pharmachologic effect
Isotretinoin is one of the biologically active forms of vitamin A. It inhibits the terminal differentiation of sebocytes, hyperproliferation of the epithelium of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands, normalizes the composition of their secretions and facilitates its evacuation. Due to this, the production of sebum is reduced, its secretion is facilitated, the composition is normalized, and the inflammatory reaction around the glands is reduced. The solution has antiseborrheic, anti-inflammatory, keratolytic effects; enhances regeneration processes in the skin.
Mode of application
Dermatologists prescribe retasol for the treatment of acne and prevention if there is a tendency to their appearance. For therapeutic purposes, the drug is used twice a day. Treatment can be lengthy and range from one to four months, it all depends on the degree of the disease.
For oily skin, liquid retasol is suitable, but for very dry and sensitive skin types, ointment is preferable. Or you can combine two drugs and use ointment in the morning, liquid in the evening - or vice versa. Apply the drug in a thin layer to dry, previously cleansed skin, avoiding the area around the mouth and eyes. If the dynamics of treatment are positive, then the number of applications of retasol is reduced, as well as the duration of use.
special instructions
The solution should not be prescribed to patients receiving other drugs from the retinoid group in order to reduce the risk of hypervitaminosis A.
It is not recommended to apply the solution to the skin around the eyes, or in cases of severe acute inflammation. Do not apply to mucous membranes. During treatment, you should avoid exposure to the sun; if necessary, use sunscreen; preventive and therapeutic use of ultraviolet rays and visiting a solarium are not recommended.
The drug does not affect the ability to drive a car or perform work that requires increased concentration.
How does Retasol interact with other medications?
You may increase your risk of developing group A hypervitaminosis if you take the product at the same time as other retinoids, this group includes substances such as:
- tretinoin;
- retinol;
- adapalene;
- acitretin and others.
Tetracyclines can increase the risk of increased intracranial pressure and to prevent this, Retasol should not be taken with isotretinoin. Isotretinoin also weakens the effect of progesterone, so during its use it is not recommended to use contraceptives that contain progesterone. If you use the drug simultaneously with medications that increase photosensitivity, then there is a possibility of sunburn.
Retinol ointment will have a weak effect if used during treatment with tetracycline antibiotics or glucocorticoids.
Contraindications and side effects
The use of retasol is not recommended in the following cases:
We also recommend reading: Salicylic-zinc paste for acne
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- with impaired fat metabolism;
- with hypervitaminosis of vitamin A and retinol;
- when planning pregnancy;
- while taking tetracycline antibiotics;
- if you have an allergic reaction to the active substance or auxiliary components of retasol.
Side effects may occur if you are allergic to retasol. It manifests itself as an itchy rash, swelling, redness, increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, migraines, and increased fatigue. With prolonged use of retasol, hypervitaminosis may develop, manifested by conjunctivitis, cheilitis, and dry skin.
Pharmaceutical research and production enterprise
Acne vulgaris or juvenile acne
- the most common skin disease in adolescents and young people, that is, the most socially active part of the population. This unpleasant disease affects about 85% of people aged 12 to 25 years in European countries, so clear skin at this age is the exception rather than the rule. The presence of inflamed pimples, pustules and ulcers, blackheads (comedones), spots and scars, a greasy, untidy appearance of the skin in the most visible places causes difficulties in communication, professional organization, reduces self-esteem, and often leads to the formation of significant psycho-emotional disorders up to the desire for complete isolation. Some young people stop leaving home, give up school and work, become isolated, and eventually a minor and completely banal skin problem develops into a personal tragedy. A patient who has consulted a dermatologist about acne has psychological difficulties. Shyness, guilt, a sense of social unacceptability, anger, depression, and disbelief in the possibility of a cure are expressed to varying degrees. Intense experiences aggravate the course of the disease. In stressful situations, especially women, they pick and squeeze out acne, which further worsens the appearance of the skin due to associated inflammation. In such injured areas, scars and spots remain that do not go away for a long time.
Acne
– a long-term disease, often exacerbating (in girls, usually monthly) and often resistant to treatment.
Currently, we know much more about acne than ten years ago, and a specialist can always help the patient. In this regard, the opinion that existed in the past that acne will go away on its own with age and that it is not worth spending effort on treating it now sounds simply absurd. It is not always possible to immediately find the right individual approach, but the efforts made and perseverance shown are always rewarded with a good result. Specialists have a number of effective medications from different groups in their arsenal. The choice of drug depends on the form of the disease, the predominance of certain symptoms, the gender of the patient, and the presence of contraindications.
Acne is most often divided into:
- Comedonal
- with a predominance of comedones (white and blackheads) with mild inflammation; - Papulopustular
- there are comedones, inflamed nodules (what are usually called pimples), pustules, sometimes single large painful lumps that gradually turn into ulcers such as boils, many spots on the sites of previously existing inflammatory rashes; - Conglobate
- along with all of the above, painful compactions exist for a long time, leaving pronounced scars after healing. Over time, most patients develop the habit of squeezing out comedones and pustules, constantly touching the inflamed skin, which is why bloody crusts, spots, and superficial scars are added to everything described.
Many factors take part in the development of acne, the action of which is ultimately realized in the pilosebaceous follicles. Not all follicles are affected, but only those with a special structure, located on the face and in the upper part of the body - with large sebaceous glands, wide (up to 2.5 mm) ducts and thin, almost invisible hairs. The sebaceous glands are the target organ for sex hormones, especially testosterone. Under the influence of testosterone, produced by the gonads especially actively in adolescence, the size and number of sebaceous glands increase significantly, the production of sebum increases, and its composition changes. In addition, excessive keratinization of the epithelium of the sebaceous gland ducts, difficulty in the outflow of sebum to the surface of the skin, increased proliferation of microbes in accumulated sebum and subsequent inflammation are essential in the development of acne. With the help of modern medicines it is possible to influence almost all factors involved in the development of the disease.
At the initial manifestations of acne (usually at the age of 8-13 years), when the clinical picture is dominated by increased oily skin and comedones (white nodules and blackheads), and there are not many inflammatory elements, preparations of retinoic and salicylic acids are used externally. Both acids have the property of dissolving comedones, and salicylic acid has a much weaker effect in this regard.
For papulopustular acne, it is advisable to use antibiotics, retinoids, benzoyl peroxide (benzoyl peroxide), traditional external agents (salicylic, chloramphenicol, resorcinol alcohols).
Severe forms of acne, including conglobate, require systemic (internal) treatment (usually with retinoids), and only if there are contraindications, other methods (antibiotics, immunomodulators) are used. At the same time, external treatment is carried out. As with papulopustular acne, it is preferable to use a combination of different drugs.
Currently, retinoids are the most effective group of drugs for the treatment of acne. Their use solves several problems at once - reducing sebum production and inflammation, preventing the appearance and elimination of comedones and scars.
Roaccutane and retinol palmitate are used for the internal treatment of conglobate acne and common papulopustular acne resistant to other external agents.
Roaccutane (isotretinoin, capsules for oral use of 0.01 and 0.02 No. 30, (“Hoffmann-La Roche”, Switzerland), prescribed at the rate of 0.5-1.0 mg/kg body weight per day, taken equal in parts 2 times a day after meals for 12-16 weeks. If repeated courses are necessary, the break should be at least 8 weeks. Roaccutane is a highly effective drug, however, its use is limited by high cost and many side effects. Treatment is always carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
Retinol palmitate (vitamin A) is a domestic drug, it is produced in an oil solution of 100,000 IU/ml. Effective doses for acne are at least 300,000 IU per day. The course of treatment is 12-16 weeks. The intervals between courses are 4-8 weeks. Retinol palmitate is inferior in effectiveness to Roaccutane, however, it is better tolerated and the cost is significantly lower.
For external treatment of mild forms of acne, two isomers of retinoic acid (tretinoin and isotretinoin) and the synthetic retinoid adapalene are used.
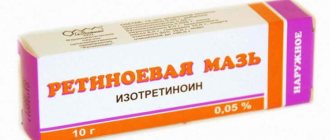
External preparations with isotretinoin, which has higher bioavailability compared to tretinoin, are produced only in Russia - Retinoic ointment 0.1% and 0.05% (in tubes of 10 g, JSC Retinoids) and Retasol® (0.025% solution in bottles of 20 ml, JSC "Retinoids").
Retinoic ointment
is available in two concentrations - 0.1% and 0.05%, which corresponds to the content of 13-cis-retinoic acid (isotretinoin). The ointment is made on an emulsion basis (that is, it has the consistency of a light moisturizing cream), has a yellowish color, odorless, is easily applied to the skin and absorbed. The ointment is applied to clean, dry skin twice a day in a thin layer on the affected areas (facial skin, if necessary, back and chest). When using a high concentration ointment on the face, do not apply it to the eyelids, area around the eyes, lips, corners of the mouth and at the entrance to the nose, and also avoid getting the drug on the mucous membranes to avoid irritation. At the beginning of treatment, Retinoic ointment 0.1% is used to achieve maximum effect in a shorter time. The exception is people with thin, sensitive skin (mainly blondes, red-haired people and children), who initially use an ointment of a lower concentration (0.05%), increasing it if it is well tolerated, usually after 2-3 weeks. Upon successful completion of the main course of treatment (3 months) with retinoic ointment 0.1%, it is necessary to smoothly transition to maintenance therapy. During the transition period (1-2 months), it is recommended to use retinoic ointment 0.05% initially 2 times a day, then once at night. Retinoic ointment is an effective treatment for all forms of acne vulgaris, but the best results are achieved for papulopustular and comedonal acne.
New original domestic drug Retasol®
is a solution for external use containing 0.025% 13-cis-retinoic acid (isotretinoin) in an alcohol-glycol base. The solution is a clear, slightly oily, light yellow liquid. Available in 20 ml dark glass bottles. A small amount of the drug is applied with a cotton swab to previously cleansed dry skin 2 times a day (morning and evening) over the entire affected area (skin of the face, back, chest). Once the effect is achieved, the frequency of application of the drug is reduced. In persons with thin, sensitive skin, at the beginning of treatment it is recommended to use the drug once a day (in the evening). To cleanse the skin, it is recommended to use liquid cosmetics - foams, washing gels, cosmetic milk, non-alcoholic tonic. To avoid drying out the skin, it is not advisable to use hard soap and alcohol-containing solutions to cleanse the skin. Avoid using the solution on the mucous membranes and eyelid area. The duration of treatment with Retasol® is 12-16 weeks. If the effect is good, treatment with Retasol® can be continued for a longer period.
In mild cases of comedonal and papulopustular acne, you can limit yourself to using Retasol® or Retinoic ointment. For severe forms - in combination with antibacterial agents, both ready-made (Dalacin, Zinerit) and prescription ones.
The presence of several external dosage forms with isotretinoin makes treatment more optimal and allows selection of the drug, that is, individualization of therapy. Thus, with significantly increased oily skin, the predominance of comedones and pustules, it is better to use Retasol® solution, and with less oily skin and the predominance of inflammatory nodules, retinoic ointment.
All drugs from the retinoid group have a number of side effects. The most serious of them are teratogenicity and embryotoxicity (damaging effects on the fetus). In this regard, women of childbearing age are prescribed oral retinoids with reliable contraception and a negative pregnancy test. In the outpatient card, when prescribing systemic treatment, a note is usually made about the woman’s awareness of possible side effects, and abroad dermatologists offer women to fill out and sign a special form in order to avoid further prosecution in the event of side effects. External treatment with drugs of this group is stopped when pregnancy occurs. Retinoids do not have a negative effect on the reproductive function of men.
In the first or second week of treatment, most patients experience an exacerbation reaction, expressed in redness, moderate itching, and peeling of the skin. The patient should be warned about the reaction, and if he is facing important life events at this time, then it is better to postpone the start of treatment. Typically, these phenomena go away on their own within a few days, after which a lasting improvement occurs. Dry lips, cracks in the corners of the mouth, peeling of the skin are common during the treatment process; they are eliminated by using a neutral moisturizing cream for the face and body, hygienic lipstick or lip gel, and limiting the use of detergents when washing and washing. When retinoids are prescribed orally, dry nasal mucosa, nosebleeds, conjunctivitis, urethritis, increased levels of transaminases and lipids in the blood, and increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight are sometimes observed. Taking this into account, before the start of treatment and monthly during treatment, a biochemical blood test is performed, it is recommended to use sun protective creams, and avoid direct sunlight.
Contraindications for prescribing drugs from the group of retinoids orally: pregnancy and lactation, abnormalities in biochemical blood tests (hyperlipidemia, increased activity of ALT, AST and alkaline phosphatase), renal and liver failure, hypervitaminosis A, intolerance to the drug.
Retinoids cannot be prescribed simultaneously internally and externally, ultraviolet irradiation, drugs with keratolytic and exfoliating effects, exfoliating cosmetic procedures and products (scrubs, peeling). The effect of retinoids is weakened by the simultaneous use of glucocorticosteroid (hormonal) drugs and alcohol intake.
prof.
IN AND. Albanova Print
Reviews
Reviews about the drug "Retasol" are mostly positive, although there is a small percentage of patients who are dissatisfied with the results of treatment. In most cases, such dissatisfaction is associated with an allergic reaction to the drug.
Olga: “Retasol was prescribed by a doctor for moderate acne. Used it as directed twice a day. In the first five days there was an aggravation, but then the number of acne began to decrease sharply. The course of treatment lasted two months, after which the skin was almost completely cleared.”
Alena: “Retasol did not suit me, because a couple of days after I started acne treatment, itching and red spots appeared. I had to turn to other drugs."
Yana: “I purchased Retasol on the advice of a friend who got rid of acne. At first I applied it twice a day, but my skin reacted with dryness and flaking. I started applying it only to areas of inflammation once a day, every other day. Gradually, the skin really became cleaner, the pores cleared and became almost invisible. At the same time, the acne spots disappeared.”