Why do black spots appear on the inside of the cheek?
Such a neoplasm often occurs on the mucous membrane after injury. A child bites the delicate tissue of his cheek while playing or accidentally falling. At the site of the bite, a small hematoma remains, resembling a lump or a black dot. This is a common bruise or bruise located inside the mouth.
- when chewing a hard toy or foreign object;
- while eating;
- with bruxism (uncontrolled grinding of teeth during night rest);
- during the period of eruption of chewing molars or sharp fangs.
Often, black dots on the inside of a child’s cheek are a sign of an incorrect bite. If the teeth are positioned asymmetrically relative to each other, constant friction and pressure on the mucous membrane is possible. In this case, miniature hematomas are formed in the middle at the level of the dentition.
The problem persists even after the braces are installed. Sometimes the orthodontist violates the technology or does not tighten the structure properly. When chewing or talking, it scratches the gums and leaves behind black bruises. In this situation, it is necessary to remove all the pads and repeat the procedure.
If such black spots appear regularly on the cheek, the dentist checks the integrity of the teeth. A love of sweets and poor nutrition often lead to caries of baby teeth. A destroyed crown with a sharp edge injures the mucous membrane and provokes the formation of a hematoma. Such molars should be filled, white spots on the enamel should be treated, and it should be strengthened with fluoridation.
If dark spots appear traumatically, no special treatment is required. Once the cause is eliminated, they will certainly resolve without a trace. Sometimes the baby bites hard on the mucous membrane and a lump filled with ichor or blood remains on it.
A repeated bite leaves an open wound on the cheek that can become infected with bacteria. Therefore, large bruises inside the cheek should be treated with special ointments:
- Troxerutin;
- Troxevasin;
- Heparin gel;
- Hepavenol.
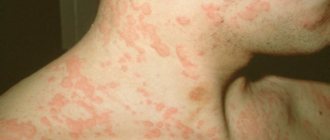
Red spots on the face - causes
A baby's face may develop rashes for various reasons. The most common of them are the following:
- trauma during childbirth;
- infectious diseases;
- various allergic reactions;
- insect bites;
- problems in the functioning of internal organs (liver, intestines, biliary tract, cardiovascular system);
- change in climate, temperature, etc.
Bright spots on the face of a newborn can form due to damage to capillaries and blood vessels as a result of their compression during childbirth. They manifest themselves very strongly during screaming and crying. As a rule, they do not require serious medical intervention and disappear on their own in the first year of the baby’s life, but it is still worth showing the child to a specialist.
Why do red spots appear on the face?
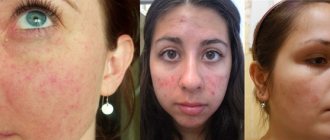
Redness of the facial skin can be caused by a number of reasons. This defect, unpleasant from an aesthetic point of view, can be inflammatory or allergic in nature, result from the location of blood vessels at a short distance from the surface of the skin, or indicate vitamin deficiency. These are not all the factors that can cause a problem.
Often, people suffering from various skin problems simply hide them with the help of cosmetic products, despite the fact that the appearance of skin rashes can be caused by malfunctions of internal organs. Reasons why red spots appear on the face in adults and children:
- Cosmetology – sensitive skin.
- Physiological - when the blood vessels are located close to the surface, the skin of the face turns red during physical exertion or nervous tension, under the influence of meteorological phenomena: sunlight, wind, due to changes in blood pressure or when taking medications.
- Allergic – allergies can be caused by food, cosmetics, dust, and medications.
- Dermatological - red dots and spots refer to the symptoms of psoriasis, eczema, lichen, demodicosis and a number of other skin diseases.
- Systemic - red dots on the skin of the face can be a sign of hormonal diseases, pathologies of the liver and kidneys, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous and vascular systems.
In cases where the face is covered with red spots, look carefully at where they are concentrated. If the skin around the eyes is covered with a rash, this may be the result of an allergic problem or a jump in blood pressure; a reddened tip of the nose may indicate a malfunction of the heart and circulatory system. Redness of the area around the mouth is associated with deterioration of the urinary system, such as the gallbladder.
Red scaly spots on the face
The shape and size of red, scaly spots on the face depend on the reasons that caused their appearance. They can itch, itch, and flake. Common areas for red dots and spots are the forehead and cheeks. The skin in the area of redness becomes dry and may crack and flake. If these manifestations are the result of an allergic reaction, there is a feeling of tightness of the skin, and the spots are very itchy.
Red spots appeared on the face and itched
To diagnose the causes of spots and spots, go to a dermatologist. With a high degree of probability, the following tests may be required:
- general blood test;
- allergy testing;
- biochemical blood test;
- scraping.
Infectious diseases
Pathogen: parvovirus B19
Method of transmission: airborne. Most often, the infection occurs in children in organized children's groups - nurseries, kindergartens and schools.
Immunity: after illness - lifelong.
Incubation period: 6-14 days.
Infectious period: the incubation period is the entire period of the disease.
Manifestations: it all starts like a normal ARVI. Within 7-10 days, the child feels some discomfort (sore throat, slight runny nose, headache), but as soon as he “gets better,” a red, confluent rash appears on the cheeks, most reminiscent of mark from a slap.
At the same time or after a few days, rashes appear on the torso and limbs, which form “garlands” on the skin, but do not itch. The red color of the rash quickly changes to bluish-red. Over the next two to three weeks, the temperature remains low, and the rash appears and disappears, depending on physical activity, air temperature, contact with water, etc.
Treatment: there is no specific treatment, only symptomatic therapy. The disease goes away on its own, complications are extremely rare.
Often, red spots on a child’s face are formed as a result of infectious diseases:
- rubella;
- chickenpox;
- measles;
- scarlet fever.
Redness also appears with erythema infectiosum. A bright rash appears on the patient's cheeks, and the area around the mouth remains pale. With erythema nodosum, swollen spots are observed on the face, forearms, and legs; with chicken pox, blisters are observed throughout the body. After a few days they burst, leaving behind itchy scabs. Red spots on the face also occur with viral hepatitis, psoriasis, dermatomyositis, systemic lupus, pityriasis rosea and other diseases.
This is an incomplete list of infectious diseases that are characterized by skin redness. Treatment of any of them should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, so for any rash it is worth showing the child to a specialist to accurately determine the problem and timely prescribe treatment, if necessary. A visit to the doctor is the only right decision in such a situation.
Red dots on a child's face
If red dots appear on your baby's face, this is a reason to immediately visit a pediatrician. In the summer, a small child may suffer from insect bites. Other causes include infectious diseases and allergic reactions. In very young children, red dots on the face can be a consequence of birth trauma. Sometimes children's skin reacts to climate change in this way. Infections that cause a red rash on a child’s face are:
In addition to the fact that the child may develop a rash, infectious diseases cause a high temperature. With a timely diagnosis, medicine can successfully treat any infection. If the doctor suspects an allergy, the child will have to take tests to identify allergens. In this case, antihistamines will help relieve symptoms.
Causes of red dots in the mouth
If redness or a pink rash forms in the child’s mouth, the help of a pediatrician or otolaryngologist is necessary. This is not always related to dentistry. Sometimes this is how infectious diseases of the larynx, a malfunction of the immune system, or serious complications of viral inflammation manifest themselves. First of all, common allergies should be ruled out. According to statistics, every third baby is predisposed to this unpleasant pathology.
| Severe form of ARVI, influenza | High temperature is one of the causes of inflammation in the larynx. If it persists for more than 3 days, red dots appear on the palate and inside of the cheeks. These are hematomas from burst capillaries. |
| Herpangina | In the first days of the disease, the child’s entire throat becomes covered with whitish sores. Once ripe, they burst and turn into bleeding bumps. Inflammation is indicated by chills, enlarged lymph nodes and complaints of painful swallowing. |
| Tonsillitis | Bacterial sore throat, in which red or pink dots are a prominent symptom. The disease is caused by bacteria such as staphylococci. It often causes complications in the upper lobes of the lungs, bronchi and nasopharynx, leading to chronic otitis media. |
| Herpetic stomatitis | A common problem in children over 3 years of age. The herpes virus, when immunity declines, manifests itself in inflammation of the mucous membranes. Red dots are aphthae, which are filled with clear liquid and contain exudate (pus). |
| Chicken pox | The disease is quickly transmitted by air in children's groups. Numerous red papules cover the child's head, spread to the chest and back, and affect the limbs. In severe cases, they occur on the inside of the cheeks or genitals. |
With herpes stomatitis, aphthae in the mouth are very painful. They provoke itching and burning, interfere with eating and distract from the game. Small sores appear on the edges of the lips, palate or larynx. The child looks tired, is fussy a lot and sleeps poorly. Therefore, such red dots should be treated as early as possible.
- Acyclovir;
- Gerpevir;
- Zovirax;
- Oxolinic ointment.
On the recommendation of a specialist, antiviral drugs are taken orally and strengthen the child’s immunity with vitamins and bifidocomplexes. Antihistamine drops and syrups help relieve itching: Zodak, Suprastin, Fenistil.
Painful areas are wiped with herbal decoctions without alcohol. Chamomile, sage, bay leaf and flax seeds are used to prepare warm medicine. On average, the disease lasts from 10 days to 3 weeks, sometimes developing into a chronic form.
Causes of discoloration
Most often you have to deal with red spots, pimples, dots - in the form of single elements or a diffuse rash. This situation occurs in many people, but to determine the cause of what is happening, the baby should be shown to a pediatrician. In this case, there is a possibility of both fairly banal and harmless conditions and serious pathology requiring qualified assistance.
In a newborn and infant
Birth hemangiomas
If you notice red or bluish spots on your baby's face in the first days or weeks after birth, you may think about vascular malformations - infantile hemangiomas. They are also called birthmarks. These are benign anomalies or malformations of skin vessels in which endothelial hyperplasia occurs.
The exact cause of hemangiomas is unknown; a violation of embiogenesis is suggested when the fetus is exposed to adverse factors during pregnancy:
- Viral infections.
- Bad habits.
- Taking medications.
- Environmental pollution.
The theory of hormonal disorders is confirmed, since vascular tumors are more common in girls. Hemangioma is a flat or slightly elevated soft cavernous formation of various shapes, ranging in size from 1 to 15 cm or more. During the first six months, the spot grows rapidly, but then the process slows down, sometimes the tumor can disappear on its own.
Hemangioma on the face is a significant cosmetic defect. But the main danger is frequent trauma and bleeding. Large tumors compress neighboring tissues; similar vascular growths can be observed in the brain, which poses a serious threat to the child.
Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor, but its development can be accompanied by a number of complications.
Small spots for prickly heat
Miliaria is considered a fairly common occurrence in infants. Due to imperfect thermoregulation and defects in care during prolonged exposure to physiological secretions, the skin responds with irritation in the form of small pimples. It usually appears in natural folds on the neck, face, back and chest.
Most often seen in young children, miliaria crystalline appears as a small, pale pink rash in the form of blisters that soon burst, leaving behind irritation and peeling. The process does not bring any subjective discomfort to the child; sometimes slight itching is possible.
Spots from diathesis
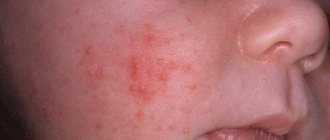
If red spots appear on the baby's cheeks, you should think about diathesis. This is a constitutional anomaly, indicating the predisposition of the child’s body to reactions of a certain type. Diathesis is characterized by other signs:
- Peeling of the skin of the cheeks.
- Seborrheic scales on the head.
- Diaper rash in the folds.
- Itchy nodules on the body.
Characterized by reduced reactivity of the mucous membranes, which is manifested by inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, oral cavity, and conjunctiva. Children with diathesis are overweight and look pasty.
Skin breaks out in rashes due to infections
Childhood infections are a separate cause of facial rashes. Skin manifestations in the form of exanthema syndrome are present in many diseases of viral and bacterial origin:
- Corey.
- Rubella.
- Chicken pox.
- Scarlet fever.
- Roseole.
In this case, the rash occurs not only on the face, but spreads throughout the body, having certain characteristics. With chickenpox, it is represented by vesicles with transparent contents, measles and roseola appear as maculopapular elements, scarlet fever - as pinpoints. In the latter case, the rash is concentrated in the folds of the skin; rubella is characterized by damage to the extensor surfaces of the extremities.
The pathology is infectious in nature, and therefore is accompanied by signs of intoxication in the form of fever, malaise, and headache. In some diseases (measles, rubella), catarrhal symptoms of the upper respiratory tract (runny nose, cough, sore throat) are observed; scarlet fever is accompanied by a sore throat. A typical sign of rubella is enlarged posterior cervical and occipital lymph nodes.
Rashes on the face due to childhood infections vary in nature and are accompanied by additional symptoms.
In a teenager
Redness due to acne
Features of adolescence make their own adjustments to the causes of red spots on the face. Changes in hormonal levels lead to the appearance of acne, which is caused by increased secretion of the sebaceous glands and blockage of their ducts. Inflammatory acne may appear as papules, pustules, or subcutaneous nodules. A mild form of acne is manifested by single elements, but in severe cases they become multiple and deep, with purulent or serous-bloody discharge, leaving behind scars.
Other diseases
Symptoms of various dermatological pathologies - atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, demodicosis - may appear on the facial skin of adolescents. Inflammatory foci must be differentiated from autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus, vasculitis). The presence of a hemorrhagic rash requires the exclusion of thrombocytopenic purpura and leukemia. It is worth taking into account such factors as mechanical injuries, allergic reactions (including against the background of helminthic infestations), and excessive insolation.
Red spots due to allergies
Allergies in children can develop as a result of exposure to various types of allergens. The most common of them:
- Food. Children often have an allergic reaction to citrus fruits, chocolate, honey, and strawberries. To accurately identify the allergen, you can take a special test that will help determine the product that causes such a reaction. In some situations, it is enough to carefully observe the baby to identify the product that causes redness.
- Mom's nutrition. In an infant, red spots may appear on the face (usually on the cheeks) if the nursing mother does not follow a diet. If a breastfed baby has spots on his face, smoked meats, citrus fruits, chocolate, fish, strawberries, honey, nuts, mayonnaise, mustard, tomatoes, eggs, and mushrooms should be excluded from the diet.
- Medicines. Allergies can occur to medications. If your child is currently taking medications and a rash appears, you should immediately inform your doctor. In some cases, taking anti-allergy medications is sufficient to eliminate the problem; sometimes it is necessary to discontinue the medication.
- Cold, temperature changes. Some children sometimes develop allergies to cold. Exposed areas of the body - face, hands - become covered with red spots that cause itching. Treatment involves minimizing exposure to the cold. The reaction to cold, changes in temperature appear in the autumn-winter period.
- Plant pollen. Rashes often occur during the flowering of plants that cause an allergic reaction. To eliminate the problem, it is worth minimizing contact with the allergen. According to indications, doctors prescribe antihistamines to eliminate symptoms.
- Care products. An allergic reaction can occur to skin care products, washing powder, and household chemicals.
- Certain types of fabrics, pet hair, dust and others.
If, after eliminating the irritating factor, the red spots on the face disappear, most likely an allergy has occurred. It is worth conducting a thorough analysis of the diet and hygiene procedures to prevent the problem from occurring in the future.
Reasons for appearance
The circulatory system in the body delivers oxygen and nutrition to all organs and cells. The smallest vessels (capillaries) located in the subcutaneous layer of the face are especially sensitive and thin. Their damage can be caused by any effort that is accompanied by overexertion. Small red dots appear on the surface layer of the skin at the site of hemorrhage. Some people confuse petechiae with heat rash , but they are two different things. Heat rash is also located on the back and chest area. It looks more like red pimples.
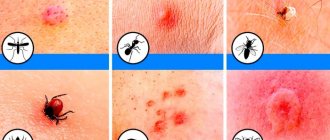
The appearance of petechiae is often preceded by the following unpleasant conditions:
- Coughing. With a strong persistent cough, increased pressure occurs in the vessels of the face, which causes their damage. Small red dots may appear on the face and neck.
- Vomit. During an attack of nausea and vomiting, a person experiences muscle strain, which also causes rupture of small vessels. Especially if the vomiting is profuse and repeated. Therefore, it may well be accompanied by the appearance of petechiae.
- Heartbreaking crying, sobbing. Another reason for the appearance of small blood spots in the face area. They are caused by the same excess muscle tone.
- Allergy. This pathology is often accompanied by manifestations on the skin, including in the form of petechiae. An allergic reaction may occur to medications or food.
In addition to these reasons, the appearance of red dots on the face can be caused by impaired blood clotting. Normally, a blood clot should immediately form at the site of damage to a small vessel, preventing further bleeding. If this does not happen, facial petechiae occur. Sometimes this phenomenon is caused by taking anticoagulants, for example, aspirin or heparin. Most often in this case, red dots appear under the eyes or on the cheeks; they go away on their own after a few days.
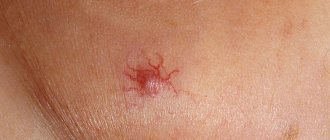
Spider veins on the face are a symptom of rosacea (dilated capillary network). Couperosis occurs as a result of impaired blood microcirculation. A red dot under the eye, on the cheeks and lips may be a hemangioma - a vascular tumor. It usually protrudes slightly above the skin and looks like a mole. In this case, the red dot on the face does not go away on its own. Hemangiomas are harmless and safe as long as they do not bleed or grow. The exact reasons for their appearance are unknown to medicine.
White dots with stomatitis
The easiest way to diagnose white spots on the inside of a child’s cheek. In 95% of cases it is candidiasis or aphthous stomatitis. Milky inclusions and spots are easy to notice when examining the oral cavity. There is always redness and slight itching around them, and an accumulation of cheesy plaque.
To quickly stop the disease, you should carefully treat the baby’s mouth with antiseptics at least 3 times a day:
- Miramistin;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Lugol's pharmaceutical solution with iodine;
- warm water with soda.
Red dots appear due to yeast activity. Therefore, 4-5 times a day, the inside of the cheeks is wiped with Candida solution, Levorin or Nystatin ointment. If the aphthae is very itchy, it is recommended to give the small patient antihistamines: Diazolin, Tavegil, Eden.
For children over 5 years old, Decamine caramel is offered as a convenient way to treat candidiasis. The drug dissolves easily like a regular candy and leaves an invisible film of antifungal agent. The pathogen quickly dies, discomfort and pain in the mouth stops.
You should definitely boost your immunity with vitamins, complexes with Echinacea purpurea extract and propolis. Light herbal decoctions without adding alcohol based on calendula and chamomile flowers are allowed as folk recipes. The gums and cheeks are smeared with a paste of honey and aloe pulp, and wiped with sea buckthorn oil.
Red rashes and peeling
Children's skin is sensitive to various types of irritants. If the spots are accompanied by peeling, the cause may be:
- wind;
- water;
- Sun;
- cosmetical tools;
- cold.
To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to remove the irritant that caused the redness and peeling. You can soften the skin with cream after first treating problem areas with chamomile infusion. If the problem does not go away, you should contact a specialist.
Chickenpox, or chickenpox
Pathogen: Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV).
Method of transmission: airborne. It is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person by talking, coughing, or sneezing.
Immunity to chickenpox: lifelong. Produced either as a result of illness or after vaccination. In children whose mothers had chickenpox or were vaccinated against it, immunity to chickenpox is transmitted from the mother in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: from 10 to 23 days.
Infectious period: the entire period of the rash is 5 days after the last rash.
Manifestations: red dots appear simultaneously with a rise in temperature. However, sometimes the temperature may remain normal or rise slightly. The spots very quickly turn into single vesicles filled with a clear yellowish liquid. Soon they dry out and become crusty. A distinctive feature of chickenpox is a rash on the head under the hair and on the mucous membranes (in the mouth, on the eyelid, etc.). Very often this rash itches.
Treatment: chicken pox goes away on its own, so treatment can only be symptomatic: lower the temperature, treat the itchy rash with brilliant green (so that by scratching the blisters, the child does not introduce additional infection there), give an antihistamine to make itching less. You can swim if you have chickenpox! But at the same time, you should not rub the affected areas; instead, you need to gently blot them with a towel.
Important: you need to use brilliant green or other dyes (fucorcin, etc.) in order not to miss the next rash, because only old spots will be smeared. It is also easier to track the appearance of the last outbreak of the rash.
When to contact specialists
If your child has redness on his face or other parts of his body, you should contact your pediatrician. After the examination, if necessary, he will give referrals to specialized specialists:
- infectious disease specialist;
- allergist;
- dermatologist;
- neurologist and others.
After a thorough examination, after interviewing the parents, the specialist will make a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. To accurately identify the causes, it is worth analyzing the situation and finding out why the redness occurred.
Every little detail is important in this matter, from nutrition in the next 24 hours to contacts with others and hereditary predisposition. Sometimes redness is evidence of serious problems in the body. Therefore, you should not resort to self-medication so as not to harm the child.
With various spots and rashes the situation is often ambiguous.
You should not delay your visit to a specialist, especially if the rash is combined with factors such as:
- bluish color of lips, skin, nail plates;
- disorder of consciousness, deterioration of attention;
- chest pain, tightness, difficulty breathing;
- increased heart rate;
- swelling of the eyes, throat, lips;
- excessive nasal congestion.
The symptoms described above may indicate serious problems that require immediate treatment. Don't be careless - take care of your children's health!
Herpes simplex
Causative agent: herpes simplex virus. There are two types: herpes simplex virus type I causes rashes in the mouth, type II - in the genital area and anus.
Method of transmission: airborne droplets and contact (kissing, shared household items, etc.).
Immunity: not developed, the disease occurs with periodic exacerbations due to stress or other infections (ARVI, etc.).
Incubation period: 4-6 days.
Contagious period: all the time of rash.
Manifestations: a few days before the rash appears, itching and soreness of the skin may occur. Then a group of closely spaced bubbles will appear in this place. The temperature rises extremely rarely.
Treatment: special antiviral ointments, for example with acyclovir, etc.
Important: use the ointment immediately after itching and pain occur, even before blisters appear. In this case, rashes may not occur at all.
What to do if red dots appear?
At the first manifestations of a rash, parents need to consult a qualified specialist:
- Symptoms may be a sign of measles, scarlet fever, rubella, chickenpox, syphilis, etc.
- Often the main culprit of red dots is a nursing mother, whose diet contains foods that provoke pathology.
- Often, if you exclude the consumption of allergens, the rash goes away within a few days without a trace and does not require medical intervention.
- When contacting the pediatrician, he is required to prescribe a full examination of the baby’s body.
Internal pathologies
Redness on the skin of a small patient can occur for the same reasons as in adults. Many people often perceive this problem solely as cosmetic, but this may indicate the presence of serious pathologies, so you should take your health and your child’s health with particular seriousness.
Redness of the face can be associated with various pathologies of organs and systems.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Redness can occur with vegetative-vascular dystonia, heart failure, and compression of the veins. With dystonia, with any irritating factor - severe anxiety, excessive physical activity - the face can completely change color. For heart problems, redness is combined with bluish lips, the tip of the nose, and nails. When veins are compressed, redness is localized in different parts of the body. It depends on which vessels are compressed and where exactly the blood flow is disrupted.
- Pathologies of the digestive tract. The reasons are quite extensive - low stomach acidity, gastritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers, chronic hepatitis, biliary dyskinesia and others. In case of pathologies of the functioning of the digestive system, redness, as a rule, forms on the cheeks, nose, and forehead. Very often they are expressed in the form of large spots of irregular shape.
- Endocrine diseases. Changes in facial skin color accompany diabetes mellitus and thyroid pathologies.
The skin may turn red due to a lack of vitamins A, C, E, B, as well as at elevated body temperature.
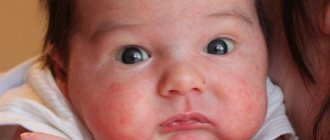
Red cheeks in a child - reasons
Possible causes of flushed cheeks include:
Erythema infectiosum
Erythema infectiosum is often called the fifth disease
, since it is the fifth of the six common viral exanthems of childhood described. A virus known as parvovirus B19 causes the infection. Some people call this condition "slapped cheek syndrome" because it causes redness in the cheek. Some children later develop a rash on their chest or neck. Other symptoms are similar to colds, such as a runny nose or fever, which often appear several days after the rash. Erythema infectiosum usually goes away on its own with few symptoms. In some adults and frail people, the condition can cause severe symptoms, such as joint pain that lasts for weeks.
Teething rash
Teething sometimes causes a red rash on the cheeks and chin. This occurs when a baby drools, which dries the skin, causing redness, irritation and cracking. The rash is usually harmless, but severe rashes may bleed, increasing the risk of infection. Parents can reduce the risk of teething rash by wiping drool from their baby's cheeks and face and applying a gentle moisturizer.
Cracked skin
Dry, irritated skin from dry air or extreme cold may appear red. Cracked skin is similar to a teething rash. Areas of skin exposed to cold air, such as cheeks and lips, are more susceptible to chapping. Children with eczema or dry skin are more prone to redness. Chapped skin may be itchy and painful, but it is not dangerous. Applying moisturizer to the affected areas may help.
Eczema
Eczema causes dry, red skin, but it's more than just dry skin. This condition is a complex disorder that causes inflammation of the skin. Skin inflammation sometimes develops in response to certain triggers, such as irritating soaps or foods. Eczema on the cheeks may appear as red or scaly patches. Children may also develop eczema on other parts of the body. Severe eczema can look very dry and even bleed. This condition also increases the risk of developing skin infections.
Skin infections
The entry of pathogens into the skin is accompanied by infection. This usually occurs when there is damage, such as a scratch, injury, or dry skin that cracks. Sometimes a skin infection can appear for no reason. One type of skin infection is phlegmon, which affects the deep layers of the skin, accompanied by redness and swelling. Sometimes red streaks appear as the rash spreads. The infection can appear on both cheeks, but it is more likely to affect one cheek.
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome
(from the English name Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease, HFMD), or enteroviral vesicular stomatitis with exanthema.
Pathogen: enteroviruses.
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral and airborne. The virus is transmitted from person to person through communication, conversation, and the use of common household items (dishes, toys, bed, etc.).
Incubation period: from 2 days to 3 weeks, on average about 7 days. Infectious period: from the onset of the disease.
Manifestations: first the temperature rises and stomatitis begins: rashes on the oral mucosa, pain when eating, excessive salivation. The temperature lasts 3-5 days, often accompanied by diarrhea, and in some cases a runny nose and cough. On the second or third day of illness, a rash appears in the form of single blisters or small spots.
Treatment: there is no specific treatment; symptomatic drugs are used to reduce fever and relieve pain during stomatitis. The disease goes away on its own; complications are possible only if a bacterial or fungal infection occurs in the oral cavity.
It is not easy to make a diagnosis of enteroviral vesicular stomatitis, because... The rash does not appear immediately and is very often regarded as a manifestation of an allergy.
Important: despite the active use of various painkillers in the treatment of stomatitis, the first few days it may be very painful for a child to eat. In such cases, it is good to use the most liquid food possible (milk, dairy products, milkshakes, baby food for babies, soups, etc.) and give it through a straw. Be sure to monitor the temperature of the food: it should not be cold or too hot - only warm.
Psychological factors
Redness often appears for psychological reasons. These include:
- stress;
- neuroses;
- depression;
- excessive emotional stress;
- excitement before important events;
- fears, uncertainty and others.
The redness may be continuous or in the form of large, uneven spots. A distinctive feature is that there are no traces of structural changes in the skin at the site of inflammation.
It is worth noting that even a healthy child’s face may periodically turn red and spots may appear due to excessive excitement or mental stress.
This is how the human body’s defensive reactions manifest themselves: when it gets excited and blushes, it seems more friendly, thereby reducing the potential danger.
Roseola
(sudden exanthema, sixth disease)
Causative agent: another representative of the glorious family of herpes viruses is herpes virus type 6.
Method of transmission: airborne. The infection spreads through talking, socializing, sneezing, etc.
Immunity: after illness - lifelong. Children under 4 months have immunity received in utero from their mother. Incubation period: 3-7 days.
Infectious period: throughout the illness.
Manifestations: sudden rise in temperature and after 3-5 days its spontaneous decrease. Simultaneously with the normalization of the temperature, a pink, small- and medium-spotted rash appears. It is located mainly on the torso and, as a rule, does not cause itching. Goes away on its own after 5 days.
Treatment: only symptomatic therapy - drinking plenty of fluids, lowering the temperature, etc.
The herpes virus worsens due to stress or infections, such as ARVI.
The disease goes away on its own, there are practically no complications.
Roseola is often called pseudorubella, because. the skin manifestations of these diseases are very similar. A distinctive feature of roseola is the appearance of rashes after a drop in temperature.
Important: as in the case of enteroviral stomatitis, a rash that does not appear on the first day of illness is often regarded as allergic. Sometimes it is really difficult to distinguish them, but an allergic rash, as a rule, itches quite a lot, but with roseola there should be no itching.
Rubella
Pathogen: rubella virus
Method of transmission: airborne. The virus is transmitted through communication, coughing, and talking.
Immunity: lifelong. It is produced either after an illness or after vaccination. For children whose mothers had rubella or were vaccinated against it, immunity to rubella is transmitted in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: from 11 to 24 days.
Infectious period: from the 7th day from infection until the complete disappearance of the rash, another 4 days.
Manifestations: temperature rises. A small, pale pink, non-itchy rash appears on the face, limbs, and torso, and at the same time the posterior cervical lymph nodes enlarge. The temperature lasts no more than 2-3 days, and the rash goes away on the 2-7th day from its onset.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy only: drinking plenty of fluids, lowering the temperature if necessary, etc. Children tolerate the disease easily, but adults often experience complications. Rubella is especially dangerous in the first trimester of pregnancy: the virus crosses the placenta and causes congenital rubella in the baby, which can result in deafness, cataracts or heart defects in the newborn. Therefore, everyone, especially girls, is strongly recommended to undergo vaccination against this disease.
Causes of red dots in children
Parents may also perceive redness and rashes as an allergic response to food, medications, etc. Then, the rash should be observed in many parts of the body; if there is none, there is no reason to worry.
- In any case, you need to exclude allergenic foods and monitor the process.
- You should also use only natural detergents - shampoos, soaps, dishwashing detergents, and wear clothes made from natural fabrics.
- With heat rash, red dots may appear on the face and other parts of the body.
- To eliminate the factors that provoke their occurrence, the baby needs to be bathed daily using medicinal herbs - chamomile, calendula, sage, or a weak solution of potassium permanganate should be added to the water.
If red blisters appear around the mouth of an infant and then begin to spread throughout the body, these are direct signs of Ritter's disease. The virus is transmitted through feeding if the mother has cracked nipples. Pemphigus with cloudy liquid may contain staphylococcus, streptococcus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Congenital pemphigus spots are often accompanied by pathology of the nail plates and vitamins and antibiotics are used as long-term treatment.
Measles
Pathogen: measles virus (Polinosa morbillarum)
Method of transmission: airborne. The unusually contagious and highly volatile measles virus can not only be transmitted through direct contact with a sick person, but also, for example, spread through ventilation pipes, infecting people in neighboring apartments.
Immunity: lifelong. It is produced either after an illness or after vaccination. For children whose mothers had measles or were vaccinated against it, immunity to measles is transmitted in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: 9-21 days.
Infectious period: From the last two days of the incubation period until the 5th day of rash/
Manifestations: fever, cough, hoarseness, conjunctivitis. On the 3-5th day of illness, bright, large, sometimes merging spots appear on the face, while the temperature remains. On the 2nd day, the rash appears on the torso, on the 3rd - on the limbs. Approximately on the fourth day from the moment of onset, the rashes begin to fade away in the same order as they appeared.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy: drinking plenty of fluids, darkened room (since conjunctivitis is accompanied by photophobia), antipyretics. Children under 6 years of age are prescribed antibiotics to prevent bacterial infection. Thanks to vaccination, measles has now become a fairly rare disease.
How to get rid
How to remove red dots on the face so that they do not spoil the appearance? It depends on the reason for their occurrence. Petechiae go away on their own within a few days and do not require any specific treatment. Traces of insect bites last a little longer on the face. Special ointments and gels can speed up their disappearance. The ointment also helps get rid of demodicosis, and it also treats the red spot caused by lichen.
Allergic symptoms are relieved by taking antihistamines and eliminating the allergen. Spider veins are removed using hardware methods. Electrocoagulation, laser therapy, cryodestruction, ozone therapy and some other methods may be used. The walls of the affected vessels stick together or collapse, and the red dots disappear.