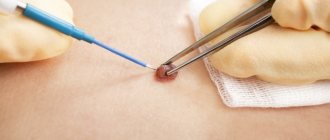
Cauterization of emerging condylomas with iodine is a traditional method of treating neoplasms. The product is characterized by its low price, availability and excellent antibacterial properties. Iodine can kill almost any type of microbe. It has a detrimental effect on the protein that makes up the microorganism. Iodine is an integral component of many antimicrobial drugs.
What are papillomas
A wart, scientifically called a papilloma , does not appear on the body just like that. In ancient times, the cause of the appearance of papillomas was considered to be the evil eye, frogs, and much more. But only now, with the advent of modern molecular diagnostic methods, has it become clear: the cause of papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Today, more than 100 types of HPV are known. It is reliably known that HPV type 2 primarily affects the skin, causing the appearance of warts, and HPV 6, 11, 16, 18, 30, 31, 33 , etc. gravitate to the mucous membranes.
The human papillomavirus has long been considered the cause of only skin and genital warts, and only relatively recently have the oncogenic properties of papillomaviruses been discovered - their ability to cause cancer and, first of all, cancer of the genital organs in both men and women.
Based on long-term research, doctors have created a classification of HPV according to its oncogenic activity:
“High-risk” HPV types ( most notably 16, 18, 31 and 45 ). Increase the risk of precancerous diseases and genital cancer. “Low risk” HPV types (mainly 6 and 11). They cause the appearance of condylomas, but are not associated with precancerous diseases and cancer of the genital organs.
The presence of “high-risk” HPV in the body increases the likelihood of developing cancer by 60 times.
Risks of HPV for the body
Human papillomavirus is a dangerous disease. This is due to the direct relationship between the development of cervical cancer and this infection. Thus, clinical trials have shown that human papillomavirus was detected in patients with the pathology “cervix (cervical) cancer” (or squamous cell carcinoma). In 65-75% these viruses of the 16th and 18th serovariants were detected. In the absence of the virus, the formation of a cancerous process does not occur.
An increased incidence of cervical cancer is observed in the average age range of women (35-55 years). The prevalence of cancer in this location is several times higher than the incidence of any other malignant neoplasms of the female reproductive system. The peculiarity of the course of the infection, namely the long absence of clinical manifestations of the disease (the incubation period can last from two weeks to several years), often leads to late diagnosis and detection of HPV after the diagnosis of cervical cancer.
In this case, warts in women serve as one of the diagnostic signs of possible infection with the human papillomavirus. Detection of this sign, diagnosis of the disease and timely treatment will help to avoid negative consequences and significantly reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer.
The predominantly sexual route of transmission plays an important role in the development of the disease, as well as the fact that barrier contraceptives (condoms) are not able to prevent infection. The size of the virus is so small that it allows it to easily penetrate through the pores and manufacturing defects of the contraceptive material.
Research conducted by the World Health Organization has shown that a woman who has had 10 or more sexual partners in her lifetime is 10 times more likely to become infected and, accordingly, develop cervical cancer than in the control group. Therefore, the problem of sexual culture is currently very acute from a medical (oncological) point of view.
How does the virus manifest itself?
An important circumstance is that clinical manifestations of HPV are not detected for quite a long time. Focusing on a long asymptomatic period, one should not underestimate the danger of human papillomavirus infection.
Already today in the United States, infection caused by HPV is the most common viral disease, predominantly sexually transmitted (in our country, large-scale studies in this direction have not yet been conducted).
Plus, HPV damage to the cervix, even in the presence of clinical manifestations, often goes undetected for a long time.
Infection with the human papillomavirus usually occurs through close contact with the source of infection. HPV can be transmitted with scales peeled off with papillomas during sexual play with hands, during sexual intercourse, and when women use hygienic tampons, it can be carried from the external genitalia into the vagina, onto the cervix. Infection of newborns during childbirth is possible.
Each wart, papilloma or condyloma (these are just different names for the same disease, differing only in the place of manifestation of the tumors) is a reservoir for the human papillomavirus.
This virus also accumulates in the tissues surrounding the tumor, which can cause changes in the DNA of epithelial cells of the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs, resulting in the development of precancerous conditions.
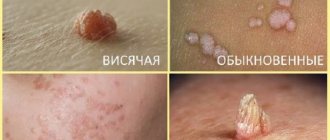
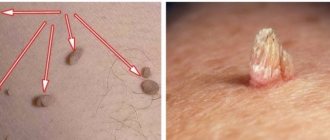
Papillomas manifest themselves as papillary growths protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane, most often have a thin stalk, and sometimes a wide base.
They can take on bizarre shapes that look like hairs, cauliflower or a cockscomb.
Causes of warts
Viruses are considered the main etiological agent for the appearance of warts on the skin. Among them, the most important role is played by human papillomaviruses, of which there are more than 25 species. Among the latter, more than 170 strains (that is, variants) of viruses are distinguished, which explains the wide variety of clinical pictures.
In more than 50% of patients, infection occurs through sexual contact. This causes infection with papillomavirus and often manifests itself in the formation of condylomas (warts) in the genital, anal and peri-umbilical areas.
However, it should be noted that contact with human papillomaviruses does not always lead to the development of the disease. The so-called “predisposing factors” are of particular importance. The latter can be both systemic - decreased immunity, and local (local changes) - abrasions and cracks in the skin (mucous membranes), increased sweating of certain places on the skin.
Certain types of warts appear due to contact with a person who has similar formations. Thus, infection can occur when using the same things as a sick person, personal hygiene items, towels, underwear and bed linen, and even dishes. Infection and development of the disease occurs when the disinfection regimes for instruments during manicure and pedicure procedures are not followed. You can also become infected by walking barefoot in a public bath, sauna, or swimming pool.
Types of papillomas
Depending on the location, the following types of external manifestations of HPV are distinguished:
- Vulgar (simple) warts , which account for up to 70% of all skin warts and are more common in school-age children. They are elevations above the surface of the skin with an uneven, keratinized surface. They most often appear on the hands, but can be on the edges of the lips, on the face and, extremely rarely, on the oral mucosa.
- Flat (juvenile) warts are less common (4%). They are found in children and young people on the back of the hands and feet, face, and oral mucosa. These are warts of different shapes; they have a smooth surface and slightly rise above the skin level.
- Palmoplantar warts are very common (34% of cutaneous warts). They are dense formations with horny layers.
- Filiform warts are soft, flesh-colored to dark brown papillomas, often pedunculated. They are located on the neck, skin of the eyelids, armpits, groin, under the mammary glands.
- Genital condylomas are multiple, less often single, soft papillomas located on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, around and inside the rectum, sometimes in the urethra. They have the appearance of simple (pyramid, ball) or complex (cauliflower) growths with a keratinizing surface on the stalk.
Removal of papillomas
The question of the need to remove papillomas is decided unequivocally - it must be removed. It is not without reason that, literally translated from some languages, a wart means “extra meat.”
In addition, damage to papillomas, when they reach large sizes or are injured by linen and clothing, leads to the formation of long-healing, easily bleeding wounds into which infection can penetrate.
Removal can be done using various methods: traditional surgery, chemical cauterization, thermal or cryodestruction.
The most modern and safe types of surgery are radio wave and laser. The impact on surrounding healthy tissue is minimized.
When removing warts and papillomas using these methods, the formation of scars or scars in their place is almost completely eliminated. Healing of the skin after removal occurs within several days. In parallel with the removal, antiviral therapy is necessarily carried out.
Useful properties of iodine
Iodine has many beneficial properties; it is recommended to cauterize condylomas and treat wounds to avoid infection
Iodine has many beneficial properties; they are recommended to cauterize condylomas, treat wounds to avoid infection, treat fungal-affected areas of the skin, and gargle during inflammatory processes.
There is such an expression as “iodine network”. External use of the drug causes reflex responses from internal organs.
This is explained by the dilation of blood vessels in the skin under the influence of iodine and the outflow of blood, which entails a contraction of tissues in which inflammation progresses.
Draw a mesh on the chest and back of a patient with bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia. This method is used for pain in muscles, lower back, and joints.
Iodine solution is taken orally in very small doses. This is done in case of severe coughing attacks, atherosclerosis, inflammation of the respiratory tract, and mercury poisoning.
A few drops of the drug are dripped into a mug of warm water and drunk. This is done for problems with the thyroid gland and during the tertiary period of syphilis.
Many medications containing iodine are aimed at treating sore throats, laryngitis, pharyngitis, and other inflammatory diseases of the larynx.
It would be wrong if we forget about the properties of iodine when removing benign skin tumors such as condylomas, papillomas, and warts.
Description of medicinal properties
Iodine provides antimicrobial and local cauterizing (if high concentration) effects, irritates damaged tissue structures, and precipitates proteins in tissues. A third of the skin that comes into contact with iodine becomes binary compounds iodides, the remaining two thirds are transformed into active iodine, partially absorbed by the tissues.
The substance is used in the treatment of skin pathologies of an infectious-inflammatory nature, damage to integumentary tissues (traumas, wounds, burns, trophic and varicose ulcers). The instructions do not contain information about the possibility of using iodine for condylomas, but this technique is practiced by a large number of patients.
Antiseptic drugs containing iodine include:
- aqueous solutions of Iodinol 1% and Iodonate (with surfactants);
- 5% solution based on ethyl alcohol;
- an aqueous solution of potassium iodide with iodine;
- iodine in combination with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP).
Is it possible to cauterize papillomas and condylomas?
Papillomas are often localized on the neck, chest, armpits, face, and arms above the elbow. All these parts of the body are considered open, and such neoplasms worsen the aesthetic appearance. Many people try to get rid of such “decorations”.
Condylomas appear on the genitals of men and women.
They often affect areas around the anus, and do not disdain the internal walls of the anus, vagina, and cervix. And, as a rule, the first thing people are interested in is the issue of treating formations in inexpensive and accessible ways at home.
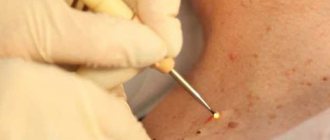
Iodine is often used to cauterize warts, but is it possible to get rid of condylomas on the body this way and is it safe?
An iodine solution promotes the coagulation of protein tissue in pathological growths on the skin and mucous membrane. This drug has found wide use in the fight against such problems and has already helped a considerable number of patients with condylomatosis.
Only when using iodine, you must be extremely careful when applying. The solution can cause a burn on healthy tissue around the tumor.
The skin, especially the mucous membrane, is very susceptible to the drying effect of iodine. At the site of the burn, pain, severe burning sensations, and later the convergence of the upper layer of the epidermis are noted.
Even after complete healing, such a process can leave a mark on the body in the form of a small scar or pigment spot.
When using this product, you should be extremely careful and apply it exclusively to the growth. Try not to touch healthy tissue next to papillomas or condylomas.
Efficacy of iodine for HPV
An alcohol solution of iodine is characterized by a cauterizing, local irritant, and antiseptic effect.
The application is effective for small formations. In order to remove large growths, it is necessary to use hardware or surgical treatment methods.
Advantages of iodine treatment:
- low price compared to hardware procedures;
- accessibility: can be bought at any pharmacy, treated at home;
- ease of use;
- is an antiseptic, the likelihood of infection is low;
- suitable for neoplasms of all types (hanging warts, vulgar warts);
- minimal number of contraindications and side effects (if used correctly).
Disadvantages of the chosen method of therapy:
- not suitable for mucous membranes (oral cavity);
- long treatment time;
- danger of re-formation of growth.
Stages of iodine treatment
The effect of treatment for genital warts will depend on factors:
- Number of neoplasms.
- Size of growths.
- Locations.
- Intensity of drug application.
- Cauterization frequencies.
It is necessary to smear the formations with a cauterizing solution 3-5 times a day, without missing a single day, until the growths disappear
Treatment of condylomas with iodine is allowed for small single formations. Multiple large growths are best removed using traditional medicine.
The method of treating genital warts can be compared with chemical coagulation, only this remedy is characterized by greater safety in comparison with the acids that are part of chemical reagents.
In order to remove condylomas with iodine, you need to be patient and be careful when applying the drug, as well as:
- Before the procedure, you need to make sure that the treatment area is clean and dry;
- It is advisable, in order to avoid burns, to treat the skin around the pathological area with cream, without touching the growth itself;
- smear the formations with a cauterizing solution 3-5 times a day, without missing a single day, until the growths fall off.
The result will take 7-10 days, provided that all stages of treatment are followed.
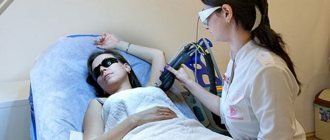
Using the laser method
Currently, this method is the safest and most effective; it is based on the fact that the affected area is exposed to high-purity fractional laser beams. Under their influence, pathological tissues are destroyed and the neoplasm disappears.
Cauterization occurs without pain and leaves no noticeable marks. To anesthetize the process, local anesthesia is used. In this regard, it is possible to use the procedure for all skin areas.
After the operation, traces appear again, but over time they disappear. The size of the consequences depends on the dimensional characteristics of the formation. To remove pointed and flat growths, specialized institutions use effective pulsed laser preparations. To deal with large growths that merge and grow together, laser beams of a constant type are used.
Contraindications for use
Cauterizing condylomas is not a harmless method of combating the growth of pathological cells. The product has contraindications:
People with particularly sensitive skin may experience an allergic reaction. It manifests itself:
- swelling of tissues;
- redness of the skin around the treatment site;
- local temperature rise;
- severe burns;
- sometimes itching, pain;
- swelling of the mucous membrane (you need to be especially careful when rinsing the larynx and using Lugol's solution to treat inflammation of the throat);
- weeping and even the appearance of blisters.
Patients who have problems with the thyroid gland, in particular its hyperfunction, are prohibited from smearing condylomas with iodine.
Those suffering from a disease such as Dühring's dermatitis are also not recommended to resort to this method of treating skin tumors.
Those who have pathological changes on the skin due to diabetes should refrain from using iodine solution on genital warts.
It is not worth cauterizing condylomas of different sizes with iodine if their location is the mucous membranes.
Sometimes the opposite effect occurs from using this remedy. Some patients complain: “I apply it, but new tumors appear.” This fact should not be overlooked and the course of therapy should be monitored.
To record changes in a positive trend or a negative effect of the drug, it is recommended to photograph the problem area during treatment to assess its condition.
IMPORTANT! Cauterization should be stopped if any adverse symptoms, changes in adjacent tissues or in the general condition of the patient are noticed.
Do not forget that the causative agent of all types of condylomas is the human papillomavirus. To effectively combat this disease, it is necessary to treat external manifestations on the skin and mucous membranes, and reduce the amount of virus in the body.
The human immune system must fight this pathogen. And in people with reduced, weak immunity, the effects of the virus are manifested by all sorts of growths on the skin.
In addition to cauterizing tumors, it is worth using antiviral drugs and immunostimulants. Otherwise, neither iodine nor other removal methods will be able to get rid of such troubles for a long time.
By the way, those who do not have a weak body’s ability to resist may never know that they were infected with HPV.
Self-removal of condylomas: cauterization with iodine
Growths that affect the genitals and mucous membranes, the appearance of which is provoked by the activation of HPV when the immune defense is weakened, are called condylomas. Most often, the virus enters the body through unprotected sexual intercourse, but contact and household transmission of the infection is also possible.
The virus spreads through blood, but it is impossible to clearly determine when infection occurred. Its activity occurs during the period when problems with the immune system arise, in which it is not able to suppress the reproduction of harmful agents, and the duration of the incubation period can range from several weeks to entire years. The basis of treatment for emerging formations is surgical intervention (destruction).
However, some people prefer to get rid of growths using traditional medicine or other alternative methods, which include cauterization of condylomas with iodine. Despite the availability and effectiveness of this method of getting rid of growths, positive results when used are not achieved in all cases.
Description of medicinal properties
Iodine provides antimicrobial and local cauterizing (if high concentration) effects, irritates damaged tissue structures, and precipitates proteins in tissues. A third of the skin that comes into contact with iodine becomes binary compounds iodides, the remaining two thirds are transformed into active iodine, partially absorbed by the tissues.
The substance is used in the treatment of skin pathologies of an infectious-inflammatory nature, damage to integumentary tissues (traumas, wounds, burns, trophic and varicose ulcers). The instructions do not contain information about the possibility of using iodine for condylomas, but this technique is practiced by a large number of patients.
Antiseptic drugs containing iodine include:
- aqueous solutions of Iodinol 1% and Iodonate (with surfactants);
- 5% solution based on ethyl alcohol;
- an aqueous solution of potassium iodide with iodine;
- iodine in combination with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP).
Acceptability of use
Self-medication is acceptable if the identified strains of the virus are not oncogenic. The formations may disappear on their own, which is rarely observed. They usually remain on the body, causing the patient a feeling of discomfort in the affected area. Mechanical damage to growths is often observed, associated, for example, with friction on clothing, increasing the likelihood of malignant degeneration of condylomas.
Cauterization with iodine is not recommended for formations that affect mucous membranes. The procedure as a whole should be carried out carefully so as not to damage the surrounding healthy dermis.
Periodic use to disinfect a specific area will not cause damage, so to remove condylomas, application must be regular.
Constant exposure to iodine on the same area of the skin can cause chemical burns due to the strong redox properties of the element.
Before treatment with this method, it is important to remember:
- Application of the product should be daily without missing sessions.
- Since the use of iodine in the form of an alcohol solution can provoke an allergic reaction, it is necessary to test the skin 24 hours before the procedure by treating a small area of skin on the elbow. If there is no redness, itching, or irritation, you can begin to treat the pathology. If a negative reaction is observed, you should use another method.
- The cauterizing effect of iodine can cause serious damage to delicate skin, so it should be applied carefully.
- Advanced condylomatosis cannot be eliminated with this remedy. Effective treatment is only possible with surgery.
Treatment method
The effect produced by iodine is similar to that of chemical drugs, but its safety is higher. It removes formations painlessly and in a short period of time by drying pathological tissues of entire clusters of condylomas.
When using, you must follow certain rules:
- Only the lesion should be treated, which will avoid damage to healthy skin;
- Application procedures must be carried out at least 3 times a day;
- growths that have reached large sizes cannot be removed with iodine.
This therapy ensures that the formations dry out and fall off, but in some cases the opposite effect is observed: condylomas begin to grow rapidly in diameter, and their number increases sharply. If negative changes occur, you should urgently visit a doctor.
Cauterizing condylomas with iodine is not only effective, but also beneficial for your own budget: every pharmacy sells it at prices that are many times lower than the cost of beauty salon services.
However, this method of removing formations has several disadvantages:
- active penetration of the element into tissue structures provokes hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, which intensively absorbs it;
- a severe allergic reaction and burns may occur if used carelessly;
- there is a risk of scar formation at the site of the fallen growth;
- Since the oral cavity is lined with mucous membrane, the use of iodine to get rid of formations in this area is strictly prohibited.
Carrying out the procedure
Treatment of condylomas with iodine should take place in several stages:
- Cleaning the area where the growth is located, removing excess moisture.
- Applying thick cream or Vaseline around the circumference of the formation.
- Lubricate the body of the condyloma with a cotton swab dipped in the solution at least 3 times during the day.
Each subsequent application must be carried out with all the specified actions performed. The use of the substance continues until the pathological elements disappear on their own: the minimum course duration is a week.
With a high pain threshold, you can gradually increase the number of daily procedures for treating formations. It is advisable to take photographs of the area where treatment is being carried out in order to assess the changes that have occurred since the first application of iodine to the lesion: has the number of growths decreased, has their location, diameter, and outline changed?
Despite the apparent harmlessness of this treatment method, it is recommended to consult with a specialist about the admissibility of its use in a particular case in order to avoid unpleasant consequences.
Some people are not able to withstand even a small amount of the substance, because they are more sensitive to pain than others. It is better for this category of patients to seek professional help, even taking into account the fact that the cost of laser and surgical destruction using anesthetics is much higher than the price of a jar of iodine.
Tips for use
Basic recommendations for iodine therapy:
- Do not mix water or other liquids with tinctures and other antiseptics containing iodine.
- To increase the effectiveness of the effect, the skin should be steamed before the procedure.
- It is recommended not only to treat the growth, but to apply it to it and hold it for up to 30 seconds with a cotton swab that has been soaked in a solution or Povidone-iodine.
- It is better to refrain from gluing cotton wool soaked in iodine to the affected area with a plaster - this will lead to a severe burn.
The use of the product is contraindicated for:
- problems with the thyroid gland (hyperfunction);
- hypersensitivity to the active component;
- Dühring's dermatitis;
- skin pathologies caused by diabetes mellitus.
Alcohol and other iodine solutions used to cauterize growths are characterized by less aggressive effects compared to alkalis, phenols, and acids.
Povidone-iodine, which has bactericidal, fungicidal, virucidal properties, is characterized by the greatest gentle effect.
When using this product, burns of the skin and mucous membranes do not occur.
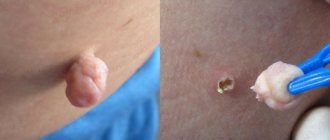
How to care for the wound after papilloma removal
The wound after removal of the papilloma is a funnel-shaped depression, which corresponds in diameter and depth to the eliminated skin formation.
The wound after removal of the papilloma is a funnel-shaped depression, which corresponds in diameter and depth to the eliminated skin formation.
Swelling and redness of the surrounding skin is likely for 24 hours after surgery. For the formation of a scab, constant ventilation of the wound is necessary.
Fresh air dries the lymphatic fluid protruding to the surface, which coagulates and forms first a film and then a crust. Under this crust, epithelization of the wound occurs, so it can be called a “biological dressing.”
After removal of papillomas, it is impossible to allow damage to the integrity or premature removal of the crust, as this provokes severe bleeding, the formation of scars and age spots, as well as infection of a fresh wound.
It is strictly forbidden to peel off the crust or unrejected papilloma tissue yourself. It should be borne in mind that the detachment of the scab can be caused by its softening or, on the contrary, overdrying. Based on this, you should temporarily not wet the wound or apply ointments, creams and other cosmetics to it.
In addition, you should limit your exposure to ultraviolet radiation as much as possible. If the wound does become infected after removal of the papilloma, and purulent contents begin to accumulate under the scab, then the crust must be removed under medical supervision.
To do this, it is thoroughly soaked in furacillin or a solution of hydrogen peroxide and, after softening, carefully lifted by the separated part.
The scab is peeled off without applying excessive force and trimmed with sterile scissors so that its fixed part remains in place. During the normal recovery process, after the crust comes off, thin skin remains, which has a bright pink tint.
After several months, the difference in color smoothes out, and the operated area ceases to differ from the surrounding tissue. The newly formed skin after removal of papillomas cannot be treated with alcohol lotions, scrubs and irritating ointments.
Avoid contact with household chemicals and any chemically active substances. During hygienic procedures, care should be taken - do not rub young skin with a washcloth or pumice stone, and do not use a razor in the operated area.
The use of foundation and other decorative cosmetics is not recommended if a papilloma has been removed from the face. At the same time, it is necessary to lubricate the skin with sunscreen, since it is very sensitive to solar radiation, prone to burns and increased pigmentation.
Official medicine
There are many ways to treat a wart. One thing will help someone, another will help someone. Even for the same person, the same method may work adequately for one wart, but not for another.
To begin with, MirSovetov will talk about folk remedies for treating warts - as less traumatic (if used wisely). When deciding to resort to folk remedies, you need to remember the likelihood that you do not have a wart, but simply something similar to it. Therefore, if the method does not help within a reasonable period (up to a month), then it makes sense to consult a doctor.
One of the desirable conditions for traditional methods of treatment is the belief that this method will help. In some cases, faith alone is enough (placebo effect).
Let's move on to specific examples. The list of folk remedies is far from complete, but from it you can already have an idea of the train of thought. At least you can try - relatively harmless options have been selected.
- Autogenic training. Sit back, close your eyes, relax - and imagine how the warts disappear. The method is good for people with a vivid imagination.
- Take a raw potato (optionally an apple, beetroot, or other vegetable/fruit), cut it in half, rub the wart with each half. Then put the two parts of the potatoes together and bury them (these steps are optional for those who don’t believe in magic). When it rots, then the wart will disappear.
- Take a silk thread (hair, rope), and tie a knot above each wart in the air, then hide the thread in a cut potato (or something else) and bury it. This is one of the treatment methods based on the belief in its effectiveness. Surprisingly, it still helps some people get rid of warts.
- Traditional medicine also suggests rubbing and dusting the wart with chalk, and then tying it in woolen cloth. Try not to get the bandage wet.
- Bandage the wart tightly, and do not remove the bandage for as long as possible - until it gets dirty. In three weeks, the wart should go away (at least, that’s what those who are sure that they got rid of warts with this method say).
- Apply the juice of freshly picked celandine to the warts 2 times a day. Be careful - the juice is quite caustic, so you should ONLY apply it to the warts, and not the surrounding skin. The same can be done using dandelion or milkweed juice.
- Apply a bandage with crushed Kalanchoe leaves for a week, changing it to a fresh one every day.
- Take 3 tablespoons of wormwood, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 2 hours in a sealed container. Make a compress. And so - every day.
- Soak the raw onion in vinegar for 2 hours and tie it to the wart overnight. Repeat several nights in a row. Caution: To avoid burning the skin around the wart, you can use a plaster or a piece of plastic bag.
- Traditional medicine offers another remedy for getting rid of warts, similar to the previous one: mix acetic acid with flour in a 1:2 ratio. Cut a hole in the patch in the shape of a wart and stick it on the skin so that the wart sticks out of the hole. Spread the mixture on the wart and seal it with a second bandage on top. Change the bandage 1-2 times a day, do not allow the mixture to come into contact with healthy skin (there may be burns). In a week the wart should go away.
- For plantar warts. Steam the foot in hot water with soda and carefully remove the stratum corneum. Wipe your leg dry, place a small piece of raw meat on the wart, cover with a piece of oilcloth and bandage/glue with a band-aid, do not wet it for 3-4 days. Then steam again, remove the softened part. If the wart is not all gone, repeat.
- Another folk remedy for the treatment of plantar warts. Bandage the inside of a banana peel to the wart.
When the wart begins to turn black on top, this is a sure sign that its roots are dying. During this period, do not try to cut off the top layer from it; it is important that the wart falls off completely - this way you will increase your chances of protecting yourself from the reappearance of a wart in the same place.
The good thing about folk remedies is that you can always try them to treat warts in children. The child may be afraid to go to the doctor, and you don’t always want to subject delicate children’s skin to radical treatment using the methods of official medicine.
Moreover, such folk remedies as cauterizing a wart with vinegar and celandine juice, although they take longer, are also more gentle on the skin.
With preschool children, traditional treatment methods can even be turned into an entertaining game: rub the wart with something suggested above, for example, an apple, and invite the child to bury the apple himself. Naturally, go along with it
child.
Official medicine can offer a whole range of methods for getting rid of warts. The choice of a specific method depends on what type of wart, as well as on the individual characteristics of your body. In addition to removing the wart itself, you will most likely be prescribed a general course of strengthening the immune system to avoid relapses.
Let's look at each of the methods in more detail.
Cryodestruction (freezing with liquid nitrogen) Destruction of warts using liquid nitrogen. It is applied to the wart using a tampon attached to a wooden stick or using a special cryoapplicator.
Freeze the wart for 10-30 seconds. In this case, the wart becomes white and dense, and after about an hour a blister forms in its place, which lasts for 5-7 days, gradually drying out.
The crust finally comes off after two weeks, leaving a light pink spot. For plantar warts, a longer course is needed - several freezing sessions with an interval of 2-3 days.
Electrocoagulation The wart is “cut off” with a thin metal loop under a high frequency current, which helps to avoid bleeding and at the same time disinfect the tissue. This leaves enough material for histological examination - if there is a suspicion of oncology, for example.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. After exposure to current, a small crust forms, which will fall off in a week (during this time it is better not to wet it or cover it with cosmetics so that there is no scar left).
Laser coagulation The wart is removed layer by layer using a laser under local anesthesia. A small depression remains at the site of the wart, which smoothes out in 2-3 weeks. If we are talking about a plantar wart, then you need to take into account that during these 2-3 weeks you will have to take care of your foot - walk as little as possible.
Surgical excision This method is used only when the warts are large enough (or several have merged into one). Under local anesthesia, all excess is cut out with a scalpel and sent for examination. The skin is sutured with a cosmetic suture, after which only a thin, light, flat scar will remain.
Chemical methods Are used relatively rarely. This is smearing the wart with a fairly caustic acid or alkali - either once or as a course of treatment.
At the same time, there is a high risk of damaging surrounding tissues or introducing an infection, and it’s not very pleasant. An exception may be the treatment of warts with salicylic acid.
It can be bought at the pharmacy in liquid form, as an ointment (in combination with something else) or as a special patch. For some types of warts this works quite well.
The main thing to remember is that you only need to remove the wart, and not the flap of skin on which it grew - that is, you need to lubricate ONLY the wart, seal it with a special plaster - also ONLY the wart. MirSovetov advises doing this: cut a hole in a regular adhesive plaster in the shape of your wart and stick it on to protect the skin.
Then apply salicylic acid in one form or another to the wart, and secure the structure with another layer of plaster. The dressing is changed 1-2 times a day.
There is only one caveat: some doctors do not recommend this method for those who have diabetes or circulatory disorders - it is better for such people to be treated under the supervision of a doctor.
How to prevent complications after papilloma removal
Zelenka also has disinfecting properties
As a rule, after removal of papilloma, complications arise as a result of improper wound care. Scarring and long recovery times are most common when the immune system is weak.
In some cases, infectious processes may occur accompanied by purulent discharge. The list of medications is compiled depending on individual indicators - the location of the wound, the condition of the skin and other characteristics, but it must include antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
How to treat the wound surface after papilloma removal? Solutions of brilliant green, iodine and potassium permanganate have a disinfecting effect.
After peeling off the crust, one percent hydrocortisone ointment can be prescribed, which is applied twice a day to the healed wound for 10 days.
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to increase the regenerative function of the skin, improve its elasticity and resistance to aggressive environmental factors.
To do this, use solutions containing vitamins A and E.
Hyaluronic acid, which is part of some creams and gels, creates a thin film on the surface of the skin, which, without interfering with oxygen exchange, stimulates the synthesis of collagen and elastin, and also revitalizes rough tissue.
Gentle peeling with glycolic acid removes dead particles and smoothes the skin structure without damaging it. After removing the papilloma, it is necessary to promptly normalize the production of elastin and collagen for the formation of connective tissue, and this is only possible with intensive nutrition of the skin.
Vitamins, minerals and amino acids entering the body significantly contribute to healing and tissue regeneration.
You can avoid adverse consequences by strictly following all medical instructions and providing your skin with gentle treatment and careful care.
Application of chemical exposure techniques
To achieve this goal, a wide range of medications are used, which are sold in any pharmacy.
The most popular medications for combating such formations are compounds such as Solkodrem, Solkovagin, Feresol.
Some drugs are prepared as solutions, and some of them are taken as ointments and gels.
The basis of most medicines is acid. Within a few minutes, necrosis of the tissue of the formation is observed, as a result of which a yellow-white film appears, acting as a protective layer. It is under this element that new epithelial cells grow. Peeling of the protective element occurs after a few days.
The procedure must be performed by a specialist whose office is equipped with special equipment and devices. After cauterization, the patient should be under the supervision of a physician. If the therapy is insufficiently effective, the procedure must be repeated.
It is important to follow the instructions for using chemical compounds, otherwise there is a risk of burns, side effects and phenomena. The total duration of treatment is limited. If the patient experiences discomfort, the doctor should be aware of this.