Basic criteria for effective treatment
One of the main objectives of treating the disease is to prevent the development and spread of the pathogen. The scabies mite first affects a small surface of the skin, then the lesions grow. Most often, traces of tick activity are found in the cubital fossa, on the inner parts of the arms, in the armpits, in the groin area and on the inner thigh. To prevent the process of skin damage, the doctor must assess the stage of development of the disease and prescribe individual treatment.
If a large area of the skin is affected, the doctor may prescribe an ointment. Treatment of scabies with ointment is one of the most effective means for humans to eliminate parasites and accelerate skin regeneration.
Disinfection of housing and household items
Outside the skin, scabies mites can live for a very short time. In addition, recent studies confirm that the likelihood of contracting scabies outside of direct contact with a patient is minimal. But it is still recommended to treat underwear, clothes and things that a person used during illness.
Bed linen, towels, and clothes are washed in hot water or boiled. Bedding, outerwear, and upholstered furniture are treated with a steam cleaner. The room where the patient was located needs to be thoroughly cleaned. In addition, you can use a special acaricidal agent.
Boiling laundry
Sulfuric ointment
Simple sulfur ointment is rarely used in the fight against the causative agent of the disease. This is due to the fact that its positive effect in the fight against scabies mites has not been proven. But the ointment has antiseptic properties, and a base of petroleum jelly or petroleum jelly helps moisturize the skin and speed up its healing. For a long time, sulfur ointment was one of the main ways to combat scabies; now this method is used extremely rarely as an adjuvant along with other medications.
Overdose: due to the fact that sulfur ointment is not absorbed into the systemic bloodstream, an overdose of sulfur when applied externally becomes impossible.
Preparations based on sulfur ointment
In the fight against scabies, simple sulfur ointment is most often used, but combined remedies are also effective:
- Sulfur-tar paste. It has antiparasitic, keratoplastic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, which improves skin condition and accelerates the wound healing process. In addition to its antiseptic properties, sulfur-tar paste has a detrimental effect on scabies mites and accelerates the exfoliation of dried skin.
- Sulfur-salicylic ointment. Due to the acid content in sulfur-salicylic ointment, it effectively kills parasites. At the same time, it helps to soften the skin that has been affected by scabies mites.
Contraindications:
- individual intolerance to the components of sulfur paste,
- increased skin sensitivity,
- child under 3 years old,
- pregnancy and breastfeeding.
When pregnant or breastfeeding a child, doctors pay attention to what harm treatment with sulfur ointment will bring and what positive effects it can cause. If the positive effects are more significant than the negative consequences for the child and mother, the doctor may consider the use of such a remedy appropriate. If soft areas of the skin are affected by mites, their treatment can be painful and cause hypersensitivity. Therefore, before using this paste, you need to pay attention to the side effects that it may cause:
- itching,
- burning,
- redness and the appearance of urticaria.
How to apply?
The ointment is applied to the entire body except the head and face. The course of treatment is carried out for five days. When applying, pay special attention to the elbows, stomach, wrists and the area between the fingers. Areas with thin epithelium (breasts, under the breasts, armpits and groin) require careful application of the paste in thin layers. These areas have very thin skin that can become hypersensitive to large amounts of sulfur ointment.
Tablets and injections for scabies in humans, what medications are used to treat adults and children
External means are used directly to kill ticks. Tablets, capsules, and dragees with similar effects have not yet been synthesized. In complex therapy, antihistamines are used in such dosage forms.
Treatment is carried out with the aim of:
- prevention of the development of local and systemic allergic reactions;
- preventing the occurrence of inflammatory swelling of the skin.
Allergies can develop not only to the pharmacological drugs used. During the process of growth and reproduction, ticks release toxic products of their vital activity into the surrounding space. They are highly allergenic, foreign to the human body, and can cause general intoxication.
To prevent allergy symptoms from occurring in people with individual intolerance to these harmful substances, doctors include the following drugs in treatment regimens:
- Loratadine;
- Tavegil;
- Claritin;
- Suprastin;
- Cetrin.
Infection with scabies causes a deterioration not only in a person’s physical, but also in his psycho-emotional state. Therefore, patients can be prescribed mild sedatives: motherwort and valerian tablets, Tenoten, Persen, Novo-Passit. If they do not have the desired effect, then tranquilizers and antidepressants are used.
Preparations in the form of injection solutions are used extremely rarely. They are prescribed for advanced scabies, manifested by severe painful sensations. To eliminate them, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, for example, Ketorolac. And in case of extensive bacterial infection, parenteral antibiotics can be used.
Crotamiton
The drug is available in the form of liniment or cream with 10% active ingredient. After application, the drug will effectively destroy adult ticks and also prevent its spread throughout the body. Crotamiton relieves itching and redness of the skin and prevents infection from getting into open wounds.
Contraindications:
- allergic intolerance,
- inflammation,
- the presence of bleeding wounds,
- The patient's age is up to 12 years.
During pregnancy and lactation, the drug is prescribed with caution and only if other treatment is ineffective.
Among the side effects, allergic manifestations on the epidermis and irritation are more common.
How to apply?
The lotion or cream is carefully applied twice a day from the chin to the feet. When applying, it is necessary to pay special attention to the folds and the most sensitive areas. After using the drug twice, there is no need to use ointment the next day, and it is recommended to repeat the procedure every other day. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician and depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s skin reaction to the drug. You can wash your body only two days after the last application of liniment.
Treatment during pregnancy
From the first days of treatment during pregnancy, the doctor prescribes response medications that can reduce itching and reduce the likelihood of hypersensitivity. These medications are taken orally and come in the form of tablets and capsules. If necessary, the obstetrician-gynecologist can also prescribe medications that support the normal development of the fetus.
How and with what to quickly cure scabies
Treatment will be most effective if all techniques are used simultaneously. The simultaneous use of medications and disinfection of household items and clothing is practiced. If the last point is neglected, then after a few days the skin will begin to itch unbearably again.
What other nuances of treating an infectious disease exist:
- antiparasitic ointments are applied to adults on the body and face, but not on the scalp;
- external agents are rubbed into the child’s entire body, including the scalp;
- It is better to use drugs before bedtime, since at night the biochemical processes in the human body occur most intensely;
- if during treatment the skin becomes very red and hurts, you need to inform your doctor about this - with a high degree of probability, a secondary bacterial infection has been added to scabies;
- During therapy, you should not have contact with healthy people to prevent their infection, as well as reinfection.
Treatment should not be completed at the first signs of improvement. The mites remaining in the skin will begin to actively reproduce again. A person is considered recovered if microscopy does not reveal traces of parasitic mites in the biomaterial.
It is necessary to simultaneously take all antihistamines prescribed by the doctor and rub in ointments. This will avoid scratching the skin and speed up its regeneration. If all these conditions are met, then after 2-3 weeks the person will fully recover.
Let's watch a video about drugs for quickly treating scabies:
Benzyl benzoate
The substance is sold in the form of an emulsion or ointment containing 20% active substance. After applying the product to the skin, the parasites begin to die, the itching is significantly reduced. Benzyl benzoate is not absorbed into the blood, which prevents overdose and undesirable consequences, while it effectively eliminates the causative agent of scabies in the upper layers of the epidermis. More often, doctors prescribe a liquid solution of the drug, which is available in 200 ml bottles.
Contraindications for use may include:
- hypersensitivity,
- age (not recommended for use in infants),
- pregnancy and breastfeeding period,
- the presence of purulent diseases (inflammation),
- the presence of bleeding or inflamed wounds on the surface of the skin.
It is worth paying special attention to the use of the substance in young children (under 3 years old). Despite the fact that benzyl benzoate is not absorbed into the blood, it evaporates readily and can enter the body through the respiratory tract and cause intolerance or intoxication in the child. With prolonged intoxication through the respiratory tract, anaphylactic shock and death can occur.
Side effects include:
- itching,
- dry skin,
- hives,
- burning,
- necrosis of the upper spheres of the epidermis.
Mode of application
Children under three years of age are not recommended to apply ointment or solution at a concentration of 20%. Before use, the medicinal substance is dissolved in 200 ml of warm water per 200 ml of the drug. The result is a liquid with a concentration of 10% of the active substance. Next, add 10 grams of baby or laundry soap to the resulting 400 ml solution; you can use shampoo. The prepared suspension must be stored in the refrigerator. The shelf life of the solution is 7 days.
Note! Storing medications on the refrigerator door is strictly prohibited. This is due to the fact that when the door is opened, the greatest temperature difference occurs, which affects the external qualities and properties of the drug. The best storage option is in the middle of the shelf or in a drawer.
For all other patients, benzyl benzoate is recommended to be applied without additional dilution, unless such therapy is prescribed by a dermatologist.
It is necessary to apply the drug after shaking it first. Body treatment begins with the collarbone area. The neck, face and scalp should not be treated. Processing is done from top to bottom. Finally, the product should be applied to the feet and between the toes. After 10 minutes, the procedure must be repeated.
For children under 3 years of age, in some cases the face and scalp are lubricated.
It is recommended to carry out the procedure 2 times a day for two days; bed linen must be changed every day. On the 3rd day of therapy, it is recommended to wash the body and change the bed linen.
Home remedies
You can treat scabies in children using homemade ointments and creams. They cope well with the signs of the disease in the initial stages of development. The most effective means are the following:
- Ointment with elecampane
. 1 tablespoon of elecampane is mixed with 25 mg of melted lard and the ingredients are simmered over low heat for 10 minutes. Then add a little tar soap and apply to the affected areas twice a day. - Cream with birch tar
. Mix 1 tablespoon of honey, melted lard, and birch tar. The resulting pasty mixture is applied to the skin 2-3 times a day for five days. You should not use the product if your child is allergic to honey. - Herbal cream
. 100 g of wild rosemary leaves and hellebore rhizomes are mixed with 100 g of melted fat. Cook over low heat for 5 minutes. The heated composition is placed in the oven for 6 hours. The prepared cream is used to treat problem areas twice a day.
You can prepare an ointment based on gunpowder and sour cream. The components are mixed in equal proportions and the resulting mixture is kept warm, stirring occasionally. The finished composition is applied in a thick layer to the skin and secured on top with a gauze bandage.
Simple recipes for anti-scabies
These remedies are easy to prepare at home. They are effective for scabies in children and adults and have no contraindications or side effects. The main thing is to follow the recipe and store the finished formulations correctly.
- Garlic ointment. Several heads of garlic are poured into 100 ml of hot vegetable oil and boiled over low heat for 10-15 minutes. Squeeze the garlic until a homogeneous consistency is obtained, mix with oil and use the prepared composition 2-3 times a day.
- Laundry soap is grated and garlic gruel is added to it. Heat over low heat for 15 minutes until the soap is completely dissolved. The finished mixture is poured into a mold and allowed to cool. Rub the problem areas of the skin until complete recovery.
- Mix 1 packet of crushed bay leaf with half a stick of butter. Rub the resulting medicine into the skin three times a day.
You can also prepare an ointment based on wood ash. 30 g of ash is mixed with 70 g of melted lard. Apply the resulting composition to a previously steamed body. Wash off after 12 hours.
Zinc-based substances
One of the features of zinc ointment is that it does not have an unpleasant odor. The main positive effects are drying and disinfecting the skin. As a rule, this substance is prescribed not to fight the parasite, but to eliminate itching and redness. That is why the substance is prescribed as an auxiliary method of combating scabies.
Zinc ointment is recommended for use by people with allergic reactions and asthma. It is necessary to apply the substance in an even layer, especially in places where the skin damage has occurred the most.
Possible complications
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease and refusing treatment will not only cause scabies to persist for a long time, but will also lead to the development of complications. The most common complication of scabies is purulent skin lesions that develop due to constant scratching and infection. Other consequences of improper treatment or lack thereof:
- the appearance of boils, abscesses, purulent ulcers;
- inflammation of the lymphatic vessels;
- dermatitis (including allergic);
- microbial eczema;
- changes in blood composition (for example, leukocytosis).
Premature cessation of therapy may cause a rapid relapse of the disease or the development of a more severe form. It is extremely rare that lack of treatment can lead to the development of pathologies of the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
Wilkinson's ointment
This substance is one of the most common means in the fight against scabies. The ointment contains sulfur and auxiliary substances that prevent the scabies mite from spreading throughout the body. The main effect is antiseptic wound healing. As a rule, such a drug is prescribed in the early stages of the development of pathology. When applying to the skin, special attention should be paid to mite-affected areas. If the disease begins to spread throughout the body, then treatment must be reconsidered.
Wilkinson's ointment is applied for 3 days only before bedtime, while patients are advised to iron and change bed and underwear. In case of individual intolerance to the active substances of the drug, it is worth replacing it. Do not use by pregnant women or infants.
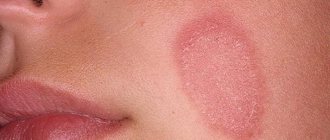
Characteristic clinical signs
The disease has many types, they all have their own characteristics, but their clinical manifestations are generally the same.
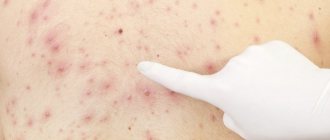
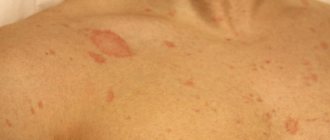
The most common symptom of the disease is unbearable itching. Although this symptom occurs in many diseases, there are a number of signs characteristic of scabies:
- Itching predominates at night. It is felt throughout the day, and at night it becomes unbearable. The patient cannot bear it, suffers, scratches the lesions into blood.
- Paired rashes in the itching area - the mite, making its way under the epidermis, begins to dig passages and lay eggs in them, from which larvae hatch. As a result of the passage, 2 pimples are formed on the skin, reminiscent of bites: this is the entrance and exit of the parasite.
- Affected area: hands are most often affected, since contact occurs mainly through them. It is important to carefully examine the skin folds between the fingers. The groin and axillary areas are much less commonly affected. It is also necessary to examine the area under the breasts in women and the scalp in children.
- Contact with an infected person - the likelihood that a person who discovers a disease will tell others about it is small, but in kindergartens and primary schools it is quite possible to track this.
- Hygiene - personal hygiene is very important; if it is lacking, it is very easy to become infected and infect someone with this disease.
There are also atypical forms of scabies, when the itching may not be so pronounced or there are no scabies.
Norwegian scabies is perhaps one of the most complex and dangerous forms. It mainly affects people with extremely weakened immune systems (various immunodeficiencies, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus and other conditions that undermine natural defense mechanisms). In patients, a huge area of the body surface is affected; the amount of pathogen is many times greater than in the typical form. The skin resembles psoriasis plaques in appearance, and skin hyperkeratosis develops. And with all this there is no itching.
Folk remedies to combat scabies
In addition to the above medications, traditional medicine, including baths with essential oils and herbal tinctures, are also effective in the fight against scabies. The oil used is lavender, cinnamon, tea, which can be applied to the skin with water or honey, and also added to the bath after completing the course of treatment with the drug. Among the herbs used are plantain, wormwood and thyme, from which tinctures are prepared that are effective for washing the body. Wormwood is often placed under a mattress or pillow for better effect.
It is worth remembering that no matter how effective the ointment for scabies is, you need to use all methods of treatment and prevention of the disease. This will allow you to get rid of the disease faster and prevent relapse.
Prevention measures
Following some preventive recommendations will help to significantly reduce the likelihood of contracting scabies:
- when visiting public baths, saunas, swimming pools, use only personal hygiene products, washcloths, towels;
- change underwear and bed linen regularly;
- monitor the condition of your nails;
- regularly do wet cleaning in the apartment;
- strengthen the immune system.
In order to prevent and protect the population from scabies, examinations are carried out of persons in close contact with the sick person, identification and elimination of foci of infection, and carrying out disinsection measures at the source of infection.
Medifox (permethrin)
The insecticidal drug inhibits the nervous system of arthropod insects, which leads to their paralysis. Medifox has little toxicity and does not have systemic effects when treated locally.
Contraindications
- increased sensitivity;
- infectious skin diseases;
- age up to 1 year;
- pregnancy (relative);
- lactation.
Side effects
- rash;
- swelling;
- burning;
- itching;
- erythematous rash.
Mode of application
For the treatment of scabies, a concentrate is prescribed, which is diluted with water in a ratio of 8 ml:100 ml. The product is thoroughly rubbed into the skin, avoiding the face and head areas. The procedure is repeated every evening for 3 days. On the fourth day they wash with soap and change their linen.