An imbalance in the functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system seriously affects both the physical and psychological well-being of the stronger sex, making men feel inferior, avoid intimate relationships and feel embarrassed about their delicate problem.
Have you had a full medical examination in the last 5 years?
Not really
Meanwhile, many unpleasant symptoms, including redness on the testicles in men, can be quickly and effectively eliminated if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. If the cause lies in an allergic reaction, then the problem can be solved by eliminating the irritant, otherwise accompanying symptoms may be observed - nagging pain in the right side, chills, rashes, etc.
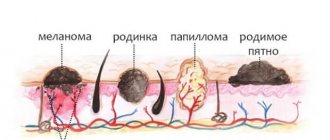
Non-infectious causes of redness of the scrotum
The main reason for redness of the scrotum in men is the filling of the skin vessels with a large amount of blood. This process occurs under the influence of internal and external factors, as well as due to the active growth and reproduction of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Redness can be either unilateral or bilateral, depending on the disease. Spots on the scrotum may protrude above the surface of the skin or may not rise.
The first among non-infectious causes of red spots on the scrotum is psoriasis. This disease is a dermatosis. There are two theories of its origin:
- Impaired function of skin cells - keranocytes;
- An autoimmune reaction that occurs against the background of an already existing autoimmune process in the body.
Triggering factors for psoriasis on the scrotum are injuries, exposure to chemical agents, and allergies. The disease occurs suddenly, usually after a nervous overstrain; the rate of development depends on the state of the man’s immune system. Also, psoriasis on the scrotum can occur against the background of HIV infection and in the presence of a chronic source of infection in the body.
The second cause of spots on the scrotum is vitiligo. This is also a type of dermatosis, however, the spots appear white due to the fact that the skin loses pigment - melanin. In this case, the spots do not tan during exposure to the sun and can grow in size. The causes of vitiligo are:
- Use of medications;
- Working with chemical reagents;
- Nervous overstrain;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Autoimmune inflammation.
The cause of blood spots on the scrotum is eczema. This disease is the most common among skin lesions of the scrotum. Eczema develops due to exposure to external and internal factors. External factors include:
- Foods that contain large amounts of preservatives;
- Foods with allergenic properties (citrus fruits, chocolate, nuts);
- Medications;
- Synthetic underwear;
- Hygiene products, soap, shower gels.
Internal factors are diseases of organs and systems (damage to the liver, kidneys, sinusitis, caries), as well as hereditary predisposition, nervous and hormonal balance disorders.
Testicular torsion
This pathology can occur against the background of physical overload, sudden careless movement, or abnormalities in the development of the reproductive system. Testicular torsion appears with sharp, intense signs that cannot be ignored.
Main features:
- Sharp pain in the scrotum (from the side of the affected testicle).
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- It is visually clear that one testicle has become significantly higher than the other.
- Change in skin color.
With such symptoms, the time to provide assistance is very limited. Torsion leads to disruption of the blood supply to the organ. A prolonged stop of blood flow will lead to the death of the organ and will require removal.
Infectious causes of redness of the scrotum
Spots and hyperemia on the scrotum due to infectious factors are much more common than due to non-infectious agents. A feature of these causative factors is a combination of redness and itching of the scrotum. Therefore, in addition to the spots, scrotal hyperemia may appear due to constant scratching.
Pubic lice can cause spots on the scrotum. This disease is called pediculosis pubis. Its peculiarity is the limited localization of the process. Pubic lice can only breed on genital hair. Itching and spots on the scrotum with pediculosis occurs due to lice bites. These insects can only feed on human blood; without food they die within a day. Pubic lice infestation occurs during sexual intercourse.
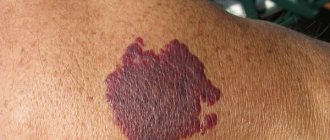
Through sexual contact you can also become infected with papillomavirus, which causes spots on the scrotum. The spots are burgundy in color and protrude above the surface of the skin. In addition to sex, the papilloma virus enters the body in the following ways:
- When damaged skin comes into contact with the skin of a virus carrier;
- Through saliva during oral sex;
- If urine gets on the injured skin of the scrotum.
Redness and spots on the scrotum can cause sexually transmitted infections:
- Syphilis. With syphilis, a red spot remains at the site of entry of the pathogen on the scrotum. Subsequently, skin hyperemia develops.
- Gonorrhea.
- Ureaplasmosis.
- Chlamydia.
You can become infected with them during sexual contact, as well as by using the patient’s personal hygiene items and wearing the same underwear.
Opportunistic microflora causes redness of the scrotum, which is accompanied by scratching marks and the appearance of red or white spots. These symptoms are caused by fungi of the genus Candida, which begin to actively grow and multiply under the influence of unfavorable factors:
- Frequent sexual activity, sex without using a condom;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, using soap when washing;
- Decreased immunity due to general illness or hypothermia.
This disease is called candidiasis. It cannot be transmitted during sexual intercourse; frequent sex is only a predisposing factor.
Causes of non-inflammatory nature
Such conditions include circulatory and lymph exchange disorders.
The most significant:
- hematocele;
- elephantiasis;
- torsion of the testicle or spermatic cord.
Hematocele
With congenital or acquired hydroceles (communicated dropsy and accumulation of fluid in the membranes of the testicle), a complication in the form of hematocele is possible. This is a hemorrhage into the cavity formed by the membranes of the testicle, which is externally manifested by local redness of a certain area of the scrotum. It is accompanied by discomfort or pain, and only when infection and suppuration are associated with increased body temperature and other nonspecific signs of inflammation.
Elephantiasis
Elephantiasis of the external genitalia is a constant increase in size due to impaired lymphatic drainage. Characterized by the development of persistent swelling, disruption of metabolic processes in the skin, subcutaneous tissue and connective tissue of the scrotum. It can be secondary (as a result of chronic infections) and congenital.
Clinical features:
- begins with the skin of the scrotum (redness and swelling), spreads to the testicles, epididymis and urethra;
- lasts for years with periods of exacerbation and subsidence of the process;
- with each exacerbation, swelling and hyperemia of the scrotum and penis increases;
- urination becomes difficult due to proboscis-shaped enlargement of the foreskin;
- painful erection and gradually emerging impotence.
Treatment of congenital elephantiasis is surgical, eliminating malformations of the lymphatic vessels. In case of acquired pathology in the early stages, conservative treatment is possible using:
- decongestant diuretics and corticosteroids;
- novocaine blockade;
- for the purpose of resorption therapy - injections or electrophoresis of trypsin, lidase;
- specific antiparasitic therapy (with confirmation of the helminthic nature of the secondary process).
Surgical correction is performed when drug treatment is insufficiently effective and the process progresses. It consists of restoring normal patency of lymphatic vessels and removing affected tissue.
Torsion of the spermatic cord
Partial compression of the vessels passing in the spermatic cord leads to venous stagnation and edema, complete compression leads to a heart attack
In case of injuries to the genital organs, sudden tension of the abdominal press against the background of anatomical features (increased mobility, lengthening of the cord), torsion of the spermatic cord is possible with cessation of local blood circulation. If it is not diagnosed in time and treatment is delayed, irreversible changes to the tissues develop, leading to death (necrosis).
Signs:
- sudden change in condition;
- intense, sharp pain in one half of the scrotum, radiating to the corresponding groin area;
- the affected testicle is located higher than usual;
- probably a drop in blood pressure due to pain;
- nausea and vomiting.
Treatment in the first hours may be conservative; the surgeon performs external manual untwisting of the testicle. If this method is ineffective or in a later period (when pain increases and blood supply to tissues deteriorates), surgical treatment is indicated.
Diagnosis of scrotal hyperemia
If a man notices redness of the scrotum or the appearance of spots on it, it is not recommended to engage in self-diagnosis. Considering that the stains are most often of an allergic nature, it is necessary to change synthetic underwear to cotton, and change personal hygiene products. You must also abstain from sexual intercourse for two weeks. You should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- The spots do not disappear within two weeks;
- Rapid growth of spots;
- The appearance of the spots was preceded by sexual intercourse without a condom with an untested partner;
- The spots are accompanied by uncontrollable itching, burning, difficulty urinating, pain in the scrotum and decreased sexual function;
- There are general symptoms, fever, malaise.
It is recommended that a man first contact a urologist, who will examine the scrotum, analyze complaints and refer him to the appropriate specialist (venereologist or allergist).
There is a standard examination plan for a patient with complaints of spots on the scrotum:
- General blood analysis. With an infectious causative factor, leukocytosis is determined with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left or, conversely, leukopenia, slight anemia, increased ESR.
- General urine analysis. Proteinuria and leukocyturia are determined.
- Blood chemistry. Dysproteinemia and changes in nitrogen metabolism are possible.
- Urine culture to determine microflora and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Wasserman reaction for diagnosing syphilis.
- Blood test for sexually transmitted diseases.
- Dermatoscopy. Using this method, under multiple magnification, you can see the detailed structure of the spot.
Other research methods are prescribed depending on the expected diagnosis. If a sexually transmitted disease is suspected, both partners should be examined if possible.
Normal scrotal color
The genital organs are a very sensitive system of the body that reacts to almost any changes in the body. Any changes in color, structure, or functioning must be responded to immediately. The shade of the scrotum cannot be constant; it changes throughout life and there are reasons for this:
- an increase in the amount of melanin, the main pigment of the skin;
- constant rubbing of the scrotum on underwear;
- the influence of chemical components present in hygiene products;
- previous injuries and other mechanical impacts.
A normal color is when the scrotum looks a little darker than the rest of the body. Over time, its shade becomes darker. The bag is divided in the middle by a seam; the two halves have different colors. If a man is healthy, then there should be no spots on the surface of the scrotum.
The color should change gradually, otherwise it may indicate a violation. Therefore, if the scrotum suddenly darkens or turns red, you should consult a doctor. The reasons for a sudden change in color may be the following factors:
- synthetic underwear does not allow the skin to “breathe”, which causes diaper rash;
- the use of hygiene products that dry out the skin is a common occurrence for soap;
- chemicals can cause allergies;
- long-term sex using special lubricant;
- groin rash;
- ignoring hygiene rules.
In medicine, redness has a scientific name - scrotal hyperemia. The causes of this disorder are infectious and non-infectious in nature, so they need to be considered separately.
Treatment of non-infectious scrotal spots
Non-infectious scrotal spots are treated by a dermatologist. The choice of therapy depends on the disease that caused the spots.
For psoriasis, medications are prescribed that inhibit the development of the disease. There is no complete cure for the disease, since no effective therapy has been developed. Sedatives, vitamins, aspirin, and antihistamines are used. It is necessary to stimulate the immune system with the help of biostimulants. Salicylic ointment or ointment with glucocorticosteroids is applied topically to the scrotum. Physiotherapy is also prescribed for the skin of the scrotum.
For eczema, hyposensitizing drugs are used. It is mandatory to influence the nervous system with bromine preparations or antipsychotics. If swelling of the scrotum develops, diuretics are used - Lasix. They also strengthen the immune system with the help of biostimulants (eleutherococcus or ginseng).
In vitiligo, white patches on the scrotum are exposed to ultraviolet light. The drugs prescribed are glucocorticosteroids, vitamins and microelements. The patient must change his lifestyle:
- Avoid stress;
- Eat properly;
- To refuse from bad habits;
- Change your place of work to one where there will be no contact with chemicals.
How to treat at home - what ointments and creams will help with itching of the scrotum?
At home, itching of the scrotum can be treated only after undergoing an examination by a dermatologist in order to know what kind of disease is being treated and what medications are advisable to use in a particular case. Most often, to stop the skin on the scrotum from itching, dermatologists prescribe the following ointments and creams for external use.
Menthol based
The main drugs for eliminating itching of the scrotum include menthol-based drugs:
Boromenthol;
- Bom-benge;
- Golden star (cream-balm);
- Menthol oil.
- Infectious inflammation as a result of the activity of various pathogenic microorganisms. They can develop throughout the entire structure of the scrotum, testicles, epididymis, seminal canals, as a result of which the body begins a protective reaction to this process and the occurrence of severe itching of the scrotum and the occurrence of hyperemia.
- The causes of inflammation of the scrotum can also be non-infectious.
- Reduced blood flow from the testicles themselves, due to scrolling of the seminiferous ducts, which contain nerve fibers and small blood vessels.
Menthol-based medications should not be used by men whose itching is caused by irritation with a violation of the integrity of the skin of the scrotum (deep scratches, wounds, ulcers).
Panthenol
A complex drug that relieves itching, swelling and inflammation of epithelial tissue in the testicular area. The ointment also promotes faster healing of irritated skin.
Nezulin
It has antiseptic properties and consists entirely of natural ingredients. Perfect for men with sensitive skin in the intimate area, which is prone to frequent allergic reactions.
Gistan
An ointment containing a substance such as betulin. It relieves the feeling of itching, swelling and inflammation of the epithelial surface of the groin area in the shortest possible period of time.
Triderm
This type of ointment can rightfully be called a universal remedy for itching of any nature. The medication effectively resists infectious, viral and fungal microorganisms, the presence of which was the reason why the man’s testicles began to itch.
All types of these ointments can be used at home by applying them to the surface of the scrotum 2 times a day. The duration of therapy depends on the type of disease and the manufacturer's recommendations, shown in the manufacturer's instructions.
Men sometimes experience redness and itching of the scrotum.
Many factors contribute to this.
Itching is a symptom of many diseases.
In today's article we will talk about the causes and consequences that can lead to itching under the scrotum.
The mechanism for the occurrence of redness is that an abundant supply of blood enters the skin of the scrotum and testicles, as a result of which it turns red.
Blood flow, in addition to the scrotum and testicles, can also flow abundantly into the epididymis and spermatic cords.
In many cases, this is evidence that an inflammatory process has begun.
There are several reasons for the occurrence of such hyperemia.
Their elimination is aimed at destroying pathogenetic factors and reducing the inflammatory process:
If we talk about the infectious appearance of scrotal hyperemia, it is caused by several groups of bacteria.
They cause both itching of the scrotum itself and its hyperemia.
A nonspecific bacterial infection can be represented by the following pathogenic microorganisms:
- staphylococcus
- Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- streptococci
- even pathogens such as protea can connect
In addition to the fact that they can affect the scrotum itself and its tissues, they can also penetrate the testicles and their appendages.
They can be introduced simply through the bloodstream or through the flow of the lymph itself.
According to many doctors, these pathogens do not have a clear direction in choosing the damaged tissue and its cells.
This indicates promiscuity towards the cells they destroy.
When a man says that his scrotum itches and begins to itch, he is mostly to blame.
He immediately begins to get nervous and remembers what he did, who he slept with or didn’t sleep with.
Basically, the causes of such itching can be ordinary failure to observe personal genital hygiene.
And it’s enough just to take a shower or go to the bathroom and wash well with soap.
After this, the itching of the scrotum can be reduced or completely eliminated if this process is of a non-bacterial type, which affects much worse.
Despite all his shyness, a man should still visit the appropriate doctor.
Namely, a urologist or dermatovenerologist.
The doctor will examine the genitals for hyperemia and inflammation, both the testicles and the scrotum itself.
But many men are embarrassed by such an examination.
Despite the fact that severe itching of the scrotum begins, they remain their ground and endure what is fraught with danger for themselves.
The process can go into a chronic stage and affect much more and worse, affecting the entire body as a whole.
Moreover, any inflammatory processes can negatively affect the reproductive function of men.
Treatment of infectious spots of the scrotum
Spots on the scrotum of an infectious nature are treated by prescribing antibiotics in cases where the disease was caused by bacteria. For sexually transmitted diseases I use benzylpenicillin sodium or potassium salt. In case of contraindications, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, and macrolides are prescribed. Viral diseases require the use of antiviral drugs.
If the disease is not sexually transmitted, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used until culture results are obtained. Antibiotics are administered both intramuscularly and applied topically in the form of ointments to the scrotum area.
If lice pubis is detected, all pubic hair is shaved off and the skin is washed thoroughly with soap. Next, for two days, the skin of the pubis and scrotum is treated with benzyl benzoate emulsion. Treatment should be carried out on all partners with whom the patient has had sexual intercourse.
Causes leading to severe itching of the scrotum and testicular area
There are many factors influencing such an unpleasant process.
Sometimes it is difficult to stop even with drugs with antihistamine effects.
Allergy
Touching the delicate skin of the genitals with poor-quality fabric of underwear, or contact with shampoo, gel, soap, little-known creams or ointments.
Sometimes behind the beautiful appearance there is hidden the treatment of linen with toxic dyes that contain large amounts of chromium.
If the underwear is made of synthetics, then this can also cause itching when worn for a long time, and leads to diaper rash in the genital area.
Many men note the occurrence of allergic itching due to the use of latex condoms.
Infections
A large number of both beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms constantly live on the surface of a man’s genitals.
If a man constantly follows the rules of personal hygiene, namely, changes his underwear daily and takes a shower, then beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms coexist peacefully.
But if a man does not follow these simple rules, then an inflammatory process may occur on the skin of the scrotum, leading to itching.
Due to damage to the delicate tissues of the skin.
Often the area where the testicles are located (the scrotum) is “attacked” by streptococcal bacteria.
Also, in addition to streptococcus, the scrotum can be “attacked” by mycoplasma and ureaplasma, and some types of fungi.
One of them is the Candida fungus (candidiasis).
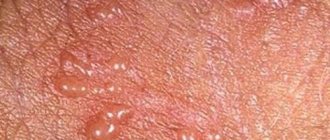
It is with infectious dermatitis that a specific rash appears on the skin of the scrotum, somewhat reminiscent of a burn, the so-called urticarial rash.
If you look closely at it, it looks like a nettle burn.
Pediculosis
Despite all the observance of personal intimate hygiene, many men who are promiscuous can pick up a very unpleasant parasite.
These are pubic or body lice.
This parasitic disease is called pediculosis.
You can get infected almost anywhere:
- in public transport, when a large crowd of people is forced to come into contact with each other
- in a public bath, swimming pool, shower, sauna
- when visiting a public toilet
Itching is caused by parasite bites on the delicate skin of the genitals.
But with the bite itself, the patient does not feel pain.
The parasite's saliva contains an anesthetic substance, which it injects immediately after the bite.
Itching at the site of the bite begins only after 5 minutes.
Itching from head lice can be very painful and is accompanied by small bloody calluses after scratching.
Chlamydia
A disease of a sexually transmitted nature provokes severe itching in the area of the scrotum and testicles located in it.
Many men with chlamydia experience immediate itching in the scrotum area.
In fact, the itching is concentrated on the inner surface of the testicles, which indicates a large population of chlamydia parasites.
In addition to itching, the man also complains of pain and burning when urinating.
With timely treatment and taking appropriate medications, itching in the testicular area usually decreases or stops altogether.
Erythrasma
Occurs when the body’s immune properties decrease.
With this progression, the parasites begin to actively multiply and release their pathogenic waste into the human body.
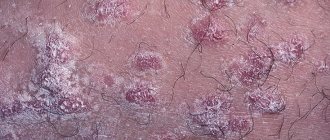
The main characteristic symptom that appears with erythrasma is that the scrotum begins to take on the color of red brick.
Itching can move between the genital area to the anus and perineum.
The itching is not constant; it usually begins in the afternoon and intensifies in the evening.
With erythrasma, this process is specific only when the immune system is reduced, when the body is not able to resist a large number of pathogens.
Athlete's inguinal
The pathology is fungal type, the main causative agent is mycotic fungal spores.
Inguinal athlete's foot can become chronic, causing very serious consequences.
It may occur with periods of both decline and exacerbation.
Men aged 32 to 45 years are most often affected.
In addition to the itching of the testicles or scrotum, patients complain of the appearance of round spots on the genitals, somewhat reminiscent of lichen planus.
Herpetic genital infection
As you know, herpes is viral in nature.
This type of itching, known as herpetic itching, occurs due to the appearance of herpes on the genitals.
The cause of its appearance is unprotected sexual intercourse with a partner who already has such an infection.
To avoid infection, you must use a condom.
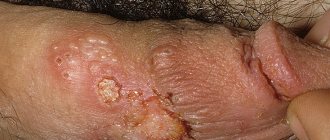
The main symptom of herpes on the genitals is the appearance of small blisters filled with a yellowish-whitish liquid.
Psoriasis
A specific autoimmune reaction of the body.
The pathogenesis of this condition has not been fully studied, and a means to completely cure this disease has not yet been found.
At the first signs of psoriasis in men, the testicles always begin to itch due to the appearance of psoriatic plaques on them.
The scrotum becomes covered with a whitish coating and peels off due to damage to the epithelial tissue.
Prevention of scrotal spots
The main method of prevention is regular personal hygiene and wearing underwear made from natural cotton fabrics. Considering that nervous overstrain plays one of the leading roles in the development of scrotal spots, it is necessary to avoid stress. It is also recommended to have sex only with condoms and avoid casual sex. Professional activities should not involve contact with chemical reagents. A healthy lifestyle will also help prevent the development of scrotal spots.
To prevent the development of diseases of the genital area, every man is regularly recommended to visit a urologist for preventive purposes. After completing the course of treatment, it is necessary to be under the supervision of a doctor to prevent relapses.