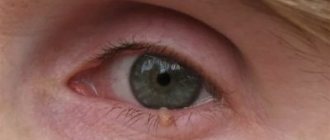
The colors of moles are shades of spots, depending on the amount of melanin. The accumulation of pigment cells - melanocytes, the cause of the appearance of moles and benign formations on the human body. The factor influencing color is blood flow in the capillaries. A person should know what color of birthmarks is normal, and what should alert them and cause them to see a doctor.
Congenital and acquired
There are various types of moles. But first of all, they are divided into congenital and acquired. There are no nevi on the body of newborns, but they begin to be visualized in the first years of life. Such neoplasms can have the following sizes:
- small (diameter ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 cm);
- medium (from 1.5 to 10 cm);
- large (diameter more than 10 cm);
- giant - occupy entire anatomical structures of the body (gluteus muscle).
Throughout life, the number of nevi constantly changes. They can spread throughout the body, and their color, contour or relief may constantly change.
Based on their location on the skin, the following types of nevi are distinguished:
- intradermal (cells that produce melanin are localized deep in the inner layer of the skin);
- epidermal (melanocytes accumulate in the upper layer of the skin);
- mixed or borderline (special cells accumulate at the border of the epidermis and dermis).
In newborns, nevi occur in 4-10% of cases, and upon reaching puberty, they are present in almost 90% of adolescents. In mature people, there can be up to 15-20 nevi on the body.
Diagnosis of the problem
If you find it difficult to determine the type of tumor by appearance, you can consult a dermatologist, oncologist or surgeon. The specialist will examine the neoplasm and also conduct an oral survey, during which he will find out the characteristics of the mole, the time of its appearance and the accompanying symptoms.
If a superficial examination is inconclusive, the doctor may use dermatoscopy, which can be used to look under the top layer of growths using a microscope-like device. If the case is complex, a biopsy may be prescribed, that is, removal of a certain portion of the growth, or complete removal of the nevus, followed by histological analysis.
Papillomatous nevus is a benign neoplasm, but in rare cases it can still transform into melanoma.
Classification by color
The color of a mole is influenced by various etiological factors. The following colors of nevi are distinguished:
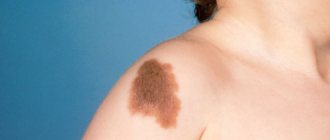
- Bloody or red moles. They belong to the group of vascular tumors. Their size can be very small (barely noticeable dot) or large (extensive spot). This depends on the depth of localization of the formation. This type of mole consists of blood vessels that have grown and merged into one whole. They are usually flat or slightly raised above the epithelium.
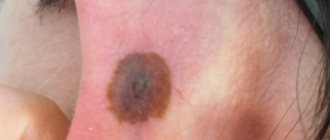
- Brown moles. This color is characteristic of most nevi, which can be localized on any part of the body. This type of coloration is caused by the pigment melanin, which is contained in melanocyte cells that make up the bulk of the cellular mass of moles and birthmarks.
- Blue mole. Most often, these neoplasms are single, benign with a characteristic dark blue or light blue color. However, they are more likely than others to develop malignancy.
Blue nevi can sometimes have a gray tint or their color is close to black. In any case, they are easily distinguished by the naked eye from classic brown moles.
Symptoms of neoplasm
To recognize a papillomatous nevus in the emerging growth, it is necessary to distinguish it from other skin neoplasms, and for this you need to know the symptoms of its manifestation. This type of mole is characterized by the following signs:
- Convex. The nevus rises significantly above the surface of the skin and is attached to it on a wide stalk.
- Density. Due to keratinized cells, the neoplasm is dense to the touch.
- Lumpy surface. Even with the naked eye it is clear that the mole is divided into segments, and with a more detailed examination using a microscope this can be seen even better.
- Clearly defined edges. The boundaries of such a neoplasm are clearly visible and not blurred, as is the case with some types of moles.
- Hue. Papillomatous growth can be either light or dark in color, but the second option is much more common.
- Diameter. The neoplasm reaches a diameter of more than one centimeter, which in many other varieties indicates negative changes, but in the case of papillomatous nevus this is a normal condition.
Classification of moles by shape
Nevi can come in a wide variety of forms, which cannot be used to judge the risk of skin cancer in the future. They can have either a standard shape (dot, circle, oval) or a non-standard shape (crescent, star). The most common type is considered to be a flat mole; convex moles are less common.
Nevus formations on the skin are also divided into moles and birthmarks. Pigmented moles and spots can have the correct shape of a circle, an oval, and they can also look like a dot or occupy large areas of the skin. They may have jagged edges and the shape may be oblong or elongated.
Treatment methods
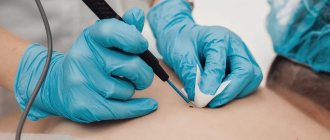
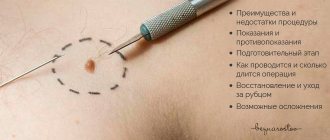
If a papillomatous mole causes discomfort and interferes with everyday life, it can be removed, but this should only be done in specialized medical institutions. Getting rid of such a tumor at home using traditional medicine is contraindicated, as it can cause irreparable harm. An inappropriate method of exposure can aggravate the situation, as a result of which the damaged mole will begin to grow rapidly, and the risk of its malignancy will also increase.
At a preliminary consultation, the doctor will be able to select the most suitable method of getting rid of the tumor without harm to the body, and an individual approach will be applied to each patient. This will reduce the risks of complications and relapses, as a result of which it will be possible to get rid of the tumor forever.
Pigmented, pilaris or verrucous papillomatous nevus can be removed with surgery. This is the oldest method, which minimizes the risk of complications and relapses. The mole is removed along with the adjacent area of skin, after which it is sent for histological analysis. The disadvantages of the operation are a long recovery period, the risk of bleeding and scars remaining after recovery.
There are also more modern procedures that can be used to remove papillomatous nevus; they are carried out using special devices and are characterized by a short rehabilitation period, bloodlessness and the absence of scars. These methods include:
- Laser therapy. The specialist removes the nevus from the skin layer by layer using a laser beam. During the procedure, damaged blood vessels are cauterized, resulting in no bleeding. If the tumor is large, it is usually removed in several sessions.
- Cryodestruction. The mole is removed by exposure to low-temperature liquid nitrogen; the entire procedure takes no more than a minute. After exposure, a white crust forms at the site of the growth, like after a burn, which disappears within 1-2 weeks.
- Electrocoagulation. The specialist acts on the tumor using an electrode in the form of a loop through which a high-frequency current passes. At the same time, the blood vessels are cauterized, which prevents the risk of bleeding.
Structural classification of moles
A dermatologist knows well what types of moles there are. Considering the structure of the nevus, he can easily distinguish pigmented, vascular or warty moles. Therefore, if unusual formations appear on the skin or if any changes occur with existing nevi, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible.
Pigmented moles
Most often, pigmented moles are a single spot from light to dark brown. The color of the skin depends on melanin, which serves as a barrier to ultraviolet rays. Pigment spots appear as melanin accumulates in large quantities in certain areas of the skin. They can be congenital or acquired.
The following types of pigment spots or moles are distinguished:
- Freckles. These are a type of small pigment spots on the skin. They are found mainly on the face, on the hands, and occasionally on the torso. However, they lack an increased number of melanocytes. With the onset of cold weather, they can completely disappear, and with the arrival of spring they appear again.
- Lentigo. Most often, this type of spots appears in geriatric patients. Most often, age spots appear on exposed areas of the skin that have been exposed to intense sun exposure for many years.
- Chloasma or melasma. They occur on the skin of the face mainly in young females. This type of spots usually has an irregular shape, and they can also merge into one large spot of an unusual shape.
Pigmented moles are formed in almost the same way as other types of pigmented formations. The main culprit for their appearance is melanin, which is improperly distributed in the skin. The accumulation of mole cells becomes visually noticeable; their color can vary between light beige and dark brown.
Vascular moles
Hemangiomas or vascular moles are a type of skin formation that is formed as a result of the proliferation of blood vessels. Most often they have a red tint. If the vessels have developmental anomalies, then as they grow, the spots may be burgundy or blue. There are also angiomas of mixed structure, which consist of blood vessels and other tissues.
Warty moles
Verrucous nevus (verrucous) visually resembles a wart. Such neoplasms are congenital and most often occur in little girls. There are two main types of warty nevus:
- Limited. Usually these are single formations that have clear boundaries. Their diameter usually does not exceed 1 cm. And larger formations are quite rare.
- System. They are garlands of moles that have a rich brown or almost black color. Most often they are diagnosed in places where large blood vessels and nerve endings pass. Such clusters of warty nevi can occupy quite large areas of the skin.
This type of formation is not characterized by dynamic growth. They usually grow in height and due to this the diameter of the formation increases.
Useful tips
To prevent the development of dangerous diseases, people with a large number of moles need to know some nuances and take a responsible attitude towards their health:
- Suspicious moles or those that have been injured should be removed in a timely manner. If it is difficult for the patient to systematically independently examine the tumors (located on the scalp, genitals and other places that are difficult to access), then experts recommend removing them.
- Carry out the procedure for removing moles exclusively in medical institutions, and do not resort to the services of beauty salons for these purposes.
- It is not recommended to overuse saunas and steam baths.
- It is necessary to minimize exposure to sunlight on exposed skin, limit time spent in the open sun, avoid sunburn, and use sunscreen. Sunbathe from 7 a.m. to 10-11 a.m. and after 4 p.m., because... It has been proven that ultraviolet radiation can trigger the development of melanoma.
- After the summer period, visit a doctor for a preventive examination.
- Avoid injuring the area of the skin where the moles are located, i.e. do not rub, do not scratch, do not do piercings or tattoos.
- Do not expose moles to any chemicals that cause burns or irritate the skin.
- Immediately contact an oncologist if a mole begins to change its appearance.
It is important for every person to carefully monitor the condition of nevi on their body. This will make it possible to identify dangerous moles in time. Remember that timely measures taken minimize possible sad consequences.
Dermal-melanocytic types
The source of their formation was dermal cells and melanocytes, these include:
- Blue nevus. The size of a smooth knot is up to 10 mm, it can be gray in color, there are also black elements, and hair sometimes grows on the surface. A simple form occurs on the hands, neck, face, and sometimes on mucous membranes. The cellular type is distinguished by its pronounced coloring and large size, grows up to 3 cm. It is located on the sacrum, buttocks, less often on the feet and the back of the hand. Poses a danger in terms of malignancy.
- The combined nevus is represented by a combination of the borderline, complex, simple form of the blue nevus and Spitz, the peculiarity of the manifestation depends on which of the novices predominates in its structure.
- Mongolian spots. Localized on the sacrum or gluteal region, it is either a single spot or several elements. Melacite pigment is located deep in the dermis.
- Nevus Ota. Usually this is a single bluish spot, but there are also multiple small moles. Found on the face under the nose, next to the eyes. It is a dangerous manifestation, as it is prone to transformation into melanoma.
- Nevus Ito. Its difference from the previous formation in the place of localization is the upper part of the body, including the neck.
Blue nevus often occurs on the hands
Species difference
What types of moles are there on the body? Differentiation of nevi occurs according to several criteria:
- Its origin is considered, whether it is congenital or appeared later.
- Types of moles are divided according to histological characteristics, taking into account which cells are included in its structure.
- There are melanoma-safe moles that will almost never threaten human health from skin cancer.
- Melanomas are spots that can degenerate into cancer.
The structure of moles is of particular importance, therefore the histological sign includes several groups of nevi, differing in location and cells involved in its formation:
Halonevus has the ability to disappear over time
The first signs of melanoma
It is possible to provide assistance to the patient only when changes begin to be identified. The diagnosis, research, and referral for surgical treatment save a person’s life.
The first signs of melanoma:
- increase in the height of the tumor;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of discharge;
- redness;
- burning, itching;
- swelling of tissues;
- softening of the nevus;
- the appearance of a crust;
- thickening;
- hair loss;
- expansion of pigmentation around the lesion.
With the further development of dangerous melanoma, the following are observed:
- significant change in size;
- the appearance of pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- surface ulceration;
- formation of new foci;
- bleeding from places of pigmentation;
- liquid separation;
- skin thickening;
- the appearance of an earthy tint;
- signs of metastases are chronic cough, weight loss, cramps, headaches.