Boots should never be tight!
- Be sure to maintain foot hygiene and take a daily shower.
- Avoid damaging the skin; you must remember that any scratch in diabetes mellitus is difficult to heal and can turn into an ulcer. For the same reason, there is no need to scratch the skin if itching occurs.
- Even minor scratches should be treated with antiseptic solutions, such as chlorhexidine. Zelenka, iodine and alcohol are contraindicated in diabetes, as they have tanning properties.
- You need to quit smoking, as nicotine causes vasospasm, and this further disrupts blood flow and aggravates the situation.
- Your legs and feet should be examined daily. If even minor defects are detected, you should consult a doctor.
- You also need to check your shoes every day to eliminate the presence of wrinkled insoles, stones and other foreign objects. Diabetic patients may simply not feel this, and the constant pressure placed on the skin contributes to the formation of ulcers.
- It is advisable to normalize your weight, this will reduce the load on your legs.
- It is necessary to monitor cholesterol levels, as atherosclerotic plaques further impede blood flow.
External and internal causes of the disease
All causes of the development of diseases on the legs are divided into two categories:
Internal ones include:
- increased sensitivity, allergic reactions to materials, cosmetics and other irritants;
- disturbances in the functioning of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys;
- deficiency of microelements and vitamins in the body;
- problems in the lymphatic system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- decreased immunity;
- dysbiosis.
External reasons include:
- injuries in the form of bruises, cuts, abrasions;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- aggressive effects of ultraviolet radiation, high humidity, high or low temperature;
- stress, depression;
- infectious diseases - bacteria, viruses, fungi.
Diagnosis of trophic ulcers
It is not difficult to diagnose a “trophic ulcer,” but it is necessary to exclude other causes of their formation, because such defects do not appear only in diabetes mellitus.
It is necessary to exclude diseases such as:
- obliterating atherosclerosis;
- Varicose veins;
- lymphostasis;
- chronic dermatitis;
- antiphospholipid syndrome.
To clarify the diagnosis, you need an examination by a specialist, general clinical blood and urine tests, Doppler ultrasound, MSCT angiography, and laser flowmetry.
Consequences and complications in the absence or improper treatment
The development of the disease in the complete absence of its therapy, or insufficiently provided medical care, is quite difficult to predict, because each clinical case is individual. The following negative consequences are identified, the occurrence of which is directly related to excessive lymph leakage:
- acute inflammation of an ulcerative neoplasm involving in the pathological process the circumferential epithelium and bone tissue of the lower limb, which previously remained healthy;
- suppuration of the wound surface with its complete filling with purulent exudate, the removal of which is possible only by performing a full-fledged surgical operation on the ulcers;
- a sharp increase in the population of bacterial microflora due to the presence of a constantly humid environment (this complication always entails the development of an even greater inflammatory process);
- the occurrence of necrosis, critical damage to leg tissue with further amputation.
No matter how the patient’s well-being deteriorates due to the lack of treatment for a trophic ulcer and relief of lymph leakage, any consequences associated with this process are extremely negative and can lead to disability of the patient.
Treatment of trophic ulcers in diabetes
As mentioned above, treating trophic ulcers in diabetes mellitus is not an easy task. A comprehensive impact on each causal factor is necessary. Also, the method of treatment depends on the neglect of the process.
General treatment
First of all, drugs that normalize glucose levels are prescribed or the already prescribed regimen is adjusted.
To improve nerve conduction, preparations based on B vitamins are used; they help restore fibers.
Drugs that improve blood flow are also prescribed, these include Pentoxifylline, Trental, Cavinton, Actovegin and others.
When a bacterial infection occurs, antibacterial drugs must be taken, primarily 3-4 generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones. But it would be more correct to take the contents from the wound for bacterial culture and, based on the results of the antibiogram, choose the appropriate drug.
Local treatment
Antiseptics
First of all, the ulcers must be washed with antiseptic solutions, such as chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide. After this, a sterile bandage and ointment with an antibacterial drug (Levomekol) are applied.
When a diabetic ulcer has stopped festering and has cleared up, it is advisable to start using ointments that improve regeneration and promote healing of the defect, such drugs include Solcoseryl.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
As an additional treatment, physical methods of influence are used, such as laser therapy, ultraviolet radiation, hyperbaric oxygenation and others. They are believed to promote tissue renewal, accelerate healing and improve the effect of local treatment.
Surgery
For non-healing ulcers that, despite treatment, only get larger, it is often necessary to resort to surgery.
There are two directions of surgical treatment, the first are aimed at restoring blood flow (vascular surgery), the second are aimed at the ulcer itself. The defect is excised and sanitized, and the wound can be closed with tissue taken from other parts of the body.
In severe cases, with the development of gangrene or massive purulent lesions, it is necessary to amputate the limb.
But everything is not as scary as it might seem at first glance. Firstly, trophic ulcers in diabetes mellitus occur with long-term elevated glucose levels, when a person does not see a doctor for years and does not take glucose-lowering drugs. Secondly, ulcerative defects noticed in time are successfully treated without the use of surgical methods. Therefore, you should be attentive to your health and listen to the recommendations of doctors.
Treatment
To treat this problem, two factors must be considered: treating the underlying causes and treating the symptoms that arise. This may include the use of medications or the use of home remedies. Prevention measures should also be taken.
Moisturizing with oils
Prevents or relieves dry feet. Coconut, olive, lavender and almond oils are excellent moisturizers. You need to soak your feet in warm water and then massage them using one or more oils, put on clean socks and leave overnight. This process should continue until the condition of the feet improves.
Apple vinegar
It has excellent potential for removing dead skin cells and also helps in preventing infections. You need to add apple cider vinegar to some warm water. Wash your feet with this solution.
Aloe vera
Its natural properties can help in healing damage. You should mix aloe vera with turmeric powder to form a paste, with which you can massage your feet. This procedure will help avoid or treat infections that cause leg ulcers and relieve itching or inflammation.
Baking soda
It can help treat inflammation, infections and gently exfoliate dead skin cells for smoother skin. You need to soak your feet in the baking soda solution for 20 minutes and then rinse them with clean water. Such baths should be repeated at least three times a week until the desired results are achieved.
There are other home remedies that can be used in this case, but you need to choose one and use it persistently and regularly to get the desired effect.