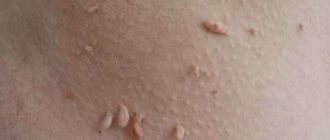
Viral warts are a viral infectious disease, which is characterized by the appearance of small benign neoplasms (skin growths) on the skin and mucous membranes. It occurs quite often and affects people of any gender and age.
Viral warts are formed under the influence of the human papillomavirus (HPV)
Causes
The agent causing the development of the disease is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Its different strains can cause damage not only to the skin, but also to the mucous membranes of the vocal cords, bladder, oral cavity, and external genitalia.
Infection occurs through contact with a sick or infected person or sick animals. The main routes of infection are:
- sexual tract – typical for warts of the anogenital area (genital warts);
- vertical route – infection of a child from an infected mother during childbirth (causes the occurrence of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis in children);
- household route - the virus is able to remain viable for a short time on objects used by the virus carrier or a sick person;
- autoinoculation (self-infection) - occurs during hair removal and shaving.
The following factors increase the risk of infection:
- promiscuous sex life;
- frequent visits to saunas, swimming pools, gyms;
- work related to cutting raw fish or meat.
The human papillomavirus enters the body through minor injuries to the skin or mucous membranes. It then enters the cells of the basal layer of the epithelium. Here it can be in one of two forms:
- Episomal. HPV is located outside the chromosomal apparatus of the affected cell. This form of the disease is regarded as benign.
- Intrasomal. The virus is embedded (integrated) into the cellular genome. This form is considered malignant.
The incubation period is long: from 15 days to several years. Human papillomavirus infection is characterized by a latent, i.e., hidden course. It enters the stage of clinical manifestations, i.e. the actual formation of warts, under the influence of various provoking factors (hypothermia, severe stress, poor living conditions), leading to a decrease in immunity.
Approximately 90% of patients with papillomavirus infection self-heal within a year from the moment of infection. In others, the disease takes a recurrent, long-term chronic course. In rare cases, warts may become malignant (infected with an oncogenic strain of HPV).
general description
Viral warts are benign tumor formations of viral etiology.
The causative agents of viral warts belong to the human papillomavirus. Infection becomes possible in case of close contact with a sick person, especially if there are minor skin injuries at the site of penetration of the virus through infected household items or shared use. Morphological changes in exophytic warts depend on their location and type of virus and are manifested by papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis and elongation of the skin papillae. More often they occur on open areas of the body, head, arms or legs, which are more often exposed to microtrauma, as well as on the skin when exposed to pressure or friction from clothing or shoes.
Types and symptoms
Depending on the location and clinical signs, several types of viral warts are distinguished:
| View | Description |
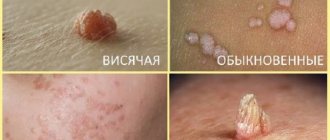
| Vulgar (simple) | They account for approximately 70% of all types of viral warts. The disease most often affects children and adolescents. Neoplasms are localized mainly on the fingers and the back of the hands. Much less often they are located on the face or on the mucous membranes. They look like dense round nodules, with a diameter from several mm to 1.5 cm. The color of the skin over them is not changed. |
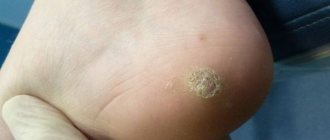
| Plantar | Outwardly they look like vulgar ones. Located on the skin of the soles. When walking they cause pain. |
| Palmoplantar | Affects adults. The neoplasms look like small growths that are firm to the touch. The spread of infection is facilitated by wearing uncomfortable and tight shoes. This form of pathology requires differential diagnosis with plantar syphilitic papule and ordinary dry calluses. |
| Periungual | They are a variant of vulgar warts. Most often they occur in children who bite hangnails or bite their nails. This form of the disease is characterized by frequent relapses. |
| Youth (flat) | They occur on the mucous membranes of the rectum and cervix, the skin of the hands and face, and the head of the penis. Most often occur in teenagers and young adults. |
| Filiform | They have the appearance of soft papules ranging from flesh-colored to dark brown. Appear on the skin of the eyelids, neck, mammary glands, armpits and groin areas. The formation often has a pedicle, which increases the risk of injury. |
| Pointed (condylomas) | Externally they resemble a cockscomb or cauliflower. Surface color from flesh to pink. When rubbed they turn crimson-red. Bleed easily when injured. They are localized in the anogenital area, and in children they can also be located in the area of the nasolabial folds. Condylomas are characterized by the presence of a thin stalk, as well as a tendency to form large conglomerates. |
Symptoms of viral condylomas
How to understand that there is a viral formation on the skin? ICD 10 describes the symptoms and treatment methods of such a disease.
Viral warts increase in size quite slowly, gradually growing and protruding to the surface. There are no special signs of the disease. A nodular formation appears on the surface of the skin. The color is initially flesh-colored, but over time it can turn into gray shades.
Warts on the hands are prone to frequent injury, which can result in bleeding and pain.
The greatest discomfort is caused by plantar warts, located on the foot, sometimes on the toe. In such a case, the patient experiences pain when walking due to the growth of a viral growth inside the epidermis.
In children, this disease develops a little differently. Many small flat growths appear on the skin. They have the ability to quickly spread throughout the body.
Adults are characterized by a single location of viral growths; a child has several warts in one place with larger ones in the center.
Sometimes viral formations can pass on their own and disappear. However, in most cases they require careful attention and therapeutic measures.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by the characteristic appearance of formations. Differential diagnosis with the following diseases is necessary:
- lichen planus;
- warty form of skin tuberculosis.
Special atlases, which present photos of various types of skin diseases, are of great help in carrying out differential diagnosis. In difficult diagnostic cases, a biopsy is performed followed by histological analysis of the tissue sample.
How can you get infected?
Human papillomavirus has many forms of transmission, as well as many routes:
- through damaged skin (enters the blood);
- through mucous membranes;
- during sexual intercourse;
- with normal contact.
Therefore, it is very easy to catch the virus, just swim in a pond or pool, go to a SPA salon, sauna, or use the personal belongings of a person who has a warty layer of skin (towel, clothes, toothbrush, razor).
This type of virus infection occurs all the time, but it is not so easy to remove it from the body, and therefore you should more carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene, since warts are only the least of the possible problems.
Treatment of viral warts
To remove viral warts, use one of the following methods:
- Laser removal. After local anesthesia, layer-by-layer burning of the tumor is performed using a laser beam. The wound heals within 10-15 days without leaving a scar.
- Electrocoagulation. Performed under local anesthesia. Using a metal electrode in the form of a loop, the wart is cut off near the very base and the tissue is cauterized (coagulated). A dense dark crust forms on the wound, which disappears after 7-10 days. If the formation is large, a barely noticeable scar may remain on the skin.
- Cryodestruction. The method is based on the destruction of pathological tissue by freezing it with liquid nitrogen.
If a large area of skin is affected, it may require excision. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The wound is sutured with cosmetic subcutaneous sutures, resulting in a very thin and almost invisible scar in its place.
Viral warts should be removed only in a medical facility and with mandatory subsequent histological analysis of the resulting material.
In the postoperative period, in order to possibly prevent the spread of infection, it is recommended to lubricate the undamaged areas of the skin around the wound with antiviral ointment (selected by the doctor).
To prevent relapses of the disease, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is usually prescribed.
It is better to remove warts in a medical facility using one of the minimally invasive methods
How to understand that these are warts?
Sometimes it is extremely difficult to understand that a person has a wart.
The clinical picture of the disease may be absent for years, since there are simply no typical symptoms. A person develops small lumps on his body, and if there are 1-2 of them and they do not hurt, then the patient does not seek medical help. People come to the hospital or to a private doctor whose warts have developed in large numbers and have begun to cause discomfort not only morally, but also physically. Upon examination, the doctor will easily understand whether it is a wart or just a pimple, but to confirm it, he will definitely prescribe a test for the presence of human papillomavirus in the body.
Treatment at home
You should not try to get rid of warts at home using traditional methods of therapy. They are not only ineffective in most cases, but can also lead to the development of a number of complications:
- wound infection with the development of purulent inflammation;
- spread to healthy areas of the skin;
- bleeding.
In some cases, viral warts can develop into malignant tumors. Therefore, when removing them, a histological examination is required, which is not possible to perform at home.
Therefore, you should not try to get rid of viral warts on your own. It is necessary to consult a doctor and carefully follow all his prescriptions and recommendations.
Treatment and removal in children
Treatment of warts in children involves the use of a variety of creams and ointments. Treatment is prescribed by a specialist after a thorough examination.
You should carefully monitor the baby's condition and his reaction to the drug. If negative signs occur, therapy should be suspended.
A variety of special patches can be used to treat warts in children. They do not cause inconvenience and help to quickly cope with an unpleasant illness.
It is necessary to support the immune system during treatment and take vitamin complexes.
ethnoscience
More and more people are using folk remedies because they are cheap and proven.
But it is worth saying that such treatment of the disease is quite doubtful, since the warts go away only temporarily, and the virus continues to remain in the body and cause the formation of new lesions. It is better to use any folk remedy in complex therapy, and not to replace all treatment with it.
They help a lot:
- celandine juice;
- garlic;
- iodine;
- vinegar;
- Castor oil.
These products are used to make lotions or simply burn the affected areas of the skin.
Pathogen
The causative agent of infectious warts is a virus from the HPV group. It forms eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions, under an electron microscope it looks like spherical bodies, sometimes crystals. The virus contains DNA, is filtered through a Berkefeld filter, preserved in 50% glycerol, and destroyed at temperatures above 50°C.
In the human body, under the influence of an introduced virus, temporary immunity is developed, which is caused by virus-neutralizing and complement-fixing antibodies.
The virus enters the human body through the skin and mucous membranes. A wart develops at the site of an invading virus. Histologically, proliferation of the epithelium and dermal papillae, hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis are observed. The cells of the spinous layer are vacuolated. Hypertrophied epithelial processes converge from the periphery to the center, forming something like a bowl. In the dermis, inflammation usually does not occur. The nuclei of the cells of the main layer increase in volume and become sharply basophilic. In the upper layers they are completely filled with a homogeneous mass.