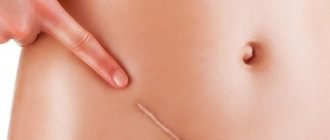
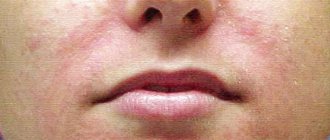
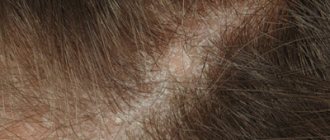
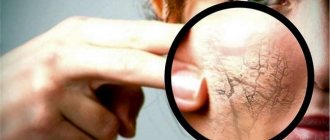
Facial dermatitis is a disease that provokes inflammatory processes on the facial skin. Pathology, in addition, causes physical discomfort and affects the psychological state, leading to the emergence of various complexes.
The disease has a particularly strong impact on women, for whom even the appearance of a small pimple becomes a real disaster.
Until recently, dermatitis on the face belonged to childhood diseases. Now it is diagnosed in 10-12% of the adult population.
Causes of dermatitis on the face
It has not yet been possible to accurately determine the factors that provoke the development of the disease.
Presumably the main causes of dermatitis on the face are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- endocrine disorders;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- deficiency of vitamins in the diet;
- insufficient facial hygiene;
- use of low-quality cosmetics.
Increase the risk of developing the disease:
- weak immunity;
- frequent stress;
- poor facial hygiene;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse.
Find out more
Diagnosis of the disease
Before treating dermatitis on the hands, you should find out the nature of the irritation, the area of localization and the time of development of acute symptoms.
A number of laboratory tests are prescribed:
- conducting clinical blood and urine tests;
- immunological and serological analysis is prescribed;
- in adults, a biopsy may be performed;
- histological examination;
- The allergen in the blood is determined.
Carrying out diagnostics that determine the causes of the development of the disease and its types becomes decisive for the doctor who makes a decision on how to treat dermatitis on the hands and how long it will take until remission occurs.
Symptoms of dermatitis on the face
Characteristic signs of dermatitis on the face can be seen in the photo. They are manifested by erythema and clearly visible acne-like rashes filled with fluid or pus. The rash is most often localized on the chin and around the mouth.
Quite often, people mistake the symptoms of dermatitis on the face for signs of simple inflammation, allergies or other diseases (for example, psoriasis). As a result, they do not take the necessary measures, which leads to the progression of the disease and the occurrence of complications.
Stages of dermatitis on the face
In its development, the disease goes through 3 stages:
- Spicy. The skin of the face turns red due to vasodilation, becomes swollen, covered with spots and blisters filled with serous fluid, and a burning sensation occurs. Any changes in environmental conditions immediately affect its condition. Timely treatment allows you to quickly and effectively get rid of the problem.
- I'll sharpen it up. The blisters burst, forming a scab, which causes itching and burning. The skin dries out and peels off in scales, becomes horny and covered with bluish, rough scars. Headaches, joint pains, and fever are possible.
- Chronic – an advanced form that cannot be completely cured and periodically manifests itself with relapses.
Timely adequate therapy will allow you to avoid the disease becoming chronic. Therefore, you should not treat dermatitis on the face at home, which may worsen the situation. It is better to consult a specialist if any rash is detected.
Signs and diagnosis
Symptoms of dermatitis manifest themselves in different ways, they depend mainly on the etiology of the disease. And this can be seen in the photo, considering the typical manifestations of infectious pathologies.
But there are also general signs, which are as follows:
- A mandatory element of the disease is a rash. Its type depends on the type of pathogen.
- Almost always a person is bothered by itching of varying intensity, sometimes there is a burning sensation, a feeling of dryness. Scratching leads to disruption of the integrity of the dermis and the addition of a secondary infection.
- The active process is often accompanied by a rush of blood in the microvasculature and redness.
- With many infectious dermatitis, peeling and peeling of the scales of the upper layers of the skin occurs.
Diagnosis begins with an examination of the patient, a survey to identify complaints, and anamnesis. The patient must also donate urine and blood.
To establish the cause of the pathological process, additional serological and virological techniques are used. If necessary, resort to histological analysis.
Classification
Skin lesions can be primary (occur as an independent nosological unit) and secondary (as a symptom of the underlying disease). Depending on the etiology, there are two groups of infectious dermatitis - viral and bacterial (pyoderma).
Viral
Viral infections that lead to the development of skin lesions differ from each other in location, degree of manifestation and type of rash, and other symptoms of pathology in the body:
- If the cause is measles, then the rash looks like spotted bumps. They gradually merge with each other and can affect the entire surface of the body. Over time, the spots darken and begin to peel off.
- With rubella, the localization of small-point lesions is typical for the face and neck; as it progresses, pinkish formations begin to occupy the entire body. At the same time, total lymphadenopathy and increased temperature are noted.
- During scarlet fever, thick rashes are initially observed in the groin and under the arms. Then they begin to cover the torso, hips and elbows. The rash consists of many very small roseola elements. After a short time before recovery, peeling begins.
- Bright spots during the introduction and active reproduction of enterovirus can appear almost anywhere. After passing the acute stage, they turn pale and then disappear without a trace.
- Chickenpox is accompanied by the appearance of red spots, which subsequently turn into blisters with liquid. The disease is characterized by a gradual addition of elements. In severe cases, they are located not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes, affecting the genitals, oral cavity and eyes. Accompanied by severe itching. After a few days, a crust appears at the site of each bubble, and then it disappears.
Any patient or carrier can infect a person with viral dermatitis.
In addition to treating the pathology, the person should be isolated by placing him in a hospital or selecting a separate room.
Bacterial (pyoderma)
According to etiology, pyoderma is divided into streptococcal, staphylococcal and mixed . The duration of the course indicates the presence of an acute or chronic process. There are also primary bacterial skin lesions and secondary ones (occur against the background of scabies, eczema, atopic dermatitis).
Streptococcal infection causes the appearance of single formations - vesicles filled with pus. They are localized around the mouth, nose and other natural openings of the body. Quite often it goes away without special treatment. In this case, the bubble opens with the formation of a yellowish crust, which then disappears.
Staphylococcal damage to the dermis is more severe. Such an infection, if left untreated and with a decrease in general and local immunity, leads to serious consequences and can result in blood poisoning and death of the patient.
Staphylococcal infectious skin lesions are divided into the following types:
- Ostiofolliculitis. Occurs in the form of single or multiple pustules, with obligatory localization in the area of the hair follicle. Such formations never merge and disappear in about 4-5 days.
- Folliculitis. Often occurs after ostiofolliculitis. Refers to a more severe lesion. The favorite localization is the back and hair growth mark. Complete cure occurs within 5-7 days, a small scar appears at the site of inflammation, and the hair follicle dies.
- Furuncle. It begins in the form of folliculitis, gradually affecting the deeper layers of the skin. An infiltrate forms around it, and necrosis forms in the middle. A boil forms everywhere except on the palms and soles (since there is no hair there). With normal treatment, it evolves over 10 days, but sometimes new foci appear, and the disease lasts for months.
- Carbuncle. It is a purulent-necrotic conglomerate from the fusion of several boils. Covers a large area, the rods pass through all layers of skin to the muscles. It is difficult, with a change in general condition. The temperature rises, body aches and other signs of intoxication occur.
Atopic infectious dermatitis
Separately, it should be noted such a deviation as atopic dermatitis. It most often appears in a child in the first year of life. Sometimes accompanied by infection. At its core, it is an allergic reaction to certain irritants - food, animal hair, insect bites or chemicals used in everyday life.
Types of dermatitis on the face
Medicine knows several types of dermatitis that affect the skin of the face. They differ in provoking factors, course characteristics and clinical manifestations.
Allergic dermatitis
Most common. Occurs when allergens (certain foods, chemical compounds, dust, pollen, wool) enter the body. In mild form, the disease is accompanied by red spots, rash and swelling.
If the necessary measures are not taken, the condition becomes more complicated: the temperature rises, migraines and rhinitis cause anxiety, and tearing occurs.
Atopic dermatitis
This type of pathology develops if allergic dermatitis is not treated. Red blisters remain permanently on the face and cause severe itching. Any mechanical stress provokes inflammatory processes. As a result, the skin becomes rough and scarred. The disease requires long-term treatment.
Contact dermatitis
This type of pathology is also allergic in nature. A distinctive feature of the disease is exposure to external allergens: washing powder, cosmetics, jewelry, fabrics. A person's skin becomes dry, red, blistered and peeling.
But all these signs appear only on areas of the skin in contact with the allergen. If you start treatment in a timely manner, you will be able to quickly cope with the disease. Otherwise, it transforms into the atopic form.
Photodermatitis
This disease is a type of contact form. Sun rays or creams that protect against ultraviolet exposure serve as an allergen.
Oral dermatitis
Another name is rosacea-like dermatitis, which is due to the similarity of symptoms with rosacea. Spots appear on the skin (usually around the mouth), changing their shade from light pink to deep red with changes in temperature and other external conditions.
In its neglected form, tubercles form at the site of the spots, which are quite difficult to remove. The main causes of the pathology are inappropriate cosmetics, improper functioning of the digestive system, hormonal changes, metabolic disorders, and stress.
Seborrheic dermatitis
For various reasons, disruptions in the activity of the sebaceous glands occur. As a result, they activate their work, which leads to excessive oiliness of the skin and provokes clogging of pores. First, the disease affects the scalp (dandruff appears), after which it spreads to the face. Acne and comedones form, which is accompanied by itching.
There are 2 types of the disease:
- oily dermatitis - the face turns gray, acquires an unhealthy shine, and becomes covered with ulcers;
- dry dermatitis - desquamation is observed - the skin flakes and flakes off in scales.
Symptoms of dermatitis
Hand skin diseases are characterized by the following manifestations:
- The appearance of red-pink (pink) spots at the site of the lesion;
- The occurrence of swelling with a strong or weak degree;
- If treatment is not treated in a timely manner, blisters may appear containing clear (turbid) liquid or serous contents;
- In place of the burst bubbles, erosion zones appear;
- During an allergic reaction, the skin thickens;
- The appearance of cracks, dryness, keratinized areas on the top layer of skin;
- The appearance of abrasions, swelling;
- The skin on the affected areas becomes too sensitive or, conversely, sensitivity disappears;
- Damaged areas of the skin acquire a bluish tint.
Important: the most common dermatitis, transmitted by contact, is absolutely calmly tolerated by the body, without causing the development of pathologies and other complications. This type of disease affects the aesthetic appearance and manifests itself in the form of scars, cicatrices, roughness, increased skin thickness, the appearance of calluses, and age spots.
If you are regularly exposed to irritants or treated incorrectly, complications may occur in the form of death of skin tissue, destruction of tissue in deeper layers, and the spread of infection, viruses, and fungi. Untimely treatment of dermatitis threatens the occurrence of diseases such as eczema and sepsis.
Sepsis
What dermatitis on the hand looks like in its symptoms can be seen in the photo. All inflammatory processes on adult and children's skin are treated with special topical medications.
Treatment of dermatitis on the face
For treatment of facial dermatitis to be successful, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of pathological changes using complex drug therapy, including:
- antihistamines – relieve itching and other manifestations of allergies;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- hormonal drugs;
- antibiotics – destroy pathogenic bacteria;
- antidepressants;
- immunomodulators – strengthen the immune system, increase the body’s defenses;
- sedatives;
- vitamin complexes.
Additionally, the doctor may recommend physiotherapeutic procedures: cryomassage - exposure to cold on the skin and laser therapy.
A prerequisite for recovery is a change in lifestyle. It is necessary to exercise, walk in the fresh air more often, sleep at least 8 hours, avoid stress, and adhere to a hypoallergenic diet.
The basis of the diet should be vegetables and fruits, cereals, fish, and boiled meat. It is recommended to avoid canned food, spicy and spicy foods, pickles, smoked meats, sweets, fast foods, chips, and alcoholic beverages.
Proper skin care is important. To select suitable cleansers, it is recommended to consult a cosmetologist-dermatologist.
Sports activities and walks in the fresh air will have a beneficial effect. They activate blood circulation and oxygen supply to facial cells, which will speed up recovery and also improve the condition of the skin and hair.
In severely advanced cases, you will have to change jobs or move to live in a different climate zone.
Features of therapy
Treatment of infectious dermatitis should always be comprehensive. When prescribing treatment, the doctor will always take into account the disease that caused it, if any. A feature of the therapy will be the use of physical therapy.
Effective physiotherapy:
- UHF;
- ozone therapy;
- Ural Federal District;
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
Also, the treatment should use rashes, which are applied to the affected areas of the skin until the symptoms disappear completely. If the disease is not treated, it can quickly recur.
How to cure atopic infectious dermatitis? Treatment for this form of the disease will be almost the same as for the treatment of simple infectious dermatitis. The use of antiseptic ointments and antibiotics can be an addition to basic general therapy.
Use of medications
Treatment of infectious dermatitis in children and adults must necessarily include the use of medications.
For treatment the following are used:
- antibacterial agents;
- antihistamines;
- anti-inflammatory (Betadine);
- antibiotics (in cases where the disease is caused by bacteria);
- antifungal drugs;
- medications containing corticosteroids.
The doctor will prescribe treatment for each patient based on the symptoms of the disease and the primary ailment.
Many people are aware of the problem of painful pimples near the mouth. This is called perioral dermatitis and is treated with certain medications, read our article.
Did you know that allergic dermatitis in children can be caused by improper nutrition of the mother during pregnancy? This is described in detail in our publication.
Read about how to prepare an ointment for dermatitis at https://psoriazweb.ru/dermatity/maz-ot-allergicheskogo-dermatita.html
Folk remedies for illness
Treatment of infectious dermatitis is also carried out using traditional methods. Folk remedies are used in combination with medications and other treatments prescribed by a doctor. They reduce symptoms, relieve itching and inflammation.
Traditional therapy recipes:
- St. John's wort cream. First, you should prepare a decoction of St. John's wort, then strain it and add 50 grams of butter. Use as a cream on affected areas of the body.
- Potato. This method is used as a compress on inflamed skin. You need to grate raw potatoes, then use the resulting mixture for treatment.
You should be careful when choosing traditional methods for treating dermatitis, so as not to harm your health even more.
You need to visit a doctor and begin treatment for the disease immediately to prevent complications and worsening symptoms.
Treatment of facial dermatitis with ointments and creams
Local treatment of dermatitis on the face using ointments and creams will help eliminate the unpleasant manifestations of the disease. When choosing a drug, the doctor takes into account the type of disease.
In case of an allergic form, antihistamine ointment is usually sufficient. In case of contact type, exposure to the allergen should be excluded and antihistamines should be used. In advanced cases, the disease can be controlled only with the help of creams containing hormones. Glucocorticosteroids will also be needed for atopic dermatitis.
For seborrhea, antimycotic ointments are used to destroy the fungus. Oral dermatitis is treated with ointments containing antihistamines. If the exact cause of the disease is unknown, hormonal drugs are additionally prescribed.
For dermatitis on the face, only glucocorticosteroid ointments belonging to the first class are recommended. They are characterized by low activity and do not irritate sensitive skin. But they should still be abandoned after the acute inflammation has resolved, since with long-term use they cause side effects and addiction.
For daily use, local products that do not contain hormones are recommended. Excellent results can be achieved with drugs from the Losterin line: cream and zinc-naphthalan paste, specially designed for the treatment of dermatitis and other skin pathologies.
They contain active substances in a balanced ratio that have a therapeutic effect on the skin. They relieve inflammation and itching, dry the skin, and have an antiseptic and disinfectant effect.
The Losterin line also contains hygiene products: cream soap, shower gel, shampoo. They gently cleanse the skin, saturate it with moisture, eliminate irritation and itching, disinfect and accelerate regenerative processes.
Degree of contagiousness and mode of transmission
During contact with a patient, a common infectious disease is transmitted, especially if it is caused by a virus. Skin manifestations are not transmitted from person to person. The chances of contracting an infectious disease are minimized if you use a special protective mask, do not eat food from the same plate, do not touch the sick person and do not use shared personal hygiene products.
Infection with the disease depends on the type of pathology and can occur in the following ways:
- through maintaining contact with an infected person (airborne);
- through blood;
- in the absence of maintaining personal hygiene.
If we talk about the danger of infectious dermatitis, then it is not the disease itself that has a detrimental effect on the body, but the presence of infection in the body.
Treatment of dermatitis on the face with folk remedies
Folk remedies will complement the medicinal treatment of dermatitis on the face:
- Tar ointment. Tar (6 grams) is mixed with any cream (tube) and heated to 60⁰C.
- Milk-glycerin ointment. Combine milk and glycerin in equal volumes, add starch from rice to thicken.
- St. John's wort ointment. The grass is poured with double the volume of vegetable oil and left for a week.
- Thyme ointment. Dry leaves are combined with butter.
- Essential applications. Add 4 drops of myrrh and cypress oils to baby cream (20 grams).
- Milk-oil solution. Pour 5 drops of geranium, peppermint and cedar oils into milk (20 milliliters).
- Potato compress. Potatoes are grated or passed through a meat grinder. You can add honey to the potato pulp.
- Wine compress. Crushed plantain leaves (8 pieces) are poured with white wine (100 milliliters) and left to brew for 6 hours.
- Walnut decoction. Tree leaves (5 pieces) are crushed and filled with water (200 milliliters). Place on fire for 6-7 minutes. They insist.
- Decoction of hops, string, nettle. Plant herbs (10 grams each) are poured with boiling water (150 milliliters) and infused for about an hour.
- Dandelion tea. The leaves of the plant are steamed with boiling water in a ratio of 1:5 and left for 5-10 minutes. Used for lotions and as a soothing drink.
The skin is wiped with decoctions of medicinal herbs and oil solutions for a month. Ointments are applied to the skin at night.
Treatment of dermatitis on the face with ointments prepared at home will not get rid of the pathology, but will improve the general condition: it will relieve inflammation, disinfect the skin, and eliminate itching.
What medications are used to treat dermatitis?
For allergic dermatitis, general hyposensitizing therapy is indicated:
- sodium thiosulfate,
- calcium chloride or gluconate intravenously,
- calcium gluconate,
- antihistamines - fenistil, terfenadine, astemizole, fenkarol and others,
- diuretics, especially in the presence of significant edema (furosemide),
- enterosorbents,
- in severe cases - corticosteroids.
As local therapy:
- corticosteroid ointments and aerosols - oxycort, polcortolone,
- shaken mixtures.
The reason for the development of the pathological process
There are a colossal number of irritants that provoke a pathological condition. There are factors of external and internal origin.
Based on this, it is worth focusing on the following categories:
- Biological (any components and substances of natural origin);
- Chemical (the broadest category, including pharmacological preparations, household chemicals, cosmetic and perfumery elements, paints and varnishes and other specific reagents);
- Physical (direct impact on tissue due to increased friction, pressure, exposure to ultraviolet radiation);
- Food (any food product that comes into contact with the skin and enters the body of an allergic person).
It has been proven that allergic reactions can occur against the background of a family history. Various diseases of the digestive tract or systematic disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system also contribute to the development of hypersensitivity.
Contact dermatitis on hands
Often contact dermatitis on the skin is one of the complications of hormonal imbalance and nervous strain. This often occurs in adolescents and children of primary school age, as well as in people with weakened “problematic” immunity.