Causes of a variety of skin tumors
Leather is a unique tool given to a person for protection from adverse environmental conditions. Life on the planet has always been dangerous due to visible - sun, wind, temperature changes - and invisible reasons. The latter are microbes. However, skin is ideal for protection against microorganisms. Human integumentary tissue plays an important role in the life of any organism every day:
- protects deeper organs from the influence of the external environment;
- acts as a barrier to pathogenic microorganisms;
- maintains the body's internal temperature;
- carries information about the surrounding world.
The skin is designed to provide the body with reliable protection and the ability to perceive the world around us through touch. This is achieved by having three layers of skin. The topmost layer - the epidermis - is constantly renewed. It consists of special cells - keratinocytes. They have a special life path - from the cell of the deepest basal layer to the dead horny scale on the surface of the epidermis. Melanocytes are scattered among the keratinocytes of the epidermis. It is thanks to these cells that the skin acquires a tan under the rays of the sun. Melanocytes are so named for the production of the pigment melanin.
Human skin consists of three layers
Deeper than the epidermis lies a layer of special intertwined fibers - the dermis. This layer also contains nerve endings - the Futter-Pacini corpuscles, thanks to which a person has the sense of touch. In addition, many vessels pass through the dermis, from which the skin receives nutrition. This is where hair follicles originate. Each follicle has its own muscle, consisting of smooth muscle cells. The dermis contains lymphatic vessels, which play a large role in metabolism, as well as two types of glands - sebaceous and sweat glands.
The skin contains many small structures - glands and nerve endings.
The deepest layer is the hypodermis. It consists of identical cells - adipocytes. Each of them contains fat. The subcutaneous fat layer is a good shock absorber from any external mechanical influences. In addition, the large number of vessels in this layer helps maintain a constant internal temperature of the body.
Skin tumors are neoplasms from various elements of the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous fat. They can be benign, borderline and malignant. Tumors of the skin are extremely diverse. They occur in both adults and children.
Features of the structure and functioning of the skin - video
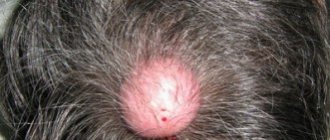
Localization of warts on the face
Warts appear on the face very often, no less often than on the body. They can be localized in absolutely any area, but most often they affect the area near the lips, nose, under the eyes and on the upper eyelids. They can be seen right in the eyebrows, next to the eyelashes, on the cheeks. Such formations are least common on the forehead; mostly flat growths appear here.
The appearance of any type of warts on the face is possible near the ears, closer to the scalp, on the inside of the lips. In these areas, predominantly ordinary formations grow, keratomas prefer to be localized on the cheeks, and genital warts and filiform warts prefer to be localized on the upper and lower eyelids.
Quite often you can see different types of warts on the face, located both nearby and far from each other. Here, both flat and ordinary growths, and pointed and thread-like formations may well be disturbing at the same time. In rare cases, they affect the entire face, which is why they resemble acne or some other serious dermatological disease.
What are the types of warts on the face - watch the video:
Whatever type of wart appears on the face, do not panic; you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will help eliminate dangerous pathologies and draw up a competent treatment regimen. Only a timely response to such formations can guarantee their safe removal.
City Dermatovenerologic Dispensary of St. Petersburg
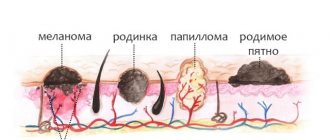
Very often you can observe strange new growths on the surface of the skin, in addition to the usual moles or acne. The appearance of a growth of an undetermined nature should cause concern and become a pretext for an immediate visit to a dermatologist. Neoplasms can cause a number of problems, including the development of skin cancer. Even the most harmless wart should be checked by a doctor to ensure it is benign. What types of skin growths are there and what they pose as a threat.
Features of malignant and benign neoplasms
All tumors form according to the same principle. The reason is the breakdown of genes that are present in every cell and contain all the information about its life path from birth. Changed genes cause skin cells to develop along a vicious path. First, one tumor cell is formed, which then gives rise to others. Each contains the wrong set of genes.
A tumor is formed from genetically altered cells
Benign cells have a number of characteristic features. Firstly, they are identical in appearance to normal ones. Secondly, they are subject to the influence of the immune system and other signals from the body. Thirdly, they grow very slowly and do not tend to spread to other organs.
Malignant skin tumors are the opposite of the previous case. They are greatly changed in appearance, grow very quickly, and deprive the body of nutrients. In addition, the tumor is not the only and often not the worst problem. Malignant cells spread through the blood and lymphatic vessels. Each tumor cell can give rise to a focus of secondary growth - metastasis.
Malignant tumors tend to spread through blood and lymphatic vessels
Benign skin tumors
Benign skin tumors are a common pathology. Most people are familiar with them firsthand. They can arise from any area of the skin. Some have a limited lifespan, others accompany a person for years and decades. Each type of tumor has all the signs of benignity - a characteristic appearance, slow growth and the absence of metastases.
Symptoms and signs of benign neoplasms on the skin - table
| Type of benign skin tumor | Time of onset of illness | Commonly Affected Gender | Favorite places for outbreaks of disease | Features of the appearance of the neoplasm | Cells that are the source of the tumor |
| Papilloma | Aged people | Any gender |
|
| Epidermis |
| Seborrheic wart |
| Any gender |
|
| Epidermis |
| Senile keratoma | Aged people | Any gender |
|
| Epidermis |
| Cutaneous horn | All age groups | Any gender | Exposed skin | Cone-shaped tumor | Epidermis |
| Keratoacanthoma |
| Men |
|
| Epidermis |
| Gottron's carcinoid papillomatosis |
| Men | Symmetrical lesions on the lower extremities |
| Epidermis |
| Trichoepithelioma | Mature people | Women |
|
| Hair follicle |
| Follicular keratoma |
| Women |
|
| Hair follicle |
| Cylinder | Boys and girls | Women |
|
| Hair follicle |
| Eccrine poroma |
| Women | Perineal skin |
| Sweat gland |
| Papillary syringocystadenoma |
| Any gender |
|
| Sweat gland |
| Syringoma | All age groups | Women |
|
| Sweat gland |
| Eccrine spiradenoma | Boys and girls | Men |
|
| Sweat gland |
| Fibroma | All age groups | Any gender | Any area of skin |
| Connective tissue |
| Dermatofibroma | Mature people | Women |
|
| Connective tissue |
| Hemangioma | Newborn period | Any gender | Entire skin |
| Blood vessels |
| Lymphangioma | Newborn period | Any gender |
|
| Lymphatic vessels |
| Leiomyoma | All age groups | Any gender |
|
| Smooth muscle cells |
Benign neoplasms - photo gallery
Syringoma is often localized on the face
Hemangioma is a benign tumor of blood vessels
Cutaneous horn is common in old age
Seborrheic keratoma is covered with greasy crusts
Keratoacanthoma rises above the surface of the skin
Follicular keratoma develops from hair follicle cells
The cylinder develops from cells of the epidermis, dermis, and skin glands
Papilloma is a common skin tumor
Prevention
For leg fibroids, as a pathology that occurs without specific causes, there is no specific prevention. According to doctors, to reduce the risk of tumor formation, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and give up bad habits. A daily routine that allows you to balance physical activity and rest is important.
Regular medical examinations will help prevent the disease and avoid unpleasant treatment procedures.
Borderline skin tumors
Borderline tumors can also form from any component of the skin - epidermis, dermis, sebaceous and sweat glands, hair follicles. At the first stage, they behave like benign neoplasms. However, it is not for nothing that scientists have identified them as a separate group. These types of tumors are characterized by transition to a malignant form with the formation of metastases. That is why they are called precancerous neoplasms.
Symptoms and signs of precancerous skin tumors - table
| Type of precancerous skin growth | Time of onset of illness | Commonly Affected Gender | Favorite places for outbreaks of disease | Features of the appearance of the neoplasm | Cells that are the source of the tumor |
| Verruciform epidermodysplasia | All age groups | Any gender | Exposed skin areas exposed to ultraviolet radiation |
| Epidermis |
| Bowenoid papulosis |
| Any gender | Crotch | Single or multiple brown growths | Epidermis |
| Giant condyloma |
| Men | Crotch | Multiple pointed projections with horny scales | Epidermis |
| Xeroderma pigmentosum | All age groups | Any gender | Exposed areas of the body exposed to ultraviolet radiation |
| Epidermis |
| Solar keratosis | Mature people | Men |
| Multiple outgrowths covered with horny scales | Epidermis |
| Radiation dermatitis | All age groups | Any gender | Entire skin surface |
| Epidermis |
| Bowen's disease | Aged people | Any gender |
|
| Epidermis |
| Erythroplasia Keira | Mature people | Men | Perineum and genitals |
| Epidermis |
| Extramammary Paget's disease |
| Any gender |
|
| Epidermis |
| Basalioma | Aged people | Any gender |
|
|
|
Borderline skin tumors - photo gallery
Giant condyloma is the result of the influence of papillomavirus
Verruciform epidermodysplasia affects exposed skin
Bowen disease occurs more often in older people
Paget's disease is common in women
Xeroderma pigmentosum is a precancerous skin condition
Basalioma contains a focus of retraction in the center
Main types of warts on the face
When considering what types of warts most often appear on the face, you need to remember that there are five of them. They all differ from each other in size, color, shape, and treatment features. Each of them gives its own symptoms, but almost always they arise for the same reason - damage to the body by the papilloma virus.
Flat warts on the face
Such formations appear due to the active activity of papillomavirus types 14, 15 or 27. They do not threaten health, as they have a low probability of degeneration into a malignant form.
Outwardly, this type of wart on the face resembles acne marks or small birthmarks.
They are characterized by a red color, a large lesion, roughness and roughness of the surface. They can have any shape, either smooth, round, or irregular. On average, their sizes are 0.3-0.6 cm.
Such growths are most often found on the cheeks, under the eyes, on the nose, and around the mouth. Due to their widespread distribution, they are difficult to treat. In most cases, they are removed either using external means or through physical therapy methods.
Simple warts on the face
This type of wart on the face is also called vulgar or common. Most often, their appearance is caused by papillomavirus type 2. Such formations in most cases occur in childhood, at 7-15 years of age, but can also occur in adults.
They are highly contagious and tend to increase in size and spread throughout the face and body. Externally, such growths look like a burn mark or callus. Their color can be white, flesh-colored, yellow, brown.
Characteristic signs of simple warts on the face are symmetry, uneven edges, and a rough surface. These formations can be found on the eyelids, forehead, cheeks, under the nose, around the lips. Usually their size does not exceed 0.3-0.5 cm; extremely rarely they grow with a large diameter.
This type of wart on the face protrudes somewhat above the skin, itches quite often and gives a burning sensation to the tissue. But it is easier to treat than flat growths. Most often, the use of external agents with a cauterization effect is sufficient for this.
Filiform warts on the face
Their more common name is acrochords. Their surface is elastic, soft, their shape is elongated, their dimensions range from 5 to 7 mm. Such formations range in color from beige to pink; when infected or tissue is damaged, they often turn black.
In the photo, these types of warts on the face look like bumps, under which you can almost always see a small stalk, rooted deep into the skin. Mostly they appear one at a time, but they can also appear in groups of 2-5 pieces. The main place of their growth is the eyelids and the area above the lips. Due to their pronounced relief, they are often compared to cauliflower.
The filamentous appearance of warts on the face is practically not prone to degeneration into a malignant form and has a low risk of malignancy. Due to its unusual shape, the growths are quite often injured, which sometimes leads to inflammation of the skin and the spread of HPV to other areas of the face, resulting in new formations appearing there.
While other warts may disappear on their own over time, without treatment, this almost never happens with the filamentous type. Moreover, sometimes with prolonged presence on the skin, the growth hardens. As a result, it becomes even more difficult to remove the formation.
Age-related warts on the face
This type of wart on the face, according to reviews, has several names - senile warts or keratomas. Unlike other types, these formations appear not at all due to infection with the papilloma virus, but due to age-related changes in the skin. They are completely safe for people because they never turn into cancerous tumors and do not threaten life.
The appearance of many keratomas gives rise to a diagnosis of “seborrheic skin disease of non-viral nature.” The cause of their occurrence is, as a rule, a lack of vitamins in the body and excessive exposure to sunlight. At the first stage, a spot forms, at the second, papules appear, at the third, the nodule turns into a dense formation, and at the last, in the absence of treatment, it turns into a “skin horn”.
The mature variety of warts on the face in the form of senile keratomas almost always has a bright brown color. For the most part, they are located separately from each other, but usually quite a lot of them appear on the face, which spoils the aesthetics of the appearance. The size of such formations is about 0.4 cm. They are sometimes confused with birthmarks or moles.
Genital warts on the face
This type of wart is not very common on the face; it mainly appears in intimate places. But still, in rare cases, these growths can also appear on the eyelids, and at times they can be seen right above the eye. They almost always consist of several layers combined into one formation about 1 cm in size.
The surface of the genital variety of warts on the face is covered with many papules or scales; it is not smooth and hard to the touch. Outwardly, they resemble a rosebud that has just begun to bloom. Their color is most often pink, so they rarely stand out against the general background, although small white inclusions are still possible inside.
Genital warts have a strong root, but most often it is not visible from the outside. They cause severe discomfort to a person, especially if they are located on the eyelids. Often their appearance is accompanied by severe itching and irritation.
Malignant skin tumors
Any component of the skin can become a source of malignant neoplasm. These tumors also arise as a result of the transformation of precancerous lesions. Skin cancer has all the signs of malignancy: rapid growth, the ability to penetrate neighboring structures. In addition, these tumors metastasize to lymph nodes and distant organs. The three most common forms are squamous cell carcinoma, Dubreuil's melanosis and malignant melanoma.
Melanoma - video
An interesting fact: among all malignant tumors of the human body, melanoma has the most aggressive growth and rapid formation of metastases. This malignant formation develops from skin pigment cells - melanocytes.
Symptoms and signs of malignant skin tumors - table
| Type of malignant neoplasm | Time of onset of illness | Commonly Affected Gender | Favorite places for outbreaks of disease | Features of the appearance of the neoplasm | Cells that are the source of the tumor |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Aged people | Any gender |
|
| Epidermis |
| Dubreuil's melanosis |
| Women |
|
| Epidermis |
| Malignant melanoma | Mature people | Any gender |
|
| Epidermis |
| Dermatofibrosarcoma | All age groups | Any gender |
|
| Connective tissue |
Malignant skin tumors - photo gallery
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer
Dubreuil's melanosis is a malignant disease
Melanoma is the most malignant tumor
Dermatofibrosarcoma is a malignant connective tissue tumor
Diagnosis of skin tumors
Correctly diagnosing a skin tumor is the task of an experienced dermatologist. The main advantage of malignant neoplasms of this kind is their location on the surface. This is why skin tumors can be recognized at a very early stage. For this purpose, the following research methods are used:
- External examination is a valuable research method. An experienced specialist, already at this stage of diagnosis, is able to predict the specific type of tumor, as well as its nature - benign or malignant;
- The decisive aspect in making a diagnosis is examining the tumor area under a microscope.
A histological preparation is prepared from the material taken. For this purpose, it is fixed in alcohols of increasing degrees, then poured into paraffin, cut using a special apparatus into the thinnest fragments. The final stage of drug preparation is staining. The finished tumor section is examined under a microscope by a specialist pathologist. It is he who determines the specific type of neoplasm; Microscopic examination is the most accurate way to make a diagnosis - After establishing a diagnosis of a malignant tumor, the next stage of diagnosis is performed - searching for metastases in the nearest lymph nodes and distant organs. The most effective in this search are ultrasound, x-ray and tomographic examinations. The presence or absence of metastases will allow the specialist to determine the stage of the disease and further treatment tactics.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with other skin diseases:
- pustular skin diseases caused by streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria;
- allergic diseases - eczema, psoriasis;
Psoriasis is an allergic skin disease - a hereditary disease in which normal keratinization of the skin is disrupted - ichthyosis;
- fungal skin diseases (trichophytia, microsporia).
What not to do
In conditions when 70% of the population are called carriers of HPV, it is really difficult not to become infected with it. When a virus is detected, it is best to determine its type so as not to worry about whether papilloma can become a real threat to life. There is a high probability that a non-oncogenic type will be discovered and then all worries can be forgotten. In all other cases, if the papilloma itches, try not to make the following mistakes:
- Do not disturb the tumor with clothing, jewelry or your own hands, trying to relieve itching. If its integument is damaged, there is a high probability that bleeding will begin, and the infection will not be long in coming and will penetrate into the layers of the skin.
- Don't be in the sun without UV filters. Apply creams to those areas of the skin where there are papillomas even if you go for a tanning session in a solarium.
- Do not avoid medical examinations. Particular vigilance should be exercised by those who have been diagnosed with genital warts.
- Do not use products that can remove tumors at home if the growths are localized in intimate places. If the papilloma begins to itch after using this drug, then consult a doctor immediately - this is an unsafe symptom.
Treatment methods
The treatment method for a specific skin tumor is chosen by a dermatologist. In the case of a benign neoplasm, it will be enough to get rid of the tumor itself. Currently, medicine offers a number of virtually painless ways to get rid of skin tumors:
- surgical excision of the tumor. This is the oldest and most proven method of eliminating tumors. The surgeon removes the tumor itself and a piece of tissue nearby. The material obtained during the operation must be examined under a microscope;
- electroexcision. In this case, the doctor uses an electric knife. Pathological tissues are vaporized by electric current;
- dermabrasion.
This method is good for eliminating tumors that lie shallow in the superficial layers of the epidermis. The doctor uses a device to polish the top layer. The depth of impact is adjustable; Dermabrasion affects the upper layers of the epidermis - cryotherapy.
In this case, the therapeutic agent is an extremely low temperature effect on the skin. Currently, such conditions are created using liquid nitrogen; Modern medicine allows you to remove skin tumors using liquid nitrogen - laser removal. The active agent in this case is a narrowly directed beam of light. This method achieves a selective effect on tissue.
At one time, the author of these lines had to deal with a benign skin tumor - papilloma. This lesion was localized on the back of the foot. At the initial stage it was dense and resembled a callus. Then growths appeared in this place, at first glance they went deep into the thickness of the skin, similar in appearance to cauliflower inflorescences. The tumor was painful and constantly experienced friction from any shoe - street, indoor, work. It was possible to cope with it using liquid nitrogen. After it fell away, not a trace remained at the site of the former papilloma.
Precancerous skin tumors must also be removed using one of the methods listed above. This event is vital, since the high frequency of transition of such diseases into malignant ones has been proven. With cancerous tumors the situation is somewhat different. In this case, removing the primary lesion on the skin does not always radically solve the problem. Typically, treatment tactics depend on the specific type of tumor and the degree of its spread (the presence of metastases in the nearest lymph nodes and distant organs). To combat the primary lesion and metastases, a complex of therapeutic measures is usually used: surgery, X-ray irradiation and chemotherapy.
Surgery for a malignant tumor requires removing, if possible, all malignant cells from the body. For this purpose, the surgeon excises the neoplasm itself on the skin, adjacent tissues, and nearby lymph nodes (lymph node dissection). Removal of tumor metastases may require a separate operation. X-ray irradiation is one of the effective ways to fight cancer. The radiation beam is directed directly to the tumor. However, neighboring tissues will also experience the negative effects of x-rays. They become thinner, change color, and inflammation develops (radiation dermatitis). Another way to fight cancer and metastasis is to prescribe chemotherapy drugs that kill malignant cells (Azathioprine, Cisplatin, Cyclophosphamide). These medications have negative side effects. First of all, during treatment, digestive disorders begin, the composition of the blood changes, and the functioning of the immune system is significantly inhibited.
Chemotherapy drugs negatively affect intestinal villi cells
Treatment of skin tumors in children and pregnant women is carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. The choice of treatment method is made by the doctor. Removal of the tumor by any agent is acceptable in all categories of patients. The dose of X-ray radiation and chemotherapy for children is calculated individually depending on age. When treating pregnant women, radiation and chemotherapy are not used due to the negative impact on the developing intrauterine fetus.