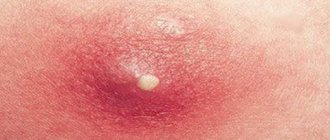
Antibiotics for the effective treatment of furunculosis
With proper treatment, you can get rid of a boil in 10-15 days.
The most effective method of getting rid of boils is taking medications that belong to the group of antibiotics. For therapy, a dermatologist can prescribe medications from the following subgroups:
Penicillins are effective antibiotics whose action is aimed at destroying gram-positive bacteria. Among the products in this category, the most popular are Bicillin, Ampiox, Ampicillin, Amoxicillin. Cephalosporins are antibiotics used to prevent the spread of infection and its further penetration into the deeper layers of tissue. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Cefuroxime, Cefazolin, and Cefipime. Macrolides - differ from the first two subgroups. They are recommended to be taken when, when a boil ripens, a person experiences a febrile state or high temperature. These drugs can stop the inflammatory process in a short time and do not harm the intestinal microflora
Antibiotics of this group should be used with caution in patients suffering from renal or hepatic dysfunction. The reason is the ability of drugs to accumulate in the body.
Among the macrolides, the most common are Macropen, Erythromycin, Azithromycin and Sumamed.
An antibiotic for the treatment of furunculosis should only be chosen by a dermatologist. Complex therapy includes the use of medicinal ointments, injections and oral administration of tablets.
Stages of treatment of boils
Purulent formations are treated in several stages under the supervision of a doctor.
After the abscess has matured, it should be opened surgically. Under no circumstances should the boil be squeezed out with your fingers. There is a huge risk of introducing another infection into the wound and causing complications. The surgeon injects the site of inflammation with an antibiotic solution with novocaine. Anesthesia relieves pain and stops the development of the purulent process.
Often people turn to doctors with the boil stage when an abscess has already begun and inflammation has led to the destruction of adjacent tissues. In this case, the surgeon will open the abscess and completely clean out the pus. Treat the open wound with antibacterial ointment and apply a sterile bandage.
If there are a large number of recurrent ulcers on the head and neck, the doctor prescribes tablet antibiotics: Lincomycin, Cephalexin, Amoxiclav, Fuzidin sodium.
Use of antimicrobial ointments
Antibacterial ointments are used during the period when the abscess is opened. The bandage is soaked in ointment and applied to the open wound.
Among ointment preparations, Levomekol, Fucidin, Bactroban, Baneocin are often prescribed. Tetracycline ointment has a wide spectrum of action, which is used not only for the treatment of boils.
Immunomodulators for furunculosis
Boils occur as a result of a bacterial attack on an immune-compromised body. Therefore, taking immunostimulating agents is part of the comprehensive treatment of furunculosis. The action of the drugs is aimed at increasing the protective functions of the body. In such cases, the doctor may prescribe Immunoglobulin, Polyoxidonium or Galavit.
Vitamin complexes
Taking vitamins will also help increase the body's strength necessary to fight the disease. Vitamin therapy includes retinol acetate, thiamine, riboflavin, ascorbic acid and many others.
Physiotherapy
For furunculosis, dermatologists often recommend physiotherapeutic procedures to patients. The most effective are UHF therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis using antimicrobial agents, baths with the addition of potassium permanganate, ozone therapy and others.
What is furunculosis
Furunculosis is a purulent-inflammatory disease that spreads to hair follicles located in different anatomical areas of the human body. The pathology is diagnosed quite often among the modern population and accounts for about 17% of all cases of skin diseases.
Furuncle
At first, the boil looks like a small elevation, accompanied by pain and itching. Over the course of 2–3 days, pus accumulates in it, which comes out and leaves an ulcer at the site of the lesion. Staphylococcus aureus causes a similar process.
Staphylococcus aureus is an opportunistic bacteria, that is, it lives on the skin constantly and leads to the development of the disease only under the influence of certain negative factors.
Boils are divided into the following types:
- A furuncle is a single abscess on the skin;
- A carbuncle is an extensive skin abscess affecting several hair follicles at the same time. With this process, a fusion of several boils occurs. Pus comes to the surface in many places.
- Cystic acne - the process of inflammation occurs in the deep layers of tissue.
- Pilonidal sinus is an abscess that occurs in the intergluteal area due to infection in the hair follicles.
- Hidradenitis suppurativa is multiple skin abscesses that occur when the sweat glands become inflamed and are localized in the armpits and groin. Treatment is carried out surgically.
Furunculosis is a purulent-inflammatory disease that spreads to the hair follicles
The following conditions can provoke the development of furunculosis:
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- diabetes;
- bad habits;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- excessive fatigue;
- lack of vitamins;
- hypothermia of the body;
- mechanical injuries;
- anemia.
Based on the type of disease, the following are distinguished:
- Acute furunculosis - on the skin there are simultaneously many boils of the same stage of resolution.
- Chronic - sequential appearance of purulent formations (some disappear, while others appear). Lasts for a very long time.
Depending on the prevalence of boils, there are the following types of disease:
- disseminated (widespread) furunculosis - purulent formations are found throughout the body;
- localized (limited) - all boils are concentrated only on a separate area of the skin.
If any changes appear on the skin, you should immediately seek medical help. This will help to correctly diagnose the disease and prevent possible complications.
Why is a boil dangerous? (video)
Antibiotics for boils on the face
A feature of boils on the face is the need to use antibiotics not only locally in the form of ointments, but also systemically. This is due to the close proximity of the brain and large vessels.
Ciprolet is the same as Ciprofloxacin, a subgroup of fluoroquinolone. One of its advantages is the slow development of microbial resistance to its administration. It is quickly and well absorbed and penetrates into tissues. Easily tolerated. Not for pregnant women, lactating women, children and adolescents.
In adults, the dose is 1 gram per day in 2 divided doses
We must remember that taking Tsiprolet disrupts concentration, so you must be careful when driving a car.
Sumamed is easy to use. The package contains 3 tablets, which must be taken over 3 days, one per day.
Doxycycline is a semisynthetic antibiotic from the tetracycline subgroup. Broad spectrum of action, blocks protein synthesis in microbial cells. Contraindicated in children under 8 years of age, pregnant women from the 2nd trimester, breastfeeding women and those with severe liver diseases. Oral and parenteral administration.
Principles of taking medications
Prescription of medications is carried out exclusively by the attending dermatologist. The main contraindications to the use of antibacterial therapy are:
- periods of gestation and feeding;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- individual allergic reaction to antibiotics;
- impaired liver function.
Medicines based on ointments are considered safer - they have a minimal number of side effects, there is no systemic effect and their use does not require specific preparation.
Tablet forms of medications can cause negative consequences that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Local forms of medications are not used for the formation of boils on the face - accidental softening of the necrotic core and further spread of purulent bacteria are possible.
After taking the pills, it is necessary to restore the internal microflora of the body using eubiotics. When using several drugs, an analysis must be carried out to determine the compatibility and perception of these substances by the body.
Basic rules for taking medications:
- Taking medications without any gaps in time - the active substance of any antibiotic must accumulate in the blood and have a certain concentration.
- It is not recommended to drink any alcohol-containing drinks - alcohol destroys pharmacological drugs.
- It is forbidden to change the recommended dosage or the medicine itself.
- If an allergic reaction occurs, you should stop taking the medication and consult your doctor.
- The use of probiotics during periods of taking pharmacological agents is prohibited - they are used after antibiotic therapy.
Any deviations from the proposed treatment regimen will lead to ineffective therapy and may cause complications of furunculosis. Antibiotics and alcohol are incompatible - if you drink alcohol once, you will have to repeat the entire course of treatment.
Causes
The causative agents of furunculosis are microbes that penetrate the sebaceous glands and hair follicles and provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
Some microorganisms are natural inhabitants of the skin
The main factors that can cause boils include:
- weakened immune system;
- HIV infection;
- lack of vitamins;
- psychoemotional disorders;
- chronic intoxication.
- mechanical damage to the skin as a result of shaving, wearing compressive clothing;
- hormonal disorders;
- restructuring of the hormonal system during puberty or menopause.
“Local” in ointments
The active components of ointments, for the most part, do not completely enter the bloodstream. Some can treat boils in children and pregnant women. The composition of creams and gels includes substances that draw out pus, accelerate wound scarring and reduce pain.
Levomekol
In addition to the main substance - chloramphenicol, the product contains methyluracil. The auxiliary component has an immunostimulating effect and accelerates the regeneration of affected tissues.
Levomekol is prescribed to combat the existing pathogenic microflora in the abscess and to prevent infection of the wound by bacteria. The cost of the ointment is about 150 rubles for a 40 g tube. Prohibited in case of individual sensitivity to the components of the drug.
Levosin
A product based on chloramphenicol, in addition to which it also contains sulfadimethoxine, methyluracil and trimecaine. Excipients are starch and calcium stearate. They dry the wound and reduce the amount of purulent discharge, which speeds up the cleansing and healing of the opened boil.
Levosin costs about 70 rubles per 40 g and is prohibited for systemic skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis, fungal infection). Not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women, as well as children under 2 years of age.
Bactroban
The basis of the ointment is mupirocin. This is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, most effective when used externally. Often prescribed by dermatologists for large-scale furunculosis.
After absorption into the blood, it is quickly converted into inactive monic acid. It has no effect on the body and is excreted in the urine. Costs 500 rubles for 15 g regular or 3 g nasal. Not prescribed to patients with severe renal failure.
You can find a list of the best ointments for boils in this article.
"Amoxicillin"
Antibiotic from the penicillin group for furunculosis in tablets for adults and children. Available in the form of granules, capsules and tablets of 250-500 mg. Quickly eliminates infection during furunculosis, stops the growth of purulent abscesses. The effect of the drug is 12 hours, does not have a harmful effect on the mucous membranes of the digestive system. For furunculosis, the drug is administered intravenously by drip or stream.
Dosage regimen:
- 2-5 years – 125 mg 3 times a day;
- 5-10 years – 250 mg three times a day;
- over 10 years old - 250-500 mg at a time, 3 times a day (the dosage can be increased to 1000 mg).
The duration of treatment is 7-14 days. Side effects include dysbiosis, tachycardia, diarrhea, nausea and headaches. Contraindications: pregnancy, breastfeeding, renal failure. If prescribed to children under 18 years of age, the drug should not be taken together with metronidazole. The cost of Amoxicillin is 50-140 rubles.
"Erythromycin"
Included in the group of macrolides. Available in the form of tablets, ointments, bottles of powder (for injection). Suitable for any age category. Advantages – minimal risk of side effects.
In newborns it can cause pylorospasm, dyspeptic disorders, and sometimes provokes allergic reactions. For furunculosis, it is prescribed to fight infection in soft tissues and skin.
Dosage regimen:
- Adults are prescribed 200-400 mg, up to 4 times a day, with an interval of 6 hours. If necessary, the dosage can be increased to 4 mg. The drug is taken one hour before meals or 2 hours after it.
- Children are prescribed 30-40 mg/kg per day. The dosage is divided into 2-4 doses.
The duration of treatment is 7-10 days. Side effects - diarrhea, rash, headaches. The drug is contraindicated during lactation, pregnant women, people with liver and kidney failure. The cost of “Erythromycin” is 50-120 rubles. depending on the release form and dosage.
"Azithromycin"
Included in the group of macrolides. Another name for the drug is “Sumamed”. Available in the form of tablets, capsules, syrup and powder for suspension. It is not administered intramuscularly or into veins. A broad-spectrum drug. Suppresses protein synthesis, slows down the proliferation of bacteria, and acts intracellularly on infectious agents.
Dosage regimen:
- Antibiotics for furunculosis in tablets for adults are prescribed one tablet (500 mg) per day (can be before or after meals).
- Elderly people and children over 12 years of age (weighing more than 45 kg) for the first 3 days – two capsules of 250 mg once a day. Then - twice a week, 250 mg.
Duration of treatment – 9 days. Side effects include allergic manifestations, gastrointestinal disorders, arrhythmia, tachycardia. You may experience dizziness and tinnitus. Not recommended for kidney and liver diseases, during lactation, up to 12 years. Take with caution when taking ari - 50-300 rubles. depending on the release form and dosage.
Tablets for boils
As mentioned above, antibiotics are an effective cure for boils. These drugs make up a huge group of drugs, which are divided into small groups depending on their effect on the bacterium and the effect on a specific type of pathogen.
Since staphylococcus is a common causative agent of boils, therapy is carried out against the background of groups of antibiotics that act specifically on this pathogen. Therefore, you need to know exactly which pills to take.
Photo 45 - A boil appears due to staphylococcus
You can give several examples of names and antibiotic treatment regimens for boils. Depending on which tablets you take and how you should treat furunculosis using a conservative method using antibiotics:
- cephalexin tablets 4 times a day;
- amoxicillin: tablet 3 times a day (10 days);
- Macrolides are prescribed if you are allergic to penicillins:
- erythromycin - ethyl succinate: 3 times a day orally (10 days);
- Clarithromycin: orally 2 times a day (10 days);
- azithromycin: 1 time per day (5-7 days);
- clindamycin: orally 4 times a day (10 days).
Many people who are faced with this question are interested in whether it is possible to take diclofenac tablets as an anti-inflammatory drug. Yes, they are used, including for purulent skin diseases.
Photo 46 - Diclofenac
Injections for boils are used quite rarely, since the result of treatment is expected to be better. Doctors use vancomycin intravenously, but due to the large number of side effects, it is used only in rare cases.
Photo 47 - Injections are rarely used
They also use ointments that have antiseptic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effects:
- Antiseptic ointments. At the initial stages of boil development, antiseptic ointments are used, as they have the effect of “pulling out” pus. These include ichthyol and heparin ointments. Ichthyol ointment is quite cheap and works great on affected skin. Heparin ointment, in addition to its antiseptic effect, has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect due to its specific composition.
- Antibacterial ointments. These include levomekol, tetracycline ointment. They also have an anti-inflammatory effect, help remove pus from the lesion and cleanse the skin lesions from bacteria.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments. Vishnevsky ointment and zinc ointment have a purely anti-inflammatory effect. These ointments relieve swelling and hyperemia, and also double wound healing.
Brewer's yeast for boils
In addition to the official treatment of such ulcers, there are also folk methods. The most common of them is the use of brewer's yeast. There is a lot of controversy about them: “Does brewer’s yeast help with boils?”
Photo 53 - Brewer's yeast
To understand this, you first need to understand what common causes lead to the formation of boils. There are two of them: metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus) and decreased immunity.
Photo 54 - Brewer's yeast cleanses the skinBrewer's yeast perfectly improves metabolism and cleanses the skin. They consist of protein complexes that are necessary for our body. Yeast contains vitamins: B, E, PP, H, nucleic acids, which compensate for the lack of various microelements in the body.
Photo 55 - Brewer's yeast consists of protein complexes
Most often, brewer's yeast is used together with the main therapy (antibiotics). How to drink them? Brewer's yeast is used twice a day, half an hour before meals. With water or milk. Adults can drink one tablespoon, children a teaspoon. Brewer's yeast is safe for children and has no side effects.
Photo 56 - Brewer's yeast is taken with antibiotics
Due to the fact that yeast contains a huge amount of nucleic acids, it is not advisable for people with old age or kidney disease to consume it.
Photo 57 - Do not consume brewer's yeast if you have kidney disease
In conclusion, let us recall that a boil is an infectious disease that most often occurs due to poor hygiene, with a certain skin structure (usually with oily skin type).
Photo 58 - A boil may be due to increased oily skin
Recommendations
The main rule of taking antibiotics is the presence of a confirmed bacterial infection. Viruses and fungi are not treated with these drugs.
Until a specific infectious agent has been identified, medications with a broad spectrum of action are prescribed.
The culprit of the disease can be determined by examining the purulent contents of the boil. In this way, an antibiotic is selected that best affects this type of bacteria.
You should follow the basic rules for taking antibiotics:
- strictly adhere to the dosage prescribed by the doctor;
- take medications at regular intervals: if once a day, then exactly 24 hours after the previous dose, if twice, then after 12 hours, three times, then every 8 hours, and so on. This is important to maintain the required concentration of the drug, otherwise its effect will not be effective enough;
- if the patient uses other medications during antibiotic treatment, he must inform the doctor about this;
- Tablets and capsules should be taken with plenty of plain water (not carbonated). Other drinks are not advisable, and a combination, for example, of grapefruit juice with some antibiotics is dangerous to health;
- It is prohibited to drink alcohol during antibiotic therapy. Even a single dose of alcohol will negate all previous treatment;
- if allergic manifestations on the skin occur during the appointment, you should urgently notify the doctor, who will decide on the further treatment regimen;
- antibiotics are used only for the treatment of furunculosis, they should not be used as a prophylactic agent;
- After a course of antibiotics, care must be taken to restore the intestinal microflora. For this purpose, probiotics consisting of beneficial bacteria are prescribed.
Indications for antibiotics
It is recommended to take drugs orally for extensive furunculosis. In the first stages, it is possible to cope with the disease using means for external use. The treatment regimen varies depending on the location of the inflammation. If the rash covers the armpits and face, a preliminary opening of the boils is performed. This is necessary to prevent purulent contents from entering the lymph nodes.
Antibacterial treatment is advisable in the following cases:
- the presence of concomitant pathologies in which it is impossible to cope with the disease without antibacterial therapy;
- high risk of developing abscesses;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- chronic course of the disease;
- massive spread of rashes.
Antibiotic therapy has disadvantages. The medicine is selected individually, taking into account the sensitivity of the flora and the reactions of the patient’s body. If boils cover the entire body, then shock therapy is required. In this case, external preparations are not enough. The patient is forced not only to take antibiotics, but also to receive the drug by injection.
The generalization of the pathological process is facilitated by improper treatment of furunculosis - squeezing out abscesses leads to infection of nearby tissues. The causative agent of the disease is not always staphylococcus. In the case of progressive furunculosis, a mixed flora is detected. Only after culture has been carried out does the doctor decide on the advisability of using a particular antibiotic.
Types and methods of treatment
The main condition for a quick recovery from furunculosis is strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene. This will prevent the infection from spreading throughout the body and reduce the risk of reinfection. But it is necessary to take into account that during the acute stage of the disease, water procedures should be limited and excessive contact with water on infected areas of the body should be avoided. Antifurunculosis therapy includes:
- treatment of infected tissues with antiseptics (anti-rot agents);
- dry heat;
- electrophoresis, ultraviolet and UHF irradiation of affected areas;
- the use of hypertonic solutions and ointments to remove pus and dead tissue from opened inflammations;
- diet;
- taking antibiotics for boils and boils.
In rare cases, in acute cases of the disease, an alternative treatment method is used - autohemotherapy, which consists of subcutaneously injecting the patient with his own venous blood. In severe cases of the disease, immediate surgery is required to avoid blood poisoning.
Use of antibiotics
Treatment of pathology is carried out after clinical diagnosis and confirmation of the presence of staphylococcal infection in the patient’s body. The results of blood, urine and skin scraping tests will allow the specialist to prescribe an antibiotic for furunculosis, which will definitely help stop and localize the spreading infection. For pustules and boils, it is customary to use the following types of antibacterial agents:
- macrolides:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- aminoglycosides;
- tetracyclines.
Macrolide drugs
Macrolides are the safest antimicrobial agents. Their principle of action is based on the destruction of microorganism proteins.
Azithromycin is a semi-synthetic antimicrobial and fungal medicine, which is a representative of the azolide subclass. It is created on the basis of the active substance of the same name. Prescribed for the treatment of external and subcutaneous suppurations. This antibiotic for furunculosis in tablets is recommended to be taken for three days in a daily dose not exceeding 3 g. Due to rapid absorption from the digestive tract and a minimal number of contraindications, the drug can be prescribed to children and pregnant women.
Macropen is an effective antibiotic for the treatment of furunculosis. The basis of the medicine is the active substance midecamycin. Available in tablets. Has a wide spectrum of bacteriostatic action. Reaches maximum concentration in the blood two hours after administration. Macropen is prescribed for the prevention and treatment of all types of pustules and boils.
Sumamed is an analogue of azithromycin, but it additionally contains active lincosamides and streptogramins. The drug is produced in powder form, due to which it is better and faster absorbed by the body. Used as an antibiotic for boils in the groin.
Penicillin drugs
Amoxiclav is a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Both components are highly soluble in water, so the drug is available in the form of a suspension. Used for skin infections, abscesses and suppurations. It is not recommended to drink it if you have hypersensitivity to penicillins, liver or kidney dysfunction.
Ampicillin is a broad-spectrum beta-lactam drug that can fight many strains of skin disease viruses. It has antiseptic properties and does not accumulate in the body, which makes it possible to use it for a long time.
Ampiox is an antibacterial agent based on oxacillin sodium salt. The medicine has proven itself in the prevention and treatment of purulent postoperative complications and skin diseases.
Cephalosporins and aminoglycosides
Cefazolin is a first-generation bactericidal agent that has a detrimental effect on gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Available in powder form, from which a solution for injections is prepared. It is introduced into the body intramuscularly or intravenously. Actively localizes foci of infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Ceftriaxone is a third-generation cephalosporin drug for systemic use. It has good resistance to viruses and fungi. The drug has proven itself in the treatment of sepsis and other infections associated with weakened immunity.
Monomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that is effective against acid-fast bacteria. Indications for its use are purulent abscesses, acne, pustules, furunculosis in the initial stages.
Tetracycline drugs
Doxycycline is a semisynthetic tetracycline antibiotic prescribed for infectious pathologies of the upper layers of the skin caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Used during the postoperative recovery period.
Tetracycline is a bacterial and antiseptic medicine that, when applied to the skin, is practically not absorbed into the blood. It has a wide range of action against microorganisms that can cause inflammatory processes on the skin. Tetracycline hydrochloride is not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age.
Antibacterial drugs for children
The drug of choice for the treatment of various infectious diseases of the skin of a child is sumamed, an antibiotic that is effective against furunculosis and belongs to the family of penicillins. In most cases, it is well tolerated, the expected effect begins to appear on the second day of therapy, and the full course of treatment lasts no more than 5-7 days. The drug can be freely purchased at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription; it is very convenient in a variety of pharmaceutical forms.
For children, powder is used to prepare a thick suspension with a sweetish taste, which makes it easier to take the drug. For convenient dosing, a special plastic syringe or cap with marks is provided. The dosage is determined in accordance with the child’s body weight and the severity of the lesions. If necessary, the doctor selects antibacterial drugs from other groups, also in the form of suspensions.
For mild cases of the disease, folk remedies in combination with pharmaceutical ointments are effective - for example, viburnum or aloe are excellent against inflammation, as lotions and compresses.
Very often you can hear complaints from patients: “I took the antibiotic prescribed by the doctor and it didn’t help me, but it only got worse, which means it’s better to be treated with folk remedies and not trust the doctors.” This is a fundamentally erroneous opinion. Antibacterial drugs are ineffective only if the patient does not adhere to the established treatment regimen and dosage or has an individual intolerance to the drug. You should not treat furunculosis yourself - this can lead to fatal consequences.
Antibiotics
When boils appear, regardless of the cause that led to such a disease, the main task will be assigned to antibacterial therapy, which will inhibit the growth of pathogenic microbes. Before you begin treatment, you need to take into account that at a certain stage of development, a boil is an accumulation of pus in the sebaceous glands. It can be localized in the groin area, on the face, under the armpit.
Antibiotics will help stop the inflammatory process
The main condition when treating a boil is to ensure the outflow of pus. Otherwise, the medicine will not be able to reach the source of infection and have a therapeutic effect. The general condition of the patient may improve after taking antibiotics, but the source of the microbes itself will not be neutralized. Before taking medications, you should definitely go for an examination with a surgeon to find out whether surgical intervention is necessary.
If there are no indications for it, you can begin antibacterial therapy. In most cases, the causative agent of this disease is Staphylococcus aureus, so it is advisable to take only those medications that will be active against this microbe.
Antibiotics for boils, which are presented in the form of tablets, include ampicillin and amoxicillin. These medications are considered one of the most effective against staphylococcus.
Recommended effective drugs
These drugs are presented on the pharmaceutical market under the following names: “Flemoxinsolutab”, “Ospamox”, “Upsamox”, “Pentrexil”.
To enhance the therapeutic effect of amoxicillin, it can be combined with clavulanic acid. Working in pairs, these substances fight the infectious agent in a short time. Such medications include: “Amoxiclav”, “Augmentin”, “Moxiclav”, “Ranklav”, etc.
A less pronounced effect in the treatment of furunculosis is observed with cephalosporins. Among them we can highlight: “Cefalexin”, “Duracef”, “Ospexin”, “Cefaclor”. Their use is appropriate only when the above medications are prohibited due to contraindications.
Both ampicillin with amoxicillin and cephalosporins are slightly toxic, however, they can cause a severe allergic reaction, so people who suffer from allergies will have to choose another drug.
Antibiotics that have a slower effect but do not cause allergies include lincomycin and clindamycin. They penetrate the skin perfectly and help treat furunculosis well. As for side effects, diarrhea may appear after taking them.
In pharmacies they can be presented under the following names - “Lincocin”, “Medoglycin”, “Dalacin”, “Klimitsin”.
Macrolides are a group of drugs that has a dozen representatives. Among them: clarithromycin, josamycin, erythromycin and others. The good thing about medications is that there are no side effects after taking them, but they act much more slowly than amoxicillin. For furunculosis, the following have proven themselves best: Azithromycin, Sumamed, Klacid, Macropen, Rulid, Vilprafen, Rovamycin. In addition to taking medications, you will need to strengthen your immune system and be meticulous about skin hygiene.
Results and answers to questions
Multiple boils can be cured with antibiotics, but the process takes a long period of time. Children can be given medications only according to the regimen prescribed by the pediatrician. Self-prescription of medications is unacceptable.
If the specialist prescribed a regimen that caused an allergic reaction in the child, then it is necessary to change the course of administration. You can seek advice again and clarify that the medicine is causing side effects.
- Do you have to take all the pills prescribed by your doctor? Take your medications before your scheduled appointment time—the boil will not go away if you interrupt the treatment.
- What is the best antibiotic? The one that the doctor recommended to use. Do not forget to take vitamins along with the antibiotics you take.
- I take medication, but the boils get bigger. If the abscess increases significantly, a visit to a dermatologist is mandatory.
If antibacterial therapy does not help in the fight against the disease, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital setting for further treatment.
How to treat boils with external medications
Antibiotics are selected for the treatment of boils depending on the location and severity of the purulent-necrotic process. For small single lesions on the body, the doctor may choose topical antimicrobial drugs and recommend concomitant restorative therapy.
External antibiotics for treating the affected skin area include ointments, gels, creams, suspensions, and mash.
These drugs differ not always in the active substance, but also in consistency and percentage of fat content. Some dosage forms penetrate quickly into the layers of the skin and dry out. Others, on the contrary, moisturize the surface of the body for a long time, saturating the epidermis with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial components.
For small boils on the face, antibiotics are recommended, which are gentle on delicate skin. You can use Levomekol gel, which is based on the antibiotic chloramphenicol. The composition contains methyluracil, which helps accelerate skin regeneration. The gel base allows for quick absorption and does not leave any spots or shine on the face. Zenerit cream has a light consistency and is used for minor ulcers and pimples on the face. Zinerit contains the antibiotic erythromycin, which affects many bacteria, including staphylococcus. For deep purulent lesions on the body, ointment-based antibiotics are used. For example, Tetracycline ointment. It contains a broad-spectrum antibiotic – tetracycline. The ointment consistency allows you to preserve the active substance on the surface and in the layers of the skin for a long time. For convenience, applications are used, that is, you need to squeeze the ointment onto a napkin, distribute it on the boil and fix it for 2-4 hours. The best remedy for skin abscesses and boils is Ichthyol ointment. Its active ingredient is ichthyol, which is obtained by distilling natural minerals and resins. As a powerful antiseptic, Ichthyol ointment helps fight many viruses, bacteria on the skin and in the wound, ensuring a reduction in the inflammatory response and healing. There are cases in practical medicine when, when using Ichthyol ointment, purulent wounds with an area of 2-4 cm healed. If furunculosis appears on the butt, antibiotics must be absorbed as quickly as possible, otherwise the skin will become wet, which will provoke increased inflammation. Antibacterial gel and non-greasy ointments work quickly on the thigh or buttock. In this localization, it is recommended to rub in Gentamicin ointment or Gentaxan; they contain the antimicrobial gentamicin. Such ointments and gels have a pronounced antimicrobial treatment, reduce the work of the sebaceous glands, and dry the skin around the abscess. To treat boils in the groin, antibiotics and antiseptics are used, such as Ichthyol ointment, Vishnevsky liniment, Levomekol, Tetracycline ointment. All of them have a pronounced antimicrobial effect and quickly destroy the cause of inflammation
In this localization, the healing process can be lengthy due to poor hygiene, so it is important to systematically maintain the cleanliness of the skin in the genital and groin area. When choosing which antibiotics to treat a boil under the arm, the doctor is guided by the characteristics of this location. There are many sweat and sebaceous glands in the armpit area, so the active ingredients must penetrate as deeply as possible into the tissues
To treat furunculosis in the armpits, ointment-based preparations containing antibiotics are used: streptomycin, chloramphenicol, syntomycin. The prescription of Ichthyol ointment and Vishnevsky's balsamic liniment is justified.
It is safe to treat boils yourself with topical antibiotics only for minor skin lesions. At the first signs of an increase in the inflammatory process, the presence of tissue necrosis, or the appearance of pustules in new locations, the help of a medical specialist is required.
The doctor will determine the correct methods of therapy, because local treatment for diffuse skin lesions is sometimes not enough. Elimination of a deep boil is based not only on the effect at the source of inflammation. Antibiotics are also prescribed that affect the entire body.
Contraindications and side effects
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed by a specialist if the patient does not have the following contraindications:
- The period of lactation, bearing an unborn child in women.
- Individual reaction to drug components.
- Severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
- Fungal skin diseases.
- Tuberculosis in severe open form.
- Diseases of the heart, blood vessels, and hematopoietic system.
- Problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Bronchial asthma.
Self-medication threatens the development of dysbiosis and worsening the course of chronic diseases. If you choose the wrong antibiotic and accompanying medications, a purulent pimple can break through and affect the lymphatic system, enter the brain, and cause death.
Furunculosis is a painful infectious disease that can affect the body in all places where there is hair.
Most often, inflammation is found in the groin, face, armpits, and buttocks. The disease causes severe pain and can disrupt the usual way of life. Numerous abscesses cause intoxication of the body, the temperature rises, and the pain becomes unbearable. Medication therapy helps to quickly draw out pus and heal the skin. With an integrated approach, new relapses can be prevented and immunity can be increased. Only a doctor can choose the right treatment. Using even popular medications, Dimexide for boils and others, can be dangerous. The article has been verified by the editors
Treatment of furunculosis with antibiotics
Therapy with antibacterial drugs for single or multiple boils on the skin is carried out with five types of antibiotics. They are produced in the form of injection solutions, tablets, suspensions, and ointments. The most common antibiotics for boils are the penicillin series, since they have been successfully fighting Staphylococcus aureus and other strains of bacteria for many decades. Cephalosporins, macrolides, tetracyclines and anthraglycosides are prescribed if pathogens are resistant to penicillin.
Ointments
After the breakthrough/opening of the abscesses, a bandage with antibacterial ointments is applied to the wound. The following drugs are used for this purpose:
- Levomekol ointment. The most popular topical antibiotic. The active component chloramphenicol destroys a wide range of bacteria, and methyluracil helps tissues regenerate faster. Gauze pads are soaked in the drug and filled into the wound. Change the dressings daily until the problem is completely eliminated. With prolonged use, skin rashes are possible.
- Bactroban ointment. It has proven itself excellent in the fight against Staphylococcus aureus. Ointment for boils with the antibiotic Bactroban exhibits powerful antibacterial properties. It is allowed to apply the drug directly to the site of skin infection 1 to 3 times a day. Course duration is 7-10 days. In some cases, the development of allergic reactions, nausea, and headaches is noted.
Pills
Antibiotics in tablet form are prescribed for recurrent furunculosis or if their location is the upper torso and head area. The difficulty of such treatment is that staphylococcus is resistant to many antibacterial drugs, so tablets are selected after a microbiological sensitivity test. The most popular medicines.
- Lincomycin. An antibiotic with a powerful bacteriostatic effect, active against a wide range of bacteria. For furunculosis, adults take the drug Lincomycin 500 mg 3 times a day before meals. The antibiotic sometimes provokes adverse reactions in the form of surges in blood pressure and allergic reactions. The course of treatment should not exceed 2 weeks.
- Cephalexin. Antibacterial drug of the cephalosporin group. Has a bactericidal effect on most strains of staphylococcus. The daily dosage is 1-4 grams. Take pills at regular intervals. Possible side effects: hand tremors, disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines, dizziness. Duration of therapy is 7-14 days.
Injections for boils
Treatment with antibiotics for furunculosis can also be carried out in the form of injections. Injections are given if therapy with other forms of drugs does not give a positive result. The most effective drugs in this form of release:
- Amoxicillin. Popusynthetic antibiotic of the penicillin series. For furunculosis, it is administered intravenously by stream and drip. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor individually. The average course of treatment is 7-10 days. During therapy, undesirable reactions of the body may occur: tachycardia, irritability, headaches, dysbacteriosis, dyspepsia.
- Levomycetin. Powder for injection with the active ingredient antibiotic chloramphenicol. For furunculosis, adults are prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly. The daily dose is 1-3 g. The drug is administered at a dose of 0.5-1 g 2-3 times a day for 5-15 days. Adverse reactions may occur in the lymphatic system, digestive tract, peripheral and central nervous systems.
Forms of antibacterial therapy for furunculosis
The antibiotic therapy industry in the pharmaceutical market occupies a significant place among other medications. Today, medicines are manufactured in all kinds of forms: tablets, solutions, powders, suspensions, capsules, syrups. Such a variety of products allows you to select an effective drug for furunculosis in each specific case.
Syrups and suspensions with different flavors are suitable for small children. They will make treatment tasty and more enjoyable. Antibiotics in tablets for furunculosis are prescribed to adults and adolescents. Injectable forms of drugs are used for severe cases. Intravenous administration of drugs allows a therapeutic dose of the drug to act on the source of inflammation as quickly as possible.
Effect of the drug on boils
Antibiotics for the development of boils are aimed at combating the pathogen:
- relieve redness;
- eliminate Staphylococcus aureus;
- restore soft tissues and skin.
In order for the capsules to work correctly, you will need to choose the right drug. The clinic carries out the following analyzes of the patient’s biological material:
- urine;
- blood;
- blood biochemistry.
Skin scraping helps to accurately identify the pathogen. Bacteriological culture analysis determines the reaction of pathogenic microorganisms to the antibiotic. Based on the test results, the doctor selects an effective form of the drug. The pharmacy sells antibacterial agents: tablets, injections, ointments. They help cope with the infection and remove pus.
What antibiotic tablets are prescribed?
For a boil that affects a large area, in the presence of several foci of a purulent-necrotic process, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics in tablets or injections.
In modern pharmacology, several hundred types of antibacterial drugs are produced. To understand this variety of antibiotics, you need to understand that many different drugs have the same active ingredient, that is, they are analogues.
Possible complications
An advanced disease can cause various complications, which often spread to healthy organs.
Complications of furunculosis may be the following:
- The development of lymphadenitis is inflammation of regional lymph nodes.
- Lymphangitis is inflammation of the lymphatic vessels.
- Blood poisoning.
- Inflammatory processes of the brain.
- Arthritis.
- Kidney diseases.
Complications can only be prevented by timely consultation with a doctor. Diagnostics and a properly selected treatment regimen will protect the patient from unwanted consequences.
Self-medication for furunculosis is strictly prohibited. Treatment and opening of abscesses at home is fraught with serious complications. Taking medications, dosage and regimen of use should be under the supervision of a dermatologist.