Rubromycosis or trichophytosis Castellani, as rubrophytosis is also called, is referred to as dermatomycosis, which occurs when the skin is infected by the parasitic fungus Trichophyton rubrum.
Rubrofitia is characterized by damage to the feet, hands, large folds and smooth skin, vellus hair of the body, and limbs. Less commonly, the fungus infects the skin of the face, scalp, and affects long hair.
The fungus Trichophyton rubrum - red trichophyton, is highly active at high humidity.
Clinical picture
Rice.
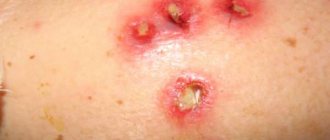
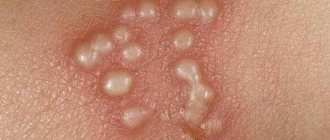
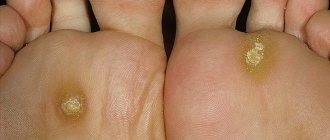
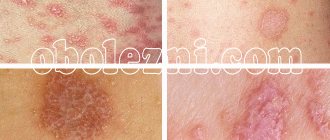
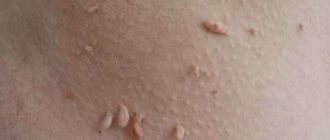
9-13. Appearance of skin and nail lesions with rubrophytosis. Rice. 9-10. Rubrophytosis of large folds: erythematosquamous lesions with clearly defined boundaries in the area of the inguinal fold, on the inner surface of the thigh and scrotum (Fig. 9), in the area of the gluteal fold, on the buttock and posterior surface of the thigh (Fig. 10). Rice. 11. Rubrophytosis of smooth skin: confluent, finely lamellar with peeling lesion on the upper third of the leg and in the area of the knee joint. Rice. 12. The foot of a patient with rubrophytosis with a hypertrophic type of lesion: the nail plates are thickened, crumble, and yellow. Rice. 13. Fingers of a patient with rubrophytosis with a normotrophic type of lesion: the nail plate of the third finger is yellowish, exfoliates. The clinical picture is varied: from mild foci of peeling and cracks in the interdigital folds of the skin of the feet to generalized lesions of large folds (tsvetn. fig. 9 and 10) and smooth skin (tsvetn. fig. 11), involving all or almost all nail plates, vellus hair, formation of deep foci of mycosis. The affected skin of the soles and palms has a reddish-bluish tint, and fine-plate peeling is noted, emphasizing the skin pattern. The boundaries of lesions in large folds of skin and on smooth skin are clear and scalloped; along the periphery there is an intermittent ridge consisting of small bubbles, nodules and crusts. Damage to the nails is characterized by their thickening due to the development of subungual hyperkeratosis (see), they acquire a yellowish-ocher color and crumble easily - a hypertrophic type of lesion (tsvetn. Fig. 12). These changes may be less pronounced - normotrophic type of lesion (tsvetn. Fig. 13). In some cases, the nail plate may be partially separated from the nail bed - an onycholytic type of lesion. R.'s course is chronic with exacerbations in the warm season.
Sometimes long hairs of the skin are affected; the process proceeds rapidly according to the Kerion Celsi type (see Trichophytosis).
Prevention
Disinfection of bed linen, clothing, shoes, and compliance with hygiene rules is a necessary condition for the prevention of rubromycosis.
After a shower or bath, carefully wipe the spaces between the fingers, leaving no moisture between the fingers. In the bathhouse or locker room of a sports club, you must use personal shoes; you cannot walk barefoot in public places.
After completing the course of treatment for rubrophytia, the patient is registered at the dispensary for a year and visits a doctor for monitoring once every three months.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is established on the basis of a wedge, a picture and data from a microscopic examination of scales and nail scrapings for fungi. Differential diagnosis in some cases is carried out with lupus erythematosus (see), non-parasitic sycosis (see), red acne (see Acne), seborrheic eczema (see), neurodermatitis (see), psoriasis (see), as well as with superficial and chronic trichophytosis (see), athlete's foot (see Athlete's foot). Often the results of mycological studies (cultural diagnostics) are decisive for diagnosis.
Oral medications
Dermatophyte fungi are sensitive to drugs based on active ingredients:
- terbinafine (Atifan, Terbinafine, Lamisil, Lamicon, Binafin, Mikofin, Terbin);
- ketoconazole (Dermazol, Ketoconazole, Nizoral, Apo-Ketoconazole);
- fluconazole (Diaflu, Fluconazole, Diflazon, Difluzol, Diflucan, Kandizol, Mikosist).
The duration of treatment for onychorubromycosis is determined by the doctor and depends on the stage and form of the disease - normotrophic, hypertrophic, atrophic - the more advanced the disease, the longer the course of treatment. As a rule, for a complete cure for rubrophytosis of the nail plates, medications are taken for two to three months.
Treatment
In the absence of contraindications, griseofulvin is prescribed based on the body weight of patients: up to 60 kg - 5 tablets (but 0.125 g) per day, from 60 to 70 kg - 6 tablets, from 70 to 80 kg - 7 tablets and St. 80 kg - 8 tablets. In the first month, griseofulvin is prescribed daily, in the second - every other day (at the same daily dose) and then once every 3 days for 8-12 months, but not less than 6 months. (time of growth of a new nail plate). The affected nail plates are removed and the stratum corneum of the soles (hands) is detached according to the Arievich method: a bandage with ointment is applied for two days (4 g of salicylic acid, 2 g of lactic acid, 24 g of petroleum jelly), covered with wax paper and bandaged, then leave the Vaseline bandage on for a day and then apply the ointment for two days. Treatment also includes treating the nail bed and smooth skin with fungicidal liquids and ointments.
Features of infection with rubrophytosis
In a humid, warm climate, infection with the fungus occurs through contact with a patient with rubromycosis. In countries with cool climates, rubrophytia is infected mainly by violating hygiene rules in public places.
Methods of infection
The fungus is transmitted in a humid environment in bathhouses, showers, changing rooms of fitness clubs, and in beach cabins.
If you do not use personal shoes in such places, the risk of infection increases. If the protective properties of the skin are weakened, symptoms of infection appear some time after infection.
The duration of the incubation period for the fungus has not been established. A fairly long period of time may pass from the moment of infection before a person discovers signs of rubromycosis.
Often the source of infection remains undetected, which contributes to the spread of the disease. A person infected with a fungus poses a threat to others, unaware of his illness.
Risk group
Diseases of the endocrine system, internal organs, and skin diseases predispose to mycoses.
The risk group includes patients with diabetes, circulatory disorders in the lower extremities, people with increased body weight, and those suffering from sweating.
Increased sweating of the feet and palms, lack of personal hygiene, and the use of someone else's shoes and gloves contribute to the spread of fungal infection.
Local preparations
Treatment of nail rubromycosis will be effective only with the simultaneous use of local drugs. These include ointments, gels, varnishes, sprays and solutions. As with oral medications, your doctor will prescribe a specific topical medication. External agents are used throughout the entire treatment period, that is, for approximately 2-3 months.
Ointments, creams and gels
The most effective in treating rubromycosis of nails are drugs with:
- terbinafine (Atifin, Lamisil, Terbinafine, Terbix, Myconorm, Terbizil);
- fluconazole (Flyukoren, Futsis);
- ketoconazole (Perhoral, Sebozol, Mycoquet, Nizoral);
- bifonazole (Mikospor, Bifasam, Bifosin, Bifonazole).
Lucky
An antimycotic effect for rubromycosis of nails is provided by varnishes, which include:
- amorolfine (Loceril, Oflomil, Exorolfinlac);
- ciclopirox (Batrafen, Cyclocutane, Cyclone).
Sprays and solutions
For onychorubromycosis, products in the form of solutions and sprays are applied to the nail plates and, in some cases, to the skin around the nails. The most effective in treating toenail rubrophytosis include:
- Lamitel, Thermikon, Lamicon (sprays and drops);
- Nitrofugin, Exoderil, Lamisil (solutions).
Skin lesions in the groin of a non-fungal nature
In addition to fungi, the skin in the groin is affected by erythrasma, intertrigo (intertrigo) and pemphigus. The groin area and genitals are very rarely affected by psoriasis.
Intertrigo (diaper rash)
Mechanical dermatitis or diaper rash occurs as a result of friction, pressure, heat and other factors, appearing in all folds of the human body, but most often in the lower abdomen in obese people, the buttocks and genitals.
The upper layers of the epidermis are involved in the process. The skin is damaged by skin secretion products, which is manifested by diffuse redness with areas of maceration, the formation of blisters and cracks. The lesions do not have clear boundaries. Patients are bothered by pain and itching. Diaper rash can be complicated by bacterial and fungal infection, as evidenced by the appearance of small blisters in areas of inflammation. At the first stage of the disease, redness appears, then, against the background of hyperemia, erosions occur; without treatment, the skin becomes bright red, the erosions merge, forming extensive foci of damage on which ulcers appear.
Rice. 15. The photo shows diaper rash in men.
Rice. 16. The photo shows diaper rash in women.
Rice. 17. The photo shows intertrigo in men on the genitals and around the anus.
Intertrigo (diaper rash) pseudomonas
Common diaper rash complicated by a bacterial infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) is called Pseudomonas intertrigo. Pseudomonas parasitizes human skin and, under certain circumstances, can cause skin damage. Triggers can be excessive sweating, obesity, poor-quality and uncomfortable clothing, an allergic mood of the body, insufficient care of one’s body, etc.
Areas of inflammation of irregular shape are dark red in color. Many small blisters filled with purulent contents appear on them. They quickly open up, forming erosions, which are then covered with crusts. Gradually, the affected area increases.
Rice. 18. Colonies of bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Rice. 19. Pseudomonas diaper rash in men. The groin area and penis are affected.
Rice. 20. Intertrigo pseudomonas in a man.
Erythrasma
The bacterial skin disease caused by Corynebactcrium minutissimum is called erythrasma. Its development is promoted by increased sweating, obesity and frequent washing with soap, which weakens the “acid mantle” of the skin, increased ambient temperature and humidity. The disease affects the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Foci of inflammation are localized mainly in the thighs, scrotum, armpits and under the mammary glands.
Erythrasma has the appearance of red-brown spots with uneven edges, slight peeling and sharp boundaries. The itching is minor. With excessive sweating, the spots become red, swelling occurs and blisters appear. In the rays of a Wood's lamp, foci of inflammation glow with a coral-red glow.
Rice. 21. Erythrasma of the inguinal region in men and women.
Rice. 22. Erythrasma of the inguinal-femoral fold and thighs in men.
Rice. 23. View of the area of inflammation during erythrasma in the rays of a Wood’s lamp.
Psoriasis
A disease with an unclear nature of occurrence and development of the pathological process. Very rarely, the groin area and genitals are affected, where swelling and bright red plaques appear.
Rice. 24. Psoriasis of the genital organs.
Pemphigus
A disease with an unknown nature of the occurrence and development of the pathological process. Pemphigus is believed to be an autoimmune disease. The patient's body produces predominantly IgG antibodies to the cementing intercellular substance of the epidermis. Autoimmune processes occurring in the body lead to the destruction of the spinous layer of the epidermis.
When the process is localized in the groin area, short-term blisters appear. After their disappearance, extensive painful erosions and fragments of epithelium remain.
Rice. 25. In the photo on the left, a man has pemphigus (bullous pemphigoid). The photo on the right shows chronic benign familial pemphigus Hailey-Hailey.