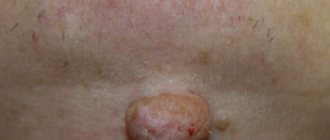
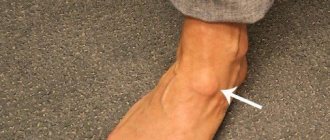
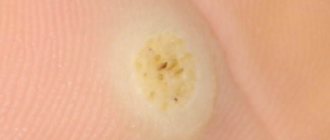
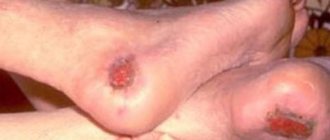
Fibroma is a benign formation on the skin that does not spread from its place of origin. It can form on any organ or soft tissue. The species has a large base on a stalk. Usually not bothered by symptoms. It can be located on the leg, neck, arm, feet, hands, etc.
Fibroids can appear in different places on the leg:
- On the knee joint;
- On the foot;
- Shin;
- In the groin area;
- On the toes.
Fibroma on a child’s leg
In children, this disease can be either congenital or acquired. Its manifestation is significantly lower in minors than in adults. It may appear with age; the older the child, the greater the likelihood of getting sick. Basically, fibroma is the same in adults and in children, since the occurrence, treatment, and localization are identical.
Causes of fibroids on the leg
Although this benign neoplasm has been studied for a long time, modern medicine is not yet able to give a clear answer about the causes of its occurrence. The manifestation of pathology is explained by the following factors:
- genetic predisposition. If someone in the family has fibroma, then there is a high probability that the tumor will appear in other relatives;
- age. Age-related changes in the human body are associated with deterioration of blood circulation. At the same time, as we age, wounds heal more slowly and the skin is restored. Abnormal scarring is one of the factors that provoke benign tumors;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin;
- hormonal changes in the body due to pregnancy, menopause, etc.;
- inflammatory processes.
A neoplasm that occurs in the subcutaneous layer of the lower extremities is typical for people who constantly experience physical activity or spend a lot of time on their feet. The same phenomenon is not uncommon for professional athletes.
Hypersensitivity of the skin is considered another reason for the formation of a benign tumor. If fibroma of the soft tissues of the thigh can be caused by tight clothing, then a plantar tumor becomes a consequence of wearing uncomfortable shoes.
Home Remedies
Home remedies for plantar focal fibroids aim to relieve pain and discomfort. These include:
ice
Applying an ice pack to your leg can reduce pain and swelling. To make a cold pack, wrap ice cubes in a thin cloth and place on the arch of your foot for 15 minutes. Repeat treatment several times daily or as needed.
height
Elevating the affected leg above the level of the heart can reduce inflammation and swelling. This can be achieved by lying down and propping up your legs on pillows whenever possible.
Over-the-counter pain relief
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are another option for people with leg pain. These drugs include:
- ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- acetaminophen (tylenol)
- naproxen sodium (Aleve)
NSAIDs should not be taken for long periods of time as overuse can cause serious side effects.
Classification of tumors
A benign connective tissue tumor is classified according to a number of characteristics. This takes into account the type, location, localization, speed of development, etc.
In the legs, tumors can affect various tissues. On this basis, fibroma is divided into:
- Skin. It can be hard and soft. The hard one is represented by a compaction or growth with a wide base. The color is practically no different from the surrounding skin or has a pinkish tint. Most often observed on the surface of the foot, lower leg, and toe. A soft fibroma is similar to a wrinkled sac, connected to the skin by a thin stalk. The formation often results from scarring of the skin after surgery;
- Chondromyxoid. Formed by cartilage tissue. It is observed quite rarely. It is localized in the joints of the legs and signals itself with pain during movements and loads. It is characterized by relapses and is dangerous due to the risk of taking on a malignant form. This type of fibroma is most common in the knee joints;
- Non-ossifying. It is located on the bones, and more often affects damaged areas, resulting in fractures and cracks. More common in children and adolescents. Often causes thinning of the bone and leads to its weakening.
Types of formations in the lower leg area
Type of dermatofibroma
Dermofibroma has the appearance of a small mobile nodule, loosely fused to the surrounding tissues. The formation does not grow into the surrounding tissues and is often separated from them by a capsule. The typical localization of dermofibroma is the deep layers of the dermis of the lower extremities and hands.
Based on the predominance of certain cells, it is customary to distinguish:
- fibrous type with an abundance of mature unidirectional and multidirectional collagen fibers and mature fibrocytes;
- the cell type is characterized by a predominance of loose, immature collagen tissue; nests of histiocytes and fibroblasts can be found;
- fibroxanthoma is characterized by a predominance of Touton cells;
- with a large number of vessels of different sizes, we can talk about sclerosing dermatofibroma.
Fibrolipoma is softer in consistency due to inclusions of fat cells. On a section, this neoplasm has a segmental structure and is always enclosed in a capsule, which does not allow it to grow into the surrounding tissues.
Based on their histological structure, there are two types of fibrolipomas:
- soft, with a predominance of fibrous connective tissue;
- hard, with a high percentage of collagen fibers.
These formations are absolutely painless and not prone to inflammation or malignancy, but to eliminate the risk of oncological degeneration, a thorough examination should be carried out.
Separately, it is worth noting non-ossified fibroma of the tibia and other bones. It often develops in patients with existing neurofibromatosis. This formation is localized in the cortical layer of the periosteum or medullary space. Since it does not cause discomfort or pain, this formation is usually discovered by chance during an x-ray examination. Hygroma of the ankle is also difficult to treat.
Non-osteogenic fibroma of the tibia is a pathological condition in which new tissue is not formed, but the cortical layer of the bone is resorbed, replacing the tissue with fibrous tissue.
The disease is dangerous because it is completely asymptomatic and can lead to a pathological fracture.
Symptoms of fibroids
Each type of fibroma has its own symptoms.
The first stages of the development of hard fibromas on the legs are practically asymptomatic. A dense, inactive formation that appears deep in the muscle tissue becomes noticeable as it grows, when it begins to rise slightly above the healthy skin. To the touch, a hard fibroma resembles a dense, homogeneous body, which can reach 1 or more centimeters in size.
As fibrous tissue grows, it puts pressure on the surrounding vessels and disrupts blood circulation. The skin raised above the fibroma becomes smooth, and the boundaries of the formation are marked by abrasions. When hyperkeratosis occurs, the skin in the area of pathology becomes glossy and acquires a reddish or bluish tint.
In appearance, the soft type of fibroma is significantly different from the hard one.
A benign tumor is represented by a wrinkled node that has a stalk and resembles a mushroom. The tumor has a heterogeneous structure and, as a rule, is located in the upper layers of the skin. Typically, a soft fibroma reaches about 3 centimeters in diameter and up to 2 centimeters in length.
However, medical practice mentions formations of much larger sizes. Unlike the solid type, this tumor is painless. However, being on the leg and on top of the skin, it is constantly at risk of injury. The formation differs little from the surrounding skin in color. Soft fibroids of the legs are common in older people, especially if they are overweight.
Description of the disease
Fibromatosis of the foot is usually understood as benign growths localized in various parts of the body. The tumor can develop on the surface of the skin and deep in the muscle tissue. Fibrous tumors are most often diagnosed in adults, and in rare cases they are observed in children and adolescents.
Experts distinguish two types of fibroids:
- Benign ones consist of fibrous tissue; cells, due to various factors, have switched to an uncontrolled and disorderly process of division.
- Malignant ones are extremely rare; they consist of cancer cells that kill healthy tissue, replacing them with various pathological formations.
It has been established that in 99% of cases benign fibroids are diagnosed , which, subject to timely examination and proper treatment, do not pose any threat to human life. However, when such tumors appear, it is necessary to perform appropriate diagnostics, including a tumor biopsy, which will exclude cancer and other dangerous diseases.
Therefore, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor for an examination and prescription of quality treatment.
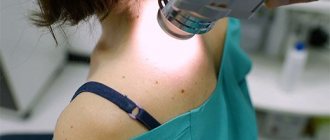
Diagnostic methods
Numerous photos of fibroids on the leg under the skin give only a superficial idea of the tumor. Without a professional approach, based on them, it is impossible to accurately determine either the nature of education or its type. Only complete histological studies allow us to assert that the tumor does not threaten a malignant form. Thus, fibroma is diagnosed using a biopsy (cutting off part of the affected tissue and studying it in the laboratory).
Features of treatment
In each specific case, the methods of treatment and removal of the tumor are chosen by the surgeon based on the patient’s clinical picture and the diagnostics performed. If the fibroma belongs to the category of limited and benign, and its size is 1-2 centimeters, then surgery or any active therapy is not required in such a case.
However, if the tumor interferes with walking, often rubs and bleeds, and constantly increases in size, then it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor to prescribe appropriate treatment.
Conservative treatment of fibroma of the left finger is possible in cases where the tumor does not increase in size. Therapy consists of introducing special drugs into the tumor, including injection of diprospan. Such treatment will be effective only for small tumors that do not tend to increase in size. If the injections do not produce any results, removal of the tumor is prescribed.
Operative methods
Most often, when a fibroma is detected, surgical treatment is prescribed, which will allow the neoplasm and affected adjacent tissues to be removed using special equipment or surgically. In each specific case, the doctor chooses therapy depending on the characteristics of the existing tumors.
During surgical removal, the operation is performed under local anesthesia, and only large and numerous formations will require the use of general anesthesia. The doctor makes an incision in the skin, excising the affected tissue. If it is necessary to remove a small soft fibroma, the pedicle is trimmed with a scalpel, cutting out the tumor with its base, after which sutures and a tightening bandage are applied.
Laser therapy is popular , when using special equipment without injection anesthesia, the affected area is excised, which eliminates pain and the formation of scars with redness at the site of the removed tumor. Injured tissues are additionally cauterized under the influence of the laser, which accelerates their healing, so the patient’s recovery after such an operation takes only a few days.
If there are contraindications for treating fibroma with a laser or removing it using the classical surgical method, the radio wave method can be used, which effectively solves the problems of soft tumors. By exposure to completely safe waves, tumor cells are separated from healthy tissue, while avoiding injury to ligaments, tendons and muscles located near the tumor. This technology is bloodless and painless, and the patient’s recovery takes no more than a week.
Also popular is the method of removing shin fibroids using electrocoagulation , which involves exposing existing tumors to electric current at a certain frequency. This technology is completely painless, the whole procedure takes only a few minutes, allowing you to remove fibroma-affected cells. Coagulation can be used to eliminate tumors with a diameter of no more than 2 centimeters.
In rare cases, patients experience self-healing, which is typical for thin-pedunculated fibroids. Such tumors appear when there is a metabolic disorder, and when the body is restored, the tumors gradually die off and soon completely resolve. However, patients should not hope for self-healing, and if such small fibroids are detected, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and quality treatment.
Prevention
For leg fibroids, as a pathology that occurs without specific causes, there is no specific prevention. According to doctors, to reduce the risk of tumor formation, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and give up bad habits. A daily routine that allows you to balance physical activity and rest is important.
Regular medical examinations will help prevent the disease and avoid unpleasant treatment procedures.