Any rash on the body is an alarming sign that should suggest an infectious or allergic disease.
Small rashes or large ones, if they are located on the genitals, are an indispensable reason to visit a urologist, dermatologist or venereologist.
Treating rashes is not the main goal.
After all, often a rash with STDs and sexually transmitted infections is just the tip of the iceberg and a signal that the system is no longer in order.
In addition to sexually transmitted infections, the causes may be hidden in oncology, connective tissue diseases, and autoimmune processes.
Causes of rash on the penis
Most often, the causes of rashes in the area of the head and leaves of the foreskin lie in:
- their irritation by discharge from the urethra,
- allergic reactions,
- toxicoderma in the program of infectious diseases,
- balanoposthitis of various origins.
Urethritis can be of different nature. Gonococcal, trichomonas, chlamydial, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, adenovirus, herpetic, gardnerellosis.
Capable of producing persistent discharge of varying degrees of abundance from the urethra.
Getting on the head of the penis, purulent, mucous or mixed discharge irritates the external opening of the urethra, the skin of the glans, and the inner layer of the foreskin.
They accumulate in the preputial space.
Such physicochemical effects can lead to irritation and even desquamation of the epithelium and increase capillary permeability.
The result is a small red rash interspersed with areas of maceration and oozing.
Small abscesses (phlyctenas) with a flaccid soft covering may appear, opening and healing without scarring.
Viral balanoposthitis is characterized by small blisters with transparent contents, which become cloudy when bacterial flora is attached.
For bacterial - red rashes on the head of the penis in the form of papules or a pustular rash.
A rash of whitish spots on the head of the penis, areas of erosion covered with a cheesy coating, indicates a candida fungal infection.
A rash on the head due to candidiasis can also begin with red spots.
In their place, the epithelium quickly sloughs off, and painful areas of weeping form.
Red rashes on the head of the penis can appear as a result of toxicoderma.
Various infectious agents (causative agents of syphilis, measles, rubella, menigococcal infection) cause local inflammatory reactions of the skin.
More often, as an immediate type of allergy, they sharply increase the permeability of small vessels.
The elements of a toxicodermic rash can be very different: spots, bumps, blisters, hemorrhages in the form of stars, dots.
Moreover, toxicoderma can develop not only at the onset of the disease, as a reaction to infection.
But also during its treatment in response to the administration of various drugs (antibiotics, antivirals, antipyretics, painkillers).
It can take a long time from the moment the pathogen enters the bloodstream until a skin reaction develops.
For example, a rash on the head with syphilis will appear no earlier than the secondary period begins.
That is, after a month and a half from the penetration of Treponema pallidum into the blood.
At the same time, allergic toxicoderma can develop in a matter of hours from the absorption of food components or medications in the intestines.
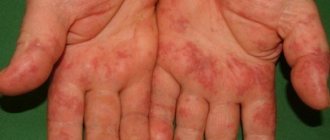
In the program of atopic, contact, allergic dermatitis or eczema, rashes on the genitals may also be heterogeneous.
And look like spots, dots, bumps, blisters, diffuse redness.
At the same time, with atopy, you can see thickening of the skin, its peeling from fine to large-plate, emphasizing its pattern.
Also general dryness of the skin, cracks, weeping, scratching due to severe itching, healing with the formation of crusts.
A rash on the head due to allergies is accompanied by swelling of varying degrees of severity.
Allergens can include food, drinks, medications, care products, latex, lubricants, and synthetic underwear.
As well as hair and skin particles of animals or insects, dust mites.
The dark rash may remain patchy after an exacerbation of chronic dermatitis has resolved due to increased pigmentation.
Rashes due to bacterial and viral infections
Rash in the anogenital area in men can occur with a number of bacterial or viral infections, as well as with scabies or lice. The most common causes leading to the appearance of various rashes include syphilis, Reiter's syndrome, herpes simplex, human papillomavirus infection, candidiasis and other fungal pathogens, as well as molluscum contagiosum and scabies. Rashes can be similar for different reasons that led to their appearance, which significantly complicates diagnosis. Most often, rashes of an infectious nature manifest themselves as spots, nodules, blisters, erosions and ulcers. Depending on the type of rash, the nature of the disease can be assumed.
So, with syphilis, the nature of the rash can be very diverse. The rashes can be represented by small papules, erosions and even ulcers, depending on the stage of the disease. A distinctive feature of syphilis rashes is the absence of subjective sensations. With Reiter's syndrome (chronic chlamydia, the process is usually represented by flat nodules that can merge with each other, and can also be covered with mealy scales. Herpes simplex is usually characterized by typical rashes: grouped blisters with serous contents on a slightly edematous-hyperemic background. Anogenital warts: The main element of this contagious dermatosis is pointed papules.Sometimes they merge into large formations that resemble “cauliflower”.
With mitotic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes of the anogenital area, reddish spots of various sizes usually appear, which are accompanied by fairly intense itching. Molluscum contagiosum or viral dermatosis is manifested by flat or hemispherical nodules, inside of which there is a crumbly mass of whitish-yellowish color. Quite often, papules have an umbilical depression in the center. With parasitic dermatosis (scabies), the rash is caused by the activity of the scabies mite and has the appearance of characteristic burrows. The tick's entrance is represented by small dots, and as it moves, small bubbles appear in the skin. Nighttime itching is very typical.
Skin pathologies and rash on the head of the penis
Rash due to skin diseases is a consequence of inflammation of a different nature or morphological restructuring of the integumentary tissues.
Parasitic lesions stand out separately.
Inflammation can be infectious, autoimmune, allergic.
It is characterized by redness, swelling, elements protruding above the surface of the body, disruption of the barrier functions of the skin, itching or pain.
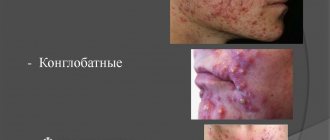
- Nonspecific inflammation is staphylo- or streptoderma. Pyoderma is distinguished by elements of purulent inflammation. These are pustular white rashes on the head of the penis and its shaft. Once opened, the ulcers heal without a scar.
- Specific inflammatory changes bring with them sexually transmitted infections. Here the rash is diverse and heterogeneous. There may be rashes of varying sizes and intensity. They are often combined with urethritis.
- Autoimmune processes are most often vasculitis, in which tubercles of a brownish, reddish or bluish color are grouped along the vessels. This category also includes pigmentation disorders, for example, white spots in vitiligo, lichen sclerosus and scleroderma. Psoriasis rashes are ill-defined pink or red patches on the skin of the penis that bleed easily and look like areas of atrophy or plaques.
Transformations of the skin epidermis are various leukoplakia (thickening and deformation of the skin with loss of natural pigmentation).
And other precancerous conditions - Buschke's, Bowen's, Paget's diseases, bowenoid papulosis, Queyra's erythroplasia.
Human papillomavirus serotype sixteen is responsible for the development of precancers.
They have a high risk of cancerous transformation of the epithelial cover.
Until the moment of transformation, papillomaviruses usually give rise to the proliferation of condylomas or papillomas.
Condylomas are larger.
They grow on areas of the penis that are injured during sex: the coronary groove, frenulum, leaves of the foreskin.
There are even growths inside the urethra.
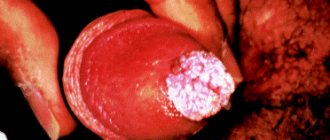
- A condylomatous rash on the head of the penis can be represented by a spot, a tubercle or a pointed growth. The last one is the most typical. These are usually single outgrowths on a broad base or stalk.
- Papillomas are often multiple, smaller, with a flat cap on a thin stalk. This is also a rash on the head of the penis, but more pigmented.
- Giant condylomas are known as Löwenstein-Buschke disease. This is a precancer requiring histological analysis and observation.
- Bowenoid papulosis produces bumps on the coronal sulcus.
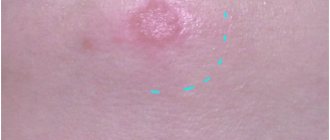
- A red rash on the head of the penis in the form of a single velvety spot with the outline of an island or plaque is suspicious for Paget's disease.
- An uneven plaque with outgrowths is very likely in Bowen's disease. It usually peels off.
- If the plaque has clear edges and is smooth, this is a symptom of Queyra's erythroplasia.
Simultaneously with lesions of the genitals, similar changes can be seen on the oral mucosa.
Penile cancer is an invasive and non-invasive form of carcinoma that looks like a growth or ulcer, gradually growing in depth and breadth.
Parasites on and inside the skin are pubic lice, scabies and demodectic mites.
All of them cause itchy skin and red rashes at the sites of penetration or bites.
- Pediculosis produces red bumps in the form of pimples at the sites of lice bites. Also, due to itching, scratching and secondary ulcers may appear due to the addition of staphylococci or streptococci. Therefore, the rash with pubic lice is often mixed: papules and pustules.
- Demodectic mange produces a dermatitis-type rash: small papules, peeling, uneven surface.
- Scabies is characterized by increased itching with increased body temperature, pinpoint mite entrances and S-shaped burrow marks on the skin. There may also be excoriations.
Rashes due to cancer processes
Rare, but extremely dangerous, are rashes as manifestations of oncological processes, including malignant neoplasms. Rashes can vary from macules, papules, to ulcerative elements. Queyra's syndrome is a precancerous disease characterized by the appearance of persistent edematous hyperemia of the glans penis. Subjective sensations are usually absent. Melanoma is an extremely dangerous disease that appears as spots of deep brown or black color. Squamous cell carcinoma manifests itself as painless erosions on the skin, prone to peripheral growth and fusion.
General signs of a possible oncological process: – long-term non-healing erosions or ulcers;
– deformation of the genital organs; – appearance and rapid growth of pigment spots.
Rash on the penis due to fungi and lichen
Fungal infections are a common companion for humans.
Skin changes typical of various mycoses do not bypass the penis.
Along with it, the groin area most often suffers.
- Candidiasis is a consequence of the flourishing of saprophytic fungi of the genus Candida. In this case, typical skin lesions are oozing and cracks covered with poorly peelable cheesy deposits. The lesions may be single or multiple. The head and inner layer of the foreskin and the external mouth of the urethra are most often affected. Balanoposthitis is associated with candidal urethritis.
- Dermatophytosis inguinal is a consequence of the activity of the fungus. It usually has pink spots with scalloped edges and clear contours. Often the spots merge into larger formations. They itch and cause discomfort. The inguinal folds and skin of the penis are affected. Complicating the disease pyoderma.
- Gilbert's pityriasis rosea is thought to be caused by a herpetiformis virus. The onset of the disease is usually tied to the moment the immunity drops (cold, hypothermia). A single tubercle appears, measuring up to two centimeters. Its central part gradually turns yellow and begins to peel off. Over the next two weeks, daughter “dropouts” appear - plaques up to a centimeter in size, pink in color and with peeling. They are oriented along the elastic stretch lines of the skin.
- Lichen versicolor is also called pityriasis versicolor. This is the result of the activity of the fungus Pityriasis versicolor, which affects the stratum corneum of the epithelium. A small skin rash consisting of clearly defined red or brown spots is typical. The most commonly affected genital areas are the chest, neck, back, shoulders and armpits. Fungal lesions do not tan under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Additionally, increased sweating and skin itching are noted.
- The rash with lichen planus is nodules on the mucous membrane and skin. In the mouth, on the torso, on the genitals. The disease develops when the human body’s immune response is faulty. Elements of skin lesions have a central recess and a different, often round, shape. Their color varies from red to bluish. A characteristic symptom is a shiny surface of the formations.
Infectious causes of red spots
If a man suspects that red spots on the head of the penis have appeared as a result of an infectious lesion of the body, then he should immediately consult a doctor.
Infectious pathologies require timely, complex and correct therapy. Self-medication is strictly prohibited, otherwise you can aggravate the course of the disease.
Red rashes on the head of the male organ - what is it? A painful symptom can signal the following diseases of an infectious nature:
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea;
- herpes;
- candidiasis;
- Balanite.
Syphilis and gonorrhea
These diseases are common causes of redness of the head of the reproductive organ. Both syphilis and gonorrhea are serious infectious pathologies that require complex and lengthy treatment to eliminate.
Advanced diseases can provoke dangerous disruptions in the body’s functioning and lead to death. A man can contract syphilis either through unprotected sexual intercourse or through a transfusion of contaminated blood.
The first, but not the only manifestation of the disease is red spots on the penis. As the disease progresses, the rashes first turn into small ulcers and then into wounds. Gradually, the rash spreads from the genitals to the entire body, and in the absence of proper and timely treatment, it becomes a cause of disfigurement in appearance and sometimes death.
Gonorrhea, unlike syphilis, is spread not only through sexual contact, but also through household contact. When the disease occurs, red rashes appear on the head of the penis, and mucous or purulent discharge flows from the urethra. A sick man constantly experiences itching in the genital area, feels pain and burning when urinating.
Herpes
With genital herpes, red spots appear not only on the head, but also on the entire surface of the penis. The affected head is dotted with fluid-filled blisters, causing intense itching, pain and burning.
When the disease is advanced, the rash spreads from the head to the shaft of the genital organ and to the scrotum. The man's body temperature rises significantly and a febrile state is observed. The spread of the herpes virus occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse.
Candidiasis
The spread of fungal infection occurs primarily through unprotected sexual intercourse.
Fungi attack the body of people with weakened immune systems; the immune system of strong and healthy men successfully resists infection.
A man can also become infected by using washcloths, towels and other hygiene items of an infected partner.
When the disease occurs in men, red dots appear on the head of the penis, accompanied by severe itching, and a whitish coating. A white lumpy mass is released from the urethra, smelling unpleasantly of something sour. If the symptoms described above occur, both partners should immediately go to a medical specialist.
Balanitis
This is the name for inflammation of the head of the male reproductive organ. The inflammatory reaction provokes the appearance of red dots on the head.
Inflammation is most often caused by the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria or fungi. But the pathological process can also be a consequence of cuts, burns and other damage to the head.
When the disease occurs, not only red rashes form on the head of the penis, but also painful ulcers and quite extensive wounds. The ulcers are large, burgundy or bluish, constantly itchy, and accompanied by intense pain. If treatment is not carried out, the ulcers begin to accumulate pus and grow deep into the tissues of the head.
In some men, balanitis is accompanied by fever, swelling of the reproductive organ, and disruption of the skin structure of the genital area. The disease develops in men who ignore the rules of intimate hygiene. The foreskin and head of the penis are covered with smegma, the secretion of the sebaceous glands.
In men who do not follow hygiene rules, pathogenic microorganisms actively multiply in the accumulated smegma, causing inflammation and redness of the glans. In rare cases, the causes of the development of the inflammatory process are endocrine pathologies or severe illnesses.
Safe options for rashes on the penis
There are known tumors that are not inflammatory or precancerous.
They do not entail any consequences other than cosmetic errors.
- These are convex tubercles in the form of small pearls up to two millimeters in diameter. They are located in the projection of the sebaceous glands. They are the result of mechanical blockage and overextension of their excretory ducts. Not contagious. Not transmitted through sexual contact. Can be considered as a variant of the norm.
- Pearly penile papules occur in approximately 20 percent of men. In them, the epithelium of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands presumably proliferates excessively, which leads to its narrowing and accumulation of sebum.
- Moles and nevi can also be considered a type of rash. If they do not exceed a centimeter, have clear outlines, do not ulcerate, do not become wet, do not grow rapidly, do not bulge or change color, then they can be considered a safe phenomenon.
Such conditions do not threaten their owner in any way.
Regarding them, men often turn to a urologist fearing uncertainty about their position and the changed appearance of the penis.
Where to go if you have rashes on your penis
If changes in the skin or mucous membrane of the genital organs appear, it is wise to immediately consult a urologist, dermatologist or venereologist.
Any of these specialists is able to deal with the initial diagnostic searches.
He will prescribe the necessary examination and, if necessary, refer the patient to a related specialist.
Ideally, a urologist also has a specialization as a dermatovenereologist.
One visit to the doctor is enough to get all the relevant research done.
Rash in various pathologies is not always strictly specific.
Identical elements of it can be found in various diseases.
Several pathologies are also possible at the same time.
For example, a sexually transmitted infection and a toxic-allergic reaction to drugs that the patient was taking for other pathologies.
Or a mixed viral-bacterial infection, or a mix of several bacterial pathogens.
Or bacterial complications of fungal infections or parasitic skin diseases.
All this makes the diagnostic search quite extensive.
Venereal diseases
Typically, sexually transmitted infections are virtually asymptomatic. But some of them provoke rashes on the genitals. At the same time, itching and burning, redness and swelling of the tissues, and pain occur. Discharge with an unpleasant odor appears, the head becomes sticky. They are a yellowish or greenish thick mass or foamy liquid. There may be an increase in temperature and enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes. For treatment, local antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial ointments are used. Systemic antibiotic therapy is also necessary.
Diagnosis of rashes on the penis
Only a qualified doctor can choose from all possible options for tests and instrumental methods.
By going to the laboratory on their own, bypassing the initial appointment with a specialist, the patient risks not only spending extra money.
But also miss some of the tests necessary in his case.
- The diagnostic search, of course, begins with the doctor asking the patient about complaints and the history of the onset and development of the disease. Previous experience of diseases and allergy history are also important.
- The examination allows you to determine the morphology of the primary and secondary elements of the skin rash and preliminarily suggest which area to start searching for the causes of the disease.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests make it possible to assume the nature of the lesion (bacterial, viral, allergic), find indications of concomitant pathologies of the liver and kidneys, and suspect autoimmune processes.
- The study of smears and scrapings from the surface of weeping skin defects and the endothelium of the urethra makes it possible to identify or exclude sexually transmitted infections, to establish their causative agent, even during their incubation period or in a latent form.
- Serological blood tests also verify STDs and determine a person’s immune status and allergic condition.
- To clarify allergens, skin prick tests can be performed.
- Skin scrapings make it possible to detect and identify fungal infections and demodicosis.
- Histology and oncocytology make it possible to identify precancerous skin degenerations and penile cancer itself.