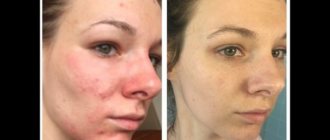
What is crusting on the skin?
The sensitivity of the human dermis to various external stimuli is very high. Therefore, the appearance of crusts on it has become a very common problem. The formation of crusts can occur due to the influence of household chemicals (soap, dishwashing detergent, washing powder), and dry air.
Also, crusts on the epithelium form as a symptom of any skin disease (psoriasis,). Therefore, if crusts are detected on the skin, you need to undergo an examination by a specialist. The dermatologist, after conducting suitable research, will create a suitable course of therapy.
- A crust on the skin is represented by a formation that is formed due to the drying of pus, serous exudate, and blood on the dermis.
- The crusts can rise above the surface of the skin at different heights, which depends on how the layering of blood and pus was performed.
- If the crust is fresh, it is quickly and easily removed because it is loose. Old dried crusts are very dense and more difficult to remove.
This video talks about caring for your baby's skin with crusty dermatitis:
Diagnostics
Examination and diagnosis of skin diseases
Diagnosis of skin pathologies depends on the observation of the patient and the qualifications of the doctor. If you notice the first signs of a change in the structure of epidermal cells, you should seek medical help and not self-medicate.
First of all, attention is drawn to lesions on the face, ears, and the appearance of dandruff on the head, especially if these areas are itchy. There are often cases of late diagnosis of pathologies of the skin of the hands and feet, especially if a person is inattentive to himself.
If the skin becomes crusty and itchy, you need to follow these rules:
Visit to a dermatologist.
Taking tests:
- clinical blood test + blood glucose level;
- blood chemistry;
- scraping analysis;
- feces on worm eggs;
- autoimmune markers.
Consultation with an angiosurgeon for varicose veins of the legs, angiography, phlebography.
Examination by other doctors: endocrinologist, immunologist, allergist.
Classification of characteristics
The crusts differ in color depending on what kind of discharge dries on top of the skin:
- Yellow crusts
formed when the serous secretion dried out; - Black-brown crusts
formed when bloody discharge dried; - Greenish-gray crusts
appeared when purulent discharge dried.
There are also mixed crusts. They are formed when purulent-bloody/serous-bloody exudate dries. Indicators such as shape, color, and size of crusts indicate the presence of primary pathological changes that provoked their formation.
- After the blisters dry out, patients develop yellowish crusts.
- Purulent crusts form after the pustules dry out.
- If bloody crusts are present, experts suspect deep damage to the skin tissue.
Crusts often appear on the dermis of the arms and legs. On the legs, the formation of crusts indicates the development of an allergic, fungal disease (seborrhea, dermatitis, eczema). Crusts on the hands occur in the presence of a microbial, allergic, or fungal disease. Eczema is often the cause of the appearance of crusts on the epithelium of the hands.
White crusts on the scalp (photo)
How to identify a symptom in yourself
It is very easy to detect such a symptom as crusts on the skin. To do this, it is recommended to carefully examine the epidermis. Typically, crusts are the final stage of almost any skin disease. The formation of a crust indicates the healing process of epithelial damage.
Crusts formed on the epithelium are secondary rashes. They are formed during the evolution of primary elements (ulcers, papules, blisters).
This video will tell you how to remove different types of crusts from your baby’s skin:
Possible diseases and disorders
Almost always, the appearance of scales indicates the presence of the following skin diseases in the body:
- Psoriasis
. This disease is accompanied by profuse peeling. After combing the pink spots, the diameter of which reaches 5 cm, silvery scales are formed. - . This disease is represented by the formation of a scaly crust on the epidermis of the head. In most cases, patients experience a symptom such as bloody discharge.
- Dermatomycoses
. This disease is represented by red spots, in the center of which peeling appears. The diameter of such spots increases very quickly. - /
. With these forms of dermatitis, a symptom such as peeling appears. Atopic dermatitis affects the popliteal and elbow bends, and contact dermatitis often occurs on the hands. - Pityriasis rosea
. The disease is represented by raised areas of the skin, which have an oval shape. The spots reach a size of 20 mm.
Less commonly, peeling of the epidermis and the formation of crusts on it are provoked by the following diseases:
- Discoid eczema.
- Lichen planus.
- Guttate psoriasis.
- Solar keratosis.
- Chronic dermatitis.
- Pityriasis versicolor.
We will tell you below what to do if dry white, brown, yellow, or black crusts appear on the scalp and body.
How to deal with this symptom
To get rid of scales that cause discomfort, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease that provokes the formation of such crusts.
Before undergoing systematic treatment, a specialist accurately determines the cause of the disease. If you find the slightest changes on the skin, a suspicious rash, spots, you need to consult a dermatologist.
This video will tell you how to remove seborrheic crusts:
Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by widespread redness, itching, blistering and a constant burning sensation. If you start treatment, the disease will only progress; if you do not fully treat it, you can confidently earn a relapse.
There are a great many types of this disease, but in children most often the true (idiopathic) and microbial forms occur. Eczema in children is localized on the hands and fingers, although it can also affect other areas of the skin.
Kinds
Idiopathic
Dermatosis is manifested by the appearance of vesicles (small blisters) and papules (serous nodules) on swollen and reddened areas of the skin. The rashes are symmetrical, their boundaries are unclear. After a certain period of time, the bubbles burst, erosion begins with the release of serous fluid. After the erosions dry out, crusts and scales (serous and hemorrhagic) form in their place. Most often, eczema on the hands occurs in children aged three to six months. Ultimately, with proper treatment, the disease disappears, but with the slightest weakening of the immune system, a relapse can occur. Exacerbation occurs in autumn and winter, during high humidity.
Microbial
This form occurs in a child with a weakened immune system due to damage by pathogenic microorganisms - staphylococci and streptococci. Eczema on the hands is characterized by the appearance of flaky erosion covered with scaly crusts. Foci of inflammation are large, with clearly defined boundaries, and occur peripherally. The course of the disease is accompanied by constant itching. During treatment, antihistamines are used to relieve swelling and make the disease easier to bear.
Coin-shaped
Refers to microbial form. It is an inflammation, with clearly defined edges, in the form of a coin. It reaches three centimeters in diameter. The surface becomes wet and after a certain time becomes covered with a serous crust. With a coin-shaped form, microbids and allergens may appear. With injuries and scratching, the lesions can merge into one, in which case eczema on the hands turns into its true form and can spread throughout the body. It is much more difficult to cure this form.
Treatment of dry eczema on hands
Treatment measures should be started immediately after verification (confirmation) of the diagnosis. The goal of treatment is to transfer acute inflammation to a stage of stable remission. The duration of the course of treatment is at least 2 weeks, but more often it is extended to 1.5-2 months. The main method of treatment is the use of all kinds of ointments and creams; all other methods are of secondary importance.
Physiotherapy
Local methods of physiotherapy for dry eczema are practically not used. Methods that influence central regulatory systems are more effective. They help reduce the degree of tension in the nervous system, favor the functioning of the endocrine glands, and help reduce the activity of local inflammation.
For dry eczema use:
- Electrosleep. The course includes up to 10 sessions lasting 40 minutes.
- Transcranial electrical stimulation in a sedative (calming) mode.
These procedures can be used in the acute period, and during remission it is recommended to visit sanatoriums. Preference should be given to cool resorts with moderately humid air.
Ointments
Topical remedies are a key element in the treatment of dry eczema. During an exacerbation, oily and moisturizing creams should be applied daily to areas of dry skin. It is not necessary to look for medicinal preparations - hygiene products (Dermaref, Biopin) are suitable for use. All the most popular cosmetic companies produce hygiene creams for dry skin - they are also suitable for dry eczema on the hands. The cream should be applied to the affected areas very generously until the drug is completely absorbed; you can apply it several times throughout the day.
Gels containing collagen or hyaluronic acid (Pectilift gel) provide a good effect for dry eczema. They moisturize the skin for a longer time, which allows you to reduce the number of applications per day.
The composition of creams and gels for dry eczema necessarily includes emollients - chemical compounds that ensure the retention of moisture on the skin. Due to emollients, the skin becomes soft and velvety.
Ointments and creams based on topical glucocorticoids for dry eczema are used mainly at the early stage of the disease. It is advisable to use a medium-strength hormonal ointment for as short a course as possible. Overuse of hormonal ointments for this type of eczema can cause more harm due to complications than benefit. Positive effects were noted from ointments with vitamins (Radevit, Retinoic ointment) with metabolites (Solcoseryl).
The addition of bacterial inflammation is an indication for prescribing ointments with an antibacterial component. They are used until signs of infectious inflammation, manifested by the appearance of purulent crusts, disappear.
Main article: Ointments and creams for eczema
Pills
Tablet drugs in the treatment of asteatotic eczema are of secondary importance or are taken as prophylactics. Antihistamines (diphenhydramine, cetrin) are used if itching bothers you. To improve metabolic processes in the skin and accelerate regeneration, it is recommended to take vitamins, preference is given to fat-soluble vitamins: tocopherol (vitamin E) and retinol (vitamin A). “Aevit” in capsules can be taken 1 capsule per day for 1-1.5 months.
Doctors often prescribe mild sedatives in tablets to eliminate the psychogenic factor: Novo-Passit, valerian tablets. More serious sedatives are prescribed according to indications, after consultation with a psychiatrist.
If there are diseases of the digestive system, which act as one of the provoking factors, treatment of these diseases is required. A consultation with a gastroenterologist is necessary, who will determine the exact treatment regimen for concomitant pathologies.
Main article: Eczema tablets
Diet
In the complex treatment of dry eczema, diet is not critical. However, as a preventive measure that reduces the frequency of exacerbations and reduces the likelihood of the addition of other dermatitis, it is actively recommended by doctors.
The following should be excluded from the diet:
- hot spices,
- chocolate,
- citrus fruit,
- alcohol,
- hard cheeses,
- chicken eggs (white).
When cooking, it is better not to fry foods, preferably stewing and boiling. It is optimal to serve porridge as a side dish for lean meats, but not pasta or potatoes.
Main article: Diet and nutrition for eczema
Treatment with folk remedies at home
Dry eczema is not an indication for hospitalization; it can be treated at home using folk remedies.
The following recipes will not cause harm:
- Rubbing in sea buckthorn oil. This method achieves a pronounced skin softening effect. The oil forms a thin film that prevents moisture evaporation, which has a beneficial effect on skin turgor (elasticity).
- Chamomile oil extract. To make it, take 50 grams of dry chamomile, add olive oil (0.5 liters) and shake. The resulting mixture is infused for at least 10 days in a dark place at room temperature. At the end of the infusion period, the oil is filtered. Apply to dry skin up to 3 times a day. A similar extract can be obtained from St. John's wort; it is used in the same way as chamomile extract.
- Egg yolk applications. Break several eggs, separate the yolks and mix them, the resulting mass should be homogeneous. The yolk mixture is applied in an even layer to the previously washed skin. Exposure time is 20-30 minutes, after which the yolks are carefully washed off with warm water.
- Goose or badger fat. These substances protect the skin very well from the effects of dry cold air, so they can be applied to the skin before going outside in the fall or winter.
- Ointment based on spruce resin. To prepare it, you need to mix equal proportions of purified spruce resin (resin), wax and lard. The components mix well in a water bath. The cooled paste is applied to the skin up to two times a day for several weeks.
In case of severe cracking of the skin, before applying any ointment, you can moisten the skin with infusions of blackberry leaves or willow bark. The preparation recipe is quite simple: 25 grams of raw materials are poured with boiling water (0.5 liters), after which they are allowed to brew for 8-10 hours. With the cooled infusion, either wipe the affected skin, or make hand baths - immerse your hands in it for 10 minutes.
There are other folk remedies for the treatment of asteatotic eczema, but recipes with aggressive ingredients such as mustard or soda should be used with extreme caution - the risk of skin burns is very high.
Main article: Treatment of eczema with folk remedies
Recommendations
Ointments with a high fat content for dry eczema should be used not only during periods of exacerbation, but also as preventive measures in the autumn-winter period.
It is strictly not recommended for people at risk to expose the skin of their hands to extreme temperature loads: rinsing things in cold water, playing snowballs.
If deep skin cracks appear on your hands, you should refrain from activities associated with an increased likelihood of infection: digging the ground, planting plants, working with pets.
Main article: Treatment of eczema
Symptoms
Since there are many types of the disease, the symptoms will also vary. But there are certain signs that are typical for any form.
Signs:
- The skin on the arms, legs and face takes on a red (sometimes bluish) tint. An area of limited inflammation appears.
- A rash appears. Depending on the form of eczema, it may have certain distinctive features.
- Constant itching affects daily activities and keeps you awake at night.
- After the bubbles open, cracks and painful wounds appear in their place.
- The temperature rises.
- After treatment, the skin loses its elasticity and becomes dry and cracked.
Causes
The causes of this insidious disease are striking in their diversity. Most often, eczema in young children occurs due to a genetic predisposition. If someone in your family has had this disease, the likelihood of it occurring in a child increases rapidly. A number of situations can serve as a trigger:
- Allergic reactions to food products, household chemicals, hygiene products.
- Stressful situations that lead to scratching of the skin on the hands.
- Diseases of internal organs (liver, kidneys, stomach).
- Impaired metabolism.
- Creams and soaps whose composition irritates the delicate skin of a child’s hands.
- Weakened immunity.
It can also appear in adolescence due to hormonal changes in the body.
Complications
If timely treatment is not prescribed and the progression of the disease is not prevented, serious complications can occur.
One of the most dangerous complications is an associated bacterial infection, which can be caused by purulent inflammation on the skin of the hands. As a result, the patient’s health deteriorates, blisters with purulent content appear on the skin, with an unpleasant odor and constant itching. In this case, treatment is recommended only under the supervision of an experienced doctor!
If you do not consult a specialist in time and do not treat eczema in the early stages, erythroderma may occur. Not only limited areas of the skin, for example, on the hands, become inflamed, but the disease spreads to the entire surface of the body. This is much more difficult to deal with. Regular ointments will be useless.
Skin of extremities
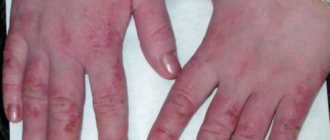
Crust on the skin of the hands and feet indicates an irritant, which may include:
- Fungal infection (keratomycosis, including lichen, dermatophytosis).
- Allergic reaction (regular contact with chemicals).
- Bacterial infection (addition of streptococcus, staphylococcus).
The disease manifests itself in the form of seborrhea, contact dermatitis, and eczematous changes. Scratching appears on the arms and legs in the affected area, a rash with blisters appears around them, they subsequently ulcerate and weeping sores with a crust appear.
Crusts on hands that itch tend to fall off with the release of serous contents and are prone to weeping due to the long-term course of the disease and frequent contact with water.
This condition can be provoked by a reduced immune response, constant stress, prolonged fatigue syndrome, regular contact with an allergen, poor diet, infectious, autoimmune and endocrine diseases.
Treatment
Nowadays, eczema can be treated in many ways. Topical corticosteroid hormones, such as hydrocortisone ointment, are prescribed. To calm the nervous system, various sedatives are prescribed: valerian, tranquilizers; vitamins that improve immunity. Treatment involves following a strict diet.
In the case of microbial eczema, antibiotic ointments are widely used, but in the case of fungal infections, the use of these ointments is strictly prohibited. You may not cure the patient, but only worsen the course of the disease.
To relieve itching, antihistamines of group H1 (diazolin, diphenhydramine, pipolfen, tavegil) are used.
For external treatment, boric and salicylic ointments, diprosalic solution, Wilkinson's ointment, and celestoderm are widely used.
When the disease is localized on the hands, it is necessary to avoid contact with cold or hot water.
Prevention
It is always better to prevent a disease than to treat it. The prevention of eczema in children must be taken seriously and responsibly. Even a past illness can leave scars on the hands and face, from which no ointments can save, and also accompany a person throughout his life, reminding him of himself with constant relapses.
It is necessary to start during pregnancy. A pregnant woman should adhere to a healthy lifestyle, a normal daily routine and a healthy diet. After the birth of a child, it is necessary to take proper care, monitor the diet and strengthen the body. Viral infections are dangerous for children suffering from dermatosis. In rare cases, Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis may develop, which can be fatal.
Maintaining hygiene is an important factor in prevention and successful treatment outcome. This will help avoid the addition of a secondary bacterial infection and prolonged relapse. For abrasions and scratches, the skin of the hands should be lubricated with antibacterial ointments. Hypothermia and overheating are enemy number one. All contacts with water are reduced to No. Children should wash their hands under close supervision. The baby's wardrobe is also subject to revision. All synthetic items must be disposed of, leaving only products made from natural materials.
Never start treating your child on your own, without first consulting a dermatologist and finding out the causes of the disease! Many medications can cause allergic reactions and only complicate the situation.
Due to the peculiarities of their localization on the hands. The point here is not only that it is unpleasant to show the affected skin of the hands, but for others to contemplate it. Treatment of dermatitis on the hands is always complicated by the fact that a person is forced to frequently wash his hands with detergents and come into contact with various substances and objects, because hands are the main operating tool. Let’s immediately say that for dermatitis accompanied by dryness, hand washing is limited; it is recommended to clean them with oil.
There are different types of dermatitis: allergic, contact, chronic. Each type of dermatitis has different forms and degrees of severity. Let us briefly consider the most typical and frequently encountered ones. develops as a response to external irritants that have allergenic properties.
Such allergens can be medications, household chemicals, cosmetics and perfumes. Factors such as overwork, low resistance to stress, and poor nutrition provoke the development of allergies. Allergic dermatitis on the hands is manifested by redness and swelling of the skin, a burning sensation, pain and itching, as well as the appearance of watery blisters (up to large blisters).
Blisters on the hands may burst, leaving behind weeping sores, scabs and pigmented areas. At the same time, my hands constantly hurt. Allergic dermatitis without treatment turns into eczema. Drug dermatitis (toxidermia) manifests itself in the form of reddish spots with swelling, itching, peeling, or later covered with blisters. Drug-induced dermatitis most often causes serious complications in the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Simple ones arise from a specific impact on an area of the skin of a mechanical (friction, squeezing), physical (ultraviolet radiation, burns, frostbite), chemical (acids, alkalis, metal salts) or biological (pollen, plants themselves) allergen.
We especially note neurodermatitis - allergic dermatitis of central origin, that is, resulting from functional disorders of the nervous system or hormonal status. In the diffuse form of neurodermatitis, there is a clear localization of foci, including on the elbow bends. Usually the disease begins with pruritus: the hands and other places itch so much that it is impossible to sleep or remain calm.
Depends on its form and severity; with mild cases of simple contact dermatitis, no treatment is required. However, in all cases it is necessary to remove the allergen from your environment. Treatment of severe allergic and drug dermatitis should be carried out only under the guidance of a physician.
In mild cases, antihistamines (tavegil, cetrin, suprastin, claritin), vitamins and dietary nutrition are prescribed internally. If necessary, sedatives are prescribed. To quickly remove allergens from the body, a course of Enterosgel is recommended. External treatment includes ointments, baths, compresses and lotions. To alleviate the condition, use baths or lotions from medicinal plants (chamomile, chamomile, hops, St. John's wort, dandelion).
After the wet procedure, you need to blot your hands with an ironed soft cloth and apply the treatment. Among non-hormonal products, Fenistil ointment, Propolis ointment, Radevit ointment, Skin-cap cream and aerosol are used. All these drugs reduce itching, have an anti-inflammatory and softening effect, and accelerate recovery processes. Fenistil ointment is a modern remedy with a delicate texture that instantly alleviates the condition and accelerates healing.
Propolis ointment (bee glue) promotes the growth of granulations, accelerates the process of epithelization of wound surfaces, it is applied 1-2 times a day. Radevit ointment contains vitamins A, E, D3, not only reduces itching, it softens and moisturizes the skin, enhances its protective function. When using Radevit, you can forget about dry hands. Before applying the ointment to open ulcers and wounds, treatment with disinfectant liquids (chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide) is necessary. In case of severe peeling, apply an ointment bandage.
Skin-cap cream or aerosol (its analogue Friederm zinc) is a zinc preparation created for the treatment of psoriasis. But practice shows that due to its powerful antipruritic, anti-inflammatory and hydrating effects, the drug has proven itself to be effective against dermatitis. However, with prolonged and excessive use of the drug in the form of an aerosol, persistent dryness and irritation of the skin occurs (you need to switch to cream). Another limiting factor in using Skin Cap is its high cost. Skin cap is not recommended for use in combination with hormonal ointments or creams.
Among hormonal ointments, Flucinar (sinaflane), Ftorokort, Lorinden (A, C), as well as the more modern and effective Advantan, Celestoderm, Triderm, Belosalik, Lokoid, are widely used. For dermatitis complicated by bacterial, viral or fungal infection, the use of hormonal ointments is contraindicated. Their use must be a course course and must be agreed with a doctor, due to contraindications and limited combination with other drugs.
• Diagnosis of diseases by symptoms • Peeling and crusts on the skin, causes, what to do, which doctor to see
Peeling is almost always accompanied by itching. When the contents of blisters, blisters, and pustules dry out, hardened crusts form. Try not to scratch them - this can lead to increased peeling, spreading and infection. Take antihistamines, hydrocortisone ointment or calamine lotion.
Causes of Dry Spots
Since this phenomenon can be either permanent or temporary, its nature can have different causes.
Thus, the constant presence of scaly spots on the skin (especially the face and hands) occupying a large area can be both a consequence of general dehydration of the senile body, and the result of living in an area with a constant sharp wind (sultry or icy).
In both cases, the reason for the appearance of dry skin over a large area is its desiccation, but if it is impossible to get rid of the first reason, then moving to a more “friendly” place is enough to eliminate the second.
The appearance of the same focal “desertification” of the skin due to its overdrying is also caused by the existence of a certain psychotype of personality – prone to creating and living in chronic stressful situations.
A few sleepless nights spent at the computer are quite enough to cause general dryness of the face and hands.
This condition occurs due to the existence of a long-term vasospasm (due to stress) in combination with a slight but prolonged effect of the device’s radiation on the areas of the skin accessible to it.
Local disorders of blood and lymph circulation, caused by reasons of either a reflex or dysmetabolic nature, can lead to the appearance of smaller foci or single spots.
Thus, the same work on the keyboard with prolonged exposure to certain skin zones of the fingers can cause a reflex slowdown in the circulation of biological fluids in the depths of a certain skin zone - the consequence will be a transient (but rather long-term) disorder of its trophism, evidenced by a change in the surface layer.
Dysmetabolic (caused by metabolic disorders with the accumulation of toxic waste products) causes of trophic disorders of the skin include almost any disease or condition with a long or chronic course - from regular constipation to diabetes, from pregnancy to menopause, from cholelithiasis to chronic ( complicated) hemorrhoids.
Lupus spots
Diseases of a systemic nature deserve special mention, the external “passport” of which is the characteristic damage to certain areas of the skin. For example, a lupus “butterfly” on the face is a red, dry spot that does not itch at any stage of its evolution.
The consequence of the presence of mental pathology (along with the phenomena of depression of the nervous system) are:
- neglect of hygiene standards;
- change in the vivacity of the body’s response to changes in the conditions of the social and natural environment;
- digestive disorders leading to vitamin deficiencies;
- parasite carriage (including giardiasis, ascariasis, demodicosis);
- tendency to allergic manifestations;
- infection with lichen infection.
Each of these factors individually, or their entire combination, can cause dry spots on the surface of the skin.
Video from Dr. Malysheva:
The main causes of skin peeling and crust formation, what to do, which doctor to see
Psoriasis
Peeling in psoriasis manifests itself as pink spots slightly raised above the skin level with a diameter of 5 mm to 5 cm. When scratched, they become covered with silvery scales.
Contact a dermatologist immediately. There is no effective treatment at home.
Atopic and contact dermatitis
Peeling in atopic and contact dermatitis is manifested by the following symptoms. The skin becomes inflamed, itchy, flaky, and sometimes weeping occurs. Atopic dermatitis often affects the elbows and popliteal folds, and contact dermatitis often affects the hands.
For treatment, use hydrocortisone ointment. If there is no improvement after a week, consult a dermatologist. Antibiotic ointment may be needed.
Dermatomycoses
Dermatomycosis - red spots with peeling in the center appear on the skin, which slowly increase in diameter. With inguinal ringworm, scaly pink (sometimes weeping) spots appear in the groin folds and on the inner thigh.
Use antifungal ointment. If there is no improvement, consult a dermatologist.
Seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema is scaly crusts on the scalp, often with an irritating discharge. Peeling may also appear on other areas of the skin.
Wash your hair with an antifungal shampoo containing selenium.
Pityriasis rosea (pityriasis rosea)
Pityriasis rosea are oval red spots 5-20 mm in size raised above the skin, arranged in a herringbone pattern. At first, one large spot usually appears. The spots disappear after a month and a half. Possible cause is viral infection.
There is no specific treatment. Regresses spontaneously.
Skin like orange peel
Almost every woman and girl faces cellulite problems. Cellulite is a violation of microcirculation in the subcutaneous fat layer, as a result of which fat accumulates, creating reserve reserves. Stagnation of fat deposits occurs. As a result, we see orange peel on the skin.
This problem can occur in both thin and plump women. And this is caused by poor nutrition, high consumption of animal fats, a sedentary lifestyle, stress, tight clothes, and an unhealthy lifestyle.
To avoid the appearance of orange peel on the body, you need to take your health very seriously, play sports, eat more vegetable fats, fruits, vegetables, and visit baths and saunas. You should take a contrast shower every day, and it is advisable to use stiffer washcloths. They promote good blood circulation.
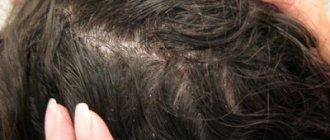
Crust on the scalp
The formation of a crust on the scalp indicates that a person has a skin disease, it could be dermatitis, mycosis, seborrhea. The appearance of crusts on the head occurs as a result of excessive sebum secretion, blockage of the sebaceous glands occurs and an inflammatory process occurs on the skin; this can be facilitated by any fungal disease, allergies, or insufficient hygiene of the scalp. In children from birth, the appearance of a crust on the head is considered normal; they need to be cleaned off and they will go away. In adults, this is a manifestation of the disease, and it is necessary not to contact a doctor; now there is a very large selection of shampoos and products for seborrhea. If you do not start treatment, there may be a complication, since the crusts are layered on top of each other, the hair breaks off, falls out and bald spots appear; this is fraught with the addition of a fungal infection, which is difficult to treat.
The skin on the face is like a crust
Enlarged pores on the face bother women with oily skin. Those with oily skin have a hard time, the pores expand due to the large secretion of sebum, the pores become very clogged, comedones and pimples form, it looks very unsightly on the skin. As a result, it is very similar to the peel of an orange. Teenagers usually suffer; for some it goes away in later life, and for others it doesn’t. If you do not start caring for such a person correctly, you can end up with dermatitis. To help your skin, you need to use lotion every day to cleanse and tighten pores, eat less sweets and animal fats. If you cannot cope with this problem yourself, it is better to consult a doctor.
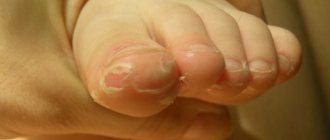
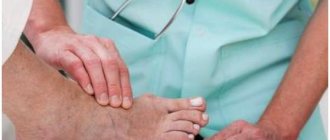
Crust on the skin of the feet
A crust on the legs can occur due to a fungal or allergic disease, it can be eczema, dermatitis, seborrhea. First, blisters appear that itch, then a weeping wound and a sore in the form of a crust appear. The disease can occur due to stress, weakened immunity, the presence of a fungal infection, or allergic reactions. You should not self-medicate; it is better to consult a dermatologist, since self-medication can lead to a chronic course of the disease. A timely visit to a doctor will help you quickly get rid of the disease.
Uncommon causes of skin peeling and crusting
- Lichen planus (itchy, scaly papules on the legs)
- Solar keratosis
- Discoid eczema
- Pityriasis versicolor (lichen versicolor) (large scaly patches caused by a fungal infection)
- Guttate psoriasis (scaly papules)
Cracks, blisters, wounds, crusts are symptoms of an eczematous inflammatory process. External signs demonstrate one or another stage of the inflammatory process in its classical manifestation.
But eczematous rashes are characterized by polyformity (variety), so often the patient exhibits all of the above symptoms at the same time. Therefore, when diagnosing a disease, a dermatologist is guided by the number of skin rashes of one type or another.
Types and causes of rashes
Depending on the cause of the experienced condition, the age of the patient, his living conditions, habits and other things, the consequences of both acute and chronic problems with the body “pop up” in the form of spots of various colors, which (very roughly) can be divided into red, white or dark.
Reds
This coloration of the spots indicates rapid processes occurring in the skin, requiring for their “burning” a significant influx of blood, ensuring the delivery of both nutritious and protective substances to the lesion. Its reverse outflow (no less rapid and intense) must organize the removal from the source of the struggle of substances formed in the microstructures of “wounded” and “killed” tissues.
The appearance of red spots with a dry surface may occur due to the occurrence of a disease in the body:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- mycotic (fungal);
- skin;
- neurological
Or they can be an echo of the process:
- allergic;
- systemic;
- oncological
Spots of viral origin include those with:
- rubella;
- measles;
- smallpox-chickenpox.
The appearance of the rash, the nature of its spread throughout the body, and the accompanying signs of intoxication and dehydration are typical for an infectious viral disease.
For bacterial rashes, a distinctive feature is a tendency to suppuration, while for allergic rashes there is significant itching and severe swelling of the affected area (it itches).
A mycotic (caused by a fungus) spot is a rough, round formation with a more or less “curly” (due to peeling) “roof”, which, with its leisurely movement along the surface, distracts attention from the simultaneous spread of its body also in the layers adjacent to it.
Spots due to so-called skin diseases (more precisely, skin rashes due to neurological diseases) - eczema, psoriasis - are distinguished by the simultaneous presence, next to already stabilized dry areas, of zones with actively occurring changes, where in parallel there exist:
- manifestations of maceration;
- formation of blisters and blisters;
- crust formation;
- tissue scarring.
The most indicative of the category of benign neoplasms is a dry, smooth spot of hemangioma with a slightly bumpy surface, which looks like a mole that has grown to a bizarre shape from red to cherry color. Pigment spots can also have the same color - a consequence of hormonal disturbances in the body; their distinctive feature is that they do not change color when pressed.
White
Due to the melanin pigment responsible for a particular color of the skin (under the influence of ultraviolet rays it acquires a darker color), cases of dry white zones appearing on its surface are variants of either melanin deficiency or its destruction due to:
- vitiligo;
- one of the lichens (pink, or Zhiber, or pityriasis versicolor, also called colored, sunny, beach);
- one of the forms of leukoderma (syphilitic, medicinal or other).
Photos of different types of lichens:
girdling
Pityriasis
Pink
Shearer
The most studied is focal lightening of the skin as a consequence of the settlement of pityriasis rosea on it, immediately forming a large area of the main focus, surrounded by many daughter screenings, oriented along the lines of natural stretching of the skin.
The spot is rough to the touch, does not cause negative sensations (itching, pain), is clearly demarcated from the adjacent healthy skin, its reduction (reverse development) does not require significant effort from the body, and after restoration of immunity, the color of the tissues is completely restored.
Small, light-colored lesions - round spots of pityriasis versicolor also easily disappear when adequate metabolism is restored in the body.
The etiology of vitiligo still remains a mystery to the scientific world (viral, endocrine, dysmetabolic theories are suggested), but the lightening of significant areas of the skin, due to completely white spots of rounded outlines coming out of nowhere, when merging, form bizarre shapes, the level and condition of the surface of which do not differ in any way from healthy skin, is an irreversible process (hair in the affected area also turns white).
Dark
The appearance of spots on the body from various shades of brown to almost black may indicate:
- the onset of senile degeneration of the skin;
- the course of pregnancy with a pronounced hormonal “tilt” towards focal darkening on the face;
- presence of melanoma;
- fungal infection.
Separately, it should be explained that the essence of brown and black moles is the deformation of skin structures, which have already been formed at the time of birth and are not subject to further transformations. This is their main difference from melanoma, a highly aggressive tumor that also forms dark brown (to black) lesions on the surface (but with the main body located deeper in the tissue).
Age-related “spots” on the skin (protruding significantly above the surface, with a brown, often deeply cracked surface, with hair growing through them) are areas of deep modification of the tissue due to disorders of trophism, blood and lymph circulation, which have reached a dead-end stage.
Pigmentation spots on the face and body of pregnant women differ from other skin only in their more intense coloring (no feelings other than aesthetic ones, not upsetting), after pregnancy they can:
- brighten;
- disappear completely;
- remain unchanged and in the same shape.
Depending on the conditions of “growth” of multi-colored lichen, its foci - dry plaques in some cases have the appearance of spots of color not white, but light brown - but its unchanged attributes always remain the tendency for them to merge and peeling of the surface of the formation.
Blisters - eczema in the early stages
Small blisters scattered over inflamed, swollen red areas of the skin are the first sign of incipient inflammation in the dermis. The size of the papules is often small, resembling millet grains. In rare cases, large blisters of red-pink or scarlet color are diagnosed. In most cases, the rashes are very itchy.
The papular stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of nodules raised on plaques. It quickly develops into a vesicular process, when serous contents form in the cavity of the blisters.
The limbs are a favorite place for localization of nodular rashes. When eczema is diagnosed, blisters on the hands and feet are most often diagnosed on the phalanges of the fingers, hands, palms, feet and legs. The rash appears much less frequently on the body and face.
Lotions and cold compresses with Burov's solution are a treatment that helps narrow blood vessels and reduce inflammation. Procedures are prescribed only if the blisters do not become wet.
Eczema, crusts on the skin
This symptom appears after the weeping stage, when the blisters burst, forming pinpoint wounds from which serous exudate oozes. Erosions dry out, forming crusts on the skin. Eczema progresses to the crustose (crust) stage.
With sufficient oxygen access, the process accelerates. If crusts form against the background of microbial dermatitis with weeping, then pus may accumulate under them. Thin, greenish-yellow formations often thicken and flake off.
The main goal of treating the crusted stage is to improve local blood circulation and relieve inflammation.
Cracks and wounds due to eczema
With eczema, cracks in the hands appear in the dry form.
Tilotic eczematous dermatitis is a form of the disease in which superficial and deep fissures are one of the main diagnostic signs. Rashes, burning, redness, weeping, itching are rare complaints of patients suffering from the horny form of the pathology. The disease is more often diagnosed on the heels and palms of women during menopause.
The microbial intertriginous form of the disease also tends to form cracks against the background of weeping, hyperemia, and burning. More often, defects form in large skin folds in the armpits, groin, elbow, and less often under the knees.
When diagnosed with dry eczema on the hands, cracks most often appear in the spaces between the fingers, the inner or outer part of the fingers at their bends, where the skin is thinnest and experiences the greatest tension when moving the hand.
Linear tears come in varying depths, from small cracks on the fingers to a deep tear like a gaping wound. Eczema in such a manifestation requires careful care and immediate treatment. Wounds and lacerations not only cause pain and discomfort for the patient, reducing the quality of daily life. This is an open gate for pathogenic microorganisms that can cause bacterial infections of the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. Bacteria trapped in a deep wound can cause blood poisoning.
Skin of the face
Pathological processes can affect the face area, as well as the ears and neck. The skin of these areas begins to itch and become crusty.
Reference! The crusts are usually white, sometimes with a yellowish tint, but if a bacterial infection occurs, they acquire a yellow-green color.
Rash on face
Causes:
- dry skin due to severe frost, prolonged sun exposure;
- medications;
- allergies due to poor nutrition, use of low-quality decorative cosmetics;
- undergoing procedures in a beauty salon that have a rough effect on the epidermis and dermis;
- fungal diseases;
- digestive, endocrine and autoimmune disorders.
One of the causes of damage to the area around the eyes and the scalp is demodicosis. It is caused by a mite - Demodex, which parasitizes on the face, in places covered with hair. Causes unpleasant sensations, eyes, eyebrows, ears itch very much. Scratching becomes covered with crusts.