Good day, dear friends of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy Lifestyle”. The fungus very often affects the fingernails, and even more often the toenails. The manifestations of this disease are very characteristic, but, nevertheless, it can be very difficult to recognize it in time. In this article I want to look at some methods that answer the question: how to identify fungus on toenails.
In what cases is examination necessary?
Hair loss may be a symptom of fungal pathogens
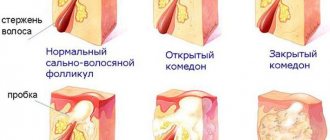
The fungus causes inflammation of the skin, nails, and can also affect the scalp. The main sign that indicates that it is necessary to visit a dermatologist is focal inflammation of the skin or the growth and separation of nail tissue with the formation of scales, itching and keratinization of the skin in the area affected by the fungus.
The scales actively peel off and contain a large number of pathogens of a certain type of mycosis, therefore they are a source of infection for healthy people. The fungus feels most comfortable in a humid environment, so most often infection occurs in a sauna, gym or swimming pool.
It is necessary to be tested for the presence of fungal pathogens if:
- increased peeling of the skin;
- characteristic rashes on the skin or mucous membranes;
- increased oiliness of the face and the appearance of lumpy skin;
- increased hair loss;
- the presence of dandruff and severe itching of the scalp.
It is worth noting that some skin diseases have similar symptoms to mycosis, therefore, in order to find the cause of the problem, you should take tests for the fungus and seek their interpretation and consultation with a dermatologist.
Clinical picture
There are 5 types of fungal infections:
- dermatomycosis;
- keratomycosis;
- candidiasis;
- systemic or visceral mycoses;
- pseudomycoses.
Dermatomycoses
This disease causes skin lesions. The causative agents are a group of dermatophyte fungi:
Infection occurs through contact with soil, animals and a sick person. Rounded areas of hyperemia appear, accompanied by itching. Subsequently, the spots are covered with scab.
With dermatophytosis, the hair follicle is involved in the inflammatory process:
- it is destroyed;
- hair falls out;
- bubbles with cloudy purulent and hemorrhagic contents and crusts appear.
Inguinal dermatomycosis manifests itself:
- pustular rashes;
- redness;
- peeling.
Keratomycosis
With lichen versicolor, pink-coffee spots with scalloped outlines appear, which subsequently become covered with peeling.
Actinomycosis appears
upon contact with cereals, mill workers get sick and the following appear:
In addition to skin manifestations, visceral pathologies are characteristic. Piedra affects the hair, but only causes aesthetic discomfort.
Candidiasis
This disease can be different:
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- thrush in women;
- severe systemic diseases (esophagitis, pneumonia and sepsis).
They are united by an etiological factor - “sweet tooth” fungi of the genus Candida. Normally, they exist in the body of every person and do not cause harm.
Visceral and systemic mycoses
- when encountering a large number of fungi;
- due to decreased immunity;
- in the absence of normal flora - the so-called “good” bacteria.
All fungi are sensitive to the pH environment, and this acidity is controlled by other microorganisms of normal human flora.
Systemic mycoses include:
Their main symptoms are associated with pathology of the lungs, heart or gastrointestinal tract, and skin lesions are not the main symptom.
All of them are difficult and difficult to diagnose and treat.
Pseudomycoses
This disease occurs under the guise of fungal infections, but the etiological factor is bacteria.
Where can I get tested for fungus?
First, you need to contact a dermatologist, who will visually assess the problem and inform you if the preliminary diagnosis suggests the possible presence of a fungus. Next, to confirm or refute this diagnosis, you will need to take an analysis. Where can I get tested for fungus? Not every laboratory can conduct tests for fungi, since such manipulations require expensive equipment, reagents and special qualifications of personnel. Therefore, it is necessary to find out in advance which medical institutions can conduct the necessary research. If the clinic you turned to for help does not do such tests, the doctor will write a referral to the nearest laboratory.
For the most accurate diagnosis, it is very important to choose the right medical institution where to get tested for nail and skin fungus. The correctness of the material collection depends on the qualifications of the laboratory technicians, and the correctness of the resulting laboratory test result depends on this factor. The sooner laboratory staff begin working with biological material, the better.
If the study is carried out by a contracting company, and only the material is collected at a selected medical institution with a small flow of clients, then the sample taken can remain on the tablet for a long time until it is completely filled and wait for its turn to be sent to the laboratory for research (which is not very good). Therefore, before choosing a laboratory, it is necessary to clarify this nuance.
Also, some laboratories offer the service of sending the results by e-mail, subject to the creation of a personal account on the website. Therefore, laboratory clients do not need to personally return and pick up a paper form with analysis results, and this is very convenient.
Causes of onychomycosis formation
Fungal infection is quite easy. The infection can be found in public showers, on beaches and in swimming pools. There is a high risk of contracting onychomycosis from infected loved ones if you use household items together.
There are the following prerequisites that provoke the entry of the pathogen into the body, in short, the reasons for the appearance of the fungus:
- minor skin damage on the feet (calluses, corns, small cracks and abrasions) that occur due to tight shoes;
- weak immunity due to previous inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- vascular diseases, impaired functioning of internal organs, leading to difficulties with blood circulation in the legs;
- violated precautionary measures, that is, visiting public places without shoes, poor foot hygiene, trying on someone else's shoes;
- ignoring severe sweating and diaper rash.
Important!
Onychomycosis begins on the thumb, and subsequently the virus can develop on the little finger.
Types of tests for fungus in the body, skin and nails
Microscopic analysis is one of the methods for detecting fungal infections
To diagnose mycosis of any kind, it is necessary to take a sample of biomaterial. This could be a piece of the affected nail plate, a scraping from the skin, a hair follicle or other material that needs to be processed in a certain way and the reaction studied. There are several methods for collecting tests, which are most often prescribed by dermatologists to confirm the diagnosis of mycosis. These include:
- Microscopic;
- Cultural;
- Immunoenzyme;
- PCR analysis.
Microscopic method
After processing the taken material, the result is examined under a microscope. The material is collected only with the help of a sterile instrument at the border of the outbreak, since there is the highest concentration of pathogens. This type of fungal examination is called microscopic. The results of the analysis will be known 3-5 days after the start of the study.
Most often, this method assumes a positive or negative result for the presence of fungus. And very rarely does it provide information about its concentration and type of pathogen.
It is considered normal if, as a result of the study, no fungi are found at all. If a low concentration of the mycosis pathogen is detected, this may indicate reduced immunity of the patient, who is an asymptomatic carrier.
Culture method
This analysis for fungus of the skin, nails or scalp provides more accurate data about the pathogen, but obtaining it will require more time. Depending on the type of fungus, you can get results either in a couple of days or in a month.
The collection of material is carried out by a laboratory assistant in the same way as for the microbiological research method. After which the biomaterial is immersed in an environment nutritious for fungi, in which they begin to grow into entire colonies. The resulting result is studied under a microscope to determine the type of fungus and its concentration. The detailed analysis provides information regarding sensitivity to certain medications.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
This type of laboratory test is often used to diagnose deep mycosis, when taking material for analysis is a problem. As a result of ELISA, it is possible to determine the most suitable type of antibodies to the identified fungus. The sensitivity of ELISA is about 80%. In this case, venous blood is taken as the material for research. A blood test for fungus is taken on an empty stomach, and the result takes one to five days to prepare and has three formulations (positive, negative, doubtful).
If necessary, ELISA may include determining the level of immunoglobulins relative to a fungal infection. The results indicate the “norm” limit with which the obtained value is compared.
PCR
PCR is a laboratory diagnostic method aimed at identifying pathogens of infectious diseases
This analysis can determine the presence of a specific type of fungal pathogen in the material. It is distinguished by accuracy and quick results, but at the same time it has a narrow direction. The use of PCR for fungi is justified when re-confirming an already established diagnosis. To carry out the analysis, a scraping of the skin or mucous membrane is done, and sometimes a urine or blood test is taken.
This research method can indicate the absence or presence of the causative agent of mycosis or their quantity in the taken material. The result of the analysis will be known the next day after taking the material or a day later, but the attending physician will never make a diagnosis based on the PCR result alone. This test is prescribed only if specific symptoms are present.
Varieties and forms
According to statistics, in 15% of a hundred, blood damage by spores occurs in clinics and hospitals where outbreaks of fungal infections have been detected. Such cases are typical when using catheterization devices for the genitourinary system and vascular tract.
Blood fungus has three main forms:
- invasive candidiasis;
- candidemia;
- disseminated candidiasis.
Each of them can occur in an acute form. And over time it becomes chronic. A dangerous type of lesion is candidemia, which develops with virtually no symptoms, only occasionally affecting the functioning of the kidneys.
results
If the test result is positive, this indicates that a laboratory test found fungal spores or mycelium in the provided biomaterial. The scraping result can provide only narrow information about the presence or absence of the pathogen. If the result is positive, then the dermatologist prescribes a wider examination of the sample, taking into account the patient’s symptoms and complaints.
To identify the DNA of a pathogenic organism, the biomaterial is placed in a special nutrient medium. As a result of cultural analysis, it is possible to more accurately determine the type of fungus and confirm the assumption with PCR results. In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor can confirm the result with multiple tests, which are carried out after a certain period of time. Depending on the analysis, the research result can be obtained within 2-3 days after collecting the biological material.
Types of infection
In total, there are more than five thousand species of fungi that cause problems. There is no single classification.
The only thing is that there are two important signs by which the disease is distinguished. This is the location and type of pathogen.
Important!
The infection can be in any part of the nail, and this is the main sign of the disease. The external appearance of the affected plate changes based on the location of the virus.
Type of pathogen
There are different pathogens, each of which has its own distinctive characteristics. They are important to consider when creating a treatment plan. The most common pathogens are:
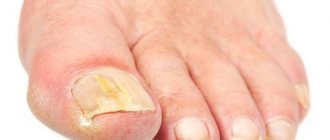
- Dermatophytes are Trichophyton red and Mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton flocculus and so on. When infected with such fungi, yellowish or grayish spots form, the remaining areas of the plate become cloudy, and the free edge changes color. In general, the entire surface changes and moves away from the bed over time.
- Mold fungi . This type is relatively harmless. It does not penetrate into the deep layers of the nails, so it only changes the plates to a dark, marshy, gray, yellowish, brownish color. This shade can affect the surface either partially or entirely.
- Yeasts of the genus Candida . They thin the nail and contribute to its peeling. Often, due to this pathogen, a white form of the disease is formed, characterized by inflammation of the cuticle. They can cause intense pain and may be accompanied by purulent discharge. If left untreated, the nail will thin, turn brown, and completely pull away from the bed.
Locations of the disease on the arms and legs
The main forms of onychomycosis:
- Lateral. The sides of the nail become infected. Its color becomes grey, yellowed and brownish. The plate begins to become cloudy, crumble and delaminate.
- Distal. This is the most common type of fungus. Infection begins from the free edge of the nail. The plate changes color to yellow, brown or gray. Over time, the damage becomes larger. The plate begins to delaminate, crumble, and become cloudy. In this case, hyperkeratosis appears under the nails, and if the entire nail is affected, tissue degeneration occurs.
- Proximal. This form involves damage to the cuticle, which swells, becomes inflamed, turns red and changes its shape and structure. As a result, the roller separates from the plate, and the nail crumbles, fades and becomes deformed. If the disease is advanced, the plate may completely fall apart.
- White superficial. It usually appears on the thumb, but occasionally on others. Externally, it appears in the form of white spots that are located over the entire nail surface. Further, the disease progresses and spreads to keratinized tissue. The spots may change color - from milky to green or yellow. The structure of the plate is made spongy and loose. If this form is not treated, the nail may completely collapse.
- Total dystrophy. It covers the entire nail surface. This is an advanced stage of distal or proximal fungus. The plate becomes thick, changes its shape to an unnatural one and eventually completely deteriorates.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
How many times do I need to get tested for fungus?
- Affected skin, hair or nails, without a doubt, cause maximum discomfort to any person. In order to diagnose the presence of a pathogen, it is necessary to take a scraping once. Only with a large affected area in complex cases can a dermatologist recommend undergoing a repeat examination in order to select treatment as accurately as possible.
What to do after receiving a positive result?
- In most cases, collection of material for the presence of fungus is carried out on the recommendation of a dermatologist. Half of the patients who contacted the laboratory get a positive result. In this case, you need to go back to the dermatologist with the result for consultation and selection of a treatment regimen. If a fungus is found on the eyelashes, you may need to consult an ophthalmologist, but during the appointment you must warn the doctor about the infection in advance.
What types of fungi are most commonly found as a result of scraping?
- As a result of a detailed analysis, laboratory assistants can detect fungal spores or branches of mycelium, which indicates the presence of onychomycosis or mycotic lesions of the feet. Shortened mycelium threads indicate the presence of pityriasis versicolor.
Diagnostics
The first signs and symptoms of a developing pathology should prompt the patient to go to the clinic as quickly as possible and conduct a series of necessary examinations.
To detect fungi of the genus Candida spp. in the blood. The specialist will carry out the following diagnostic measures:
- X-rays of light.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract and internal organs;
- Bacteriological blood culture (carried out 2-3 times a day to identify the habitat and type of fungus).
- Biopsy with selection of histological material from identified affected tissues.
- Culture from the inner wall of a vascular or genitourinary catheter (if any).
The main result, confirming or refuting the suspected diagnosis, is provided by blood culture to identify a fungus such as Candida spp. with severe inflammation and high temperature. Acute disseminated candidiasis, which is a consequence of the spread of pathology and changes in blood composition, is diagnosed using histological laboratory examinations based on tissue sampling from the affected organs.
Preparing for the study
When taking a blood test for fungus, you should stop drinking alcohol one day before.
Before getting tested for nail or skin fungus, you need to prepare for this procedure in advance. To ensure that the research result is as accurate as possible, it is recommended:
- at least 24 hours, or better yet 48 hours, before collecting the biomaterial, do not wash the affected area with soap or other aggressive detergents;
- refrain from treating the fungus-affected area with lotions, creams and other products containing a high content of synthetic ingredients;
- remove nail polish when taking material from the nail plate;
- stop taking medications a few days before the tests so that the results are as accurate as possible;
- stop taking antibiotics and other systemic antimycotics one day before.
If you need to take a blood test for fungus in the body, then you need to:
- come to the laboratory in the morning to donate blood on an empty stomach;
- one day before going to the laboratory, you should avoid excessive physical activity and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- do not take any medications unless absolutely necessary, and if this point has not been observed, then warn the laboratory assistant about this;
- refuse donation;
- 12 hours before the test, do not smoke or drink coffee or strong tea.
Prevention
Personal prevention is as follows:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- use of individual manicure and pedicure accessories;
- wearing personal shoes when visiting swimming pools, baths, saunas;
- lack of contact with unknown and homeless animals without protective equipment;
- use of a respirator, gloves and protective suit in hazardous work;
- treatment of chronic diseases;
- blood sugar control;
- maintaining a normal weight and physical activity;
- adequate antibiotic therapy;
- treatment of sick family members.
Testing process
So that tests for fungus in the body are as complete as possible. In the laboratory, they first take a blood test to determine the presence of the pathogen, and then scrape off any exfoliated scales or secretions from the affected area of the skin. A sample of biological material is taken with sterile instruments and placed in a nutrient medium in a standard container, where it grows until a certain point, until a colony of fungi becomes visible under a microscope in the form of mold.
Depending on the chosen analysis, its results may display the type of pathogen, its concentration, and sensitivity to certain medications.
To get tested for athlete's foot (scraping), you must allow a laboratory technician to take a sample of dead skin from the foot or nail. The specialist, having examined the affected area, will decide where it is best to get the biomaterial from. The resulting skin particles are immediately placed in a sterile box and sent for examination.
When you have decided where you can get tested for nail or skin fungus, it is advisable to conduct the examination in two stages. First, the laboratory will determine the presence or absence of fungus. If the result is positive, then it is necessary to take a culture to determine the type of pathogen and its concentration. The selection of the optimal treatment regimen and its effectiveness depend on the accuracy of these indicators.
Private clinics with modern laboratories provide their services at a frankly inflated price, but the accuracy of the result will be higher than in a public clinic with outdated equipment and approach to work.
If you identify the problem in a timely manner and know what the fungal test is called in order to order it in the laboratory, you can identify the pathogen at the initial stage of the disease. This moment will help to get rid of the disease faster, which will save the patient’s money and the attending physician’s time. But in an advanced situation or if the type of fungus is incorrectly determined, the doctor may incorrectly draw up a treatment regimen, which will not give the expected result and treatment may take a long period.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of candidemia is similar to bacterial sepsis. The condition of the infected person worsens; there are complaints of dull aching pain in the muscles, both during movement and at complete rest.
Signs that a fungus is developing in the blood are as follows:
- Reduced susceptibility to broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Body temperature rises to 39°C.
- In almost 20% of cases, patients experience a suffocating cough with breath holding.
- 15% of those infected experienced toxic shock.
- Gradual infection of internal organs occurs.
In rare cases, when the blood is infected with a fungus, an alternation of stomach upsets and constipation occurs.
A distinctive feature is stool containing white flakes or splashes of blood. In this case, the patient does not experience the sensation of complete bowel movement.
If candidemia has entered the chronic phase, ulcers begin to form in the colon and rectum with gradual destruction of the walls, appetite disappears, body temperature rises greatly, and general weakness and malaise appear. The prognosis is disappointing - such an exacerbation, most often, leads to general intoxication of the body, and after this - to death.
How to take the material
Material for fungal analysis is collected with a special instrument. The specialist puts on gloves and removes a piece of the nail plate that has obvious signs of damage. The nail may be discolored or, conversely, darkened. If the plate peels off, the doctor will take 1-2 flakes.
In some cases, it is more advisable to take a piece of skin from the inflamed pad that surrounds the diseased nail. The seized material is crushed and then examined. The tissue is examined under a microscope. It is then placed in separate containers for more detailed analysis. Even if you need to conduct several tests, the material is taken only once.