Mechanism of appearance and causative agent of boils
Doctors associate the mechanism of occurrence of the disease with reduced immunity and hypothermia. Opportunistic microflora begins to actively attack the body. Staphylococcus aureus is the main pathogen. The microorganism lives on clothing, skin, in poorly ventilated areas, and dust. Penetrates into the papillary layer of the skin through traumatic injuries and microcracks. The bacterium provokes inflammatory changes in the hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and surrounding tissue.
The pathological process is manifested by redness, swelling, pain, and increased local temperature at the site of pathogen penetration. The listed changes develop at the infiltration stage.
Over time, an abscess forms - a purulent pustule with a necrotic core. The stage of abscess formation begins. The boil opens independently or with surgical help. Lack of treatment, severe course ends in hospital. The disease is complicated by abscess, phlegmon, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, and septic shock.
Timely seeking medical help, proper treatment, and compliance with medical recommendations prevent the development of complications. The disease goes away in 10-14 days.
Is boil (furunculosis) contagious to others: how is it transmitted and methods of prevention
Boils are a common problem. That is why many people are concerned about the question: can you get infected with boils? It is impossible to become infected in cases where there are no certain prerequisites for this, from which every person is not insured. The factors that contribute to the appearance of furunculosis need to be understood in more detail.
Boils that affect one person do not pose a threat to people around him.
The causative agent of furunculosis
Furunculosis is an inflammatory process in the hair follicles, during which a rod with pus is formed. The causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. However, sometimes Staphylococcus epidermidis can also contribute to the appearance of the disease.
Both types of bacteria are widely distributed in the external environment. Excessive amounts of them are found in dust on the street, in rooms with poor ventilation, in clothing and even in residential apartments. Staphylococci often exist on people’s skin and mucous membranes, without causing the development of diseases.
According to research, about 70% of people are carriers of these microorganisms.
Features of the infection
The main causative agents of such a pathology as boils are purulent bacteria - Staphylococcus aureus. When these cells enter the hair follicle, an inflammatory process begins to develop. Infection of others and the development of furunculosis does not occur on its own; a person is surrounded by numerous provocative factors.
These include:
- weak immunity;
- certain diseases;
- skin injuries (burns or open wounds);
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- metabolic disease.
It is difficult to protect yourself from staphylococcal infection; the risk of infection is high. But, if you follow the rules of contact with a sick person, a completely healthy person will not catch furunculosis, even after close contact. It should be remembered that boils can be infected by airborne droplets if hygiene rules are not followed.
How is it transmitted person to person?
Is there a chance of catching furunculosis from an infected person? Transmission of the microorganism is not excluded, but the development of furunculosis requires a number of internal and external factors. The disease, like other infectious diseases, involves interaction between the pathogen and the macroorganism.
For infection with furunculosis, it is not so much the microorganism itself that is important, but the factors that contribute to its progression. Based on this, we can conclude that furunculosis is transmitted from person to person only in the form of microorganisms, which in most cases are not infectious and do not provoke the development of boils.
External reasons
External factors that provoke the onset of furunculosis:
- minor injuries caused by particles of fine graphite or metal dust, for example, emitted in industrial conditions;
- the process of rubbing items of clothing on certain places of the human body, for example, on the buttocks, due to which staphylococci from a form that is not dangerous to humans turns into a dangerous one and is rubbed into the deep layers of the skin;
- scratching the skin when other skin diseases (scabies or eczema) are present.
Internal factors
Internal reasons due to which furunculosis manifests itself:
- decreased immunity;
- vitamin deficiency;
- diabetes;
- excess body weight;
- anemia;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- alcohol abuse;
- frequent overheating and then hypothermia.
Internal causes contribute to the deterioration of immunity, and external causes cause damage to the skin. It is into these lesions that staphylococcus penetrates.
Finding itself in a favorable habitat, it begins vigorous life activity and reproduction, which ultimately becomes the cause of inflammatory processes. Furunculosis is not contagious.
Infestation by neem is impossible even through sexual contact when another person has boils on the genitals (one of the most common places where boils appear), if the person does not have prerequisites for this in the form of the above factors.
Origin of the disease and its manifestations
The main pathogenic factor in the formation of such a disease is bacterial infection of the skin with staphylococcal infection. Pathogenic pathogens under the influence of exogenous and endogenous factors contribute to the manifestation of furunculosis.
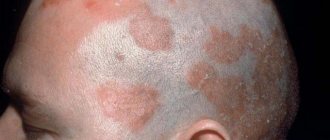
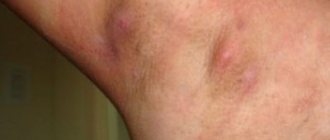
The disease itself has a fairly long process of development, progression and extinction. Frequent boils affecting the neck, face, back, hips usually indicate progression of the disease.
The clinical picture of the disease is as follows:
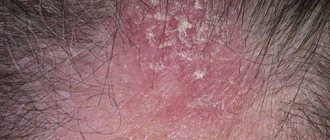
- At the initial stage, a small node forms and matures in the cup of the hair follicle.
- After a few days, a sensitive cone-shaped boil with a necrotic formation in the center forms on the skin.
- Along with the follicle, the sebaceous gland and adjacent areas of the epidermis are damaged.
- A mature formation causes severe tissue swelling and an increase in throbbing pain.
When the focus of inflammation is opened, abundant discharge of purulent masses is observed. In the cleared cavity, an ulcer with a necrotic core of a greenish tint forms.
The presence of such a basis indicates that the presumed diagnosis is confirmed by furunculosis, the inflammatory course of which decreases only in the case of rejection of necrotic tissue.
After the rod leaves the bed with the remains of pus and blood discharge, the pain subsides along with swelling of the skin. In addition, this disease has the following characteristic features:
- if the components of furunculosis are single in nature, then the patient’s condition can be diagnosed within normal limits;
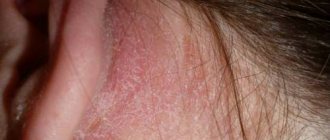
- if the nasolabial triangle, nasal area and external tissues of the auditory organ are affected, symptoms of general intoxication, increased body temperature and severe headaches are observed;
- in case of injury to the affected components of furunculosis or independent non-sterile removal of the lesion, there may be a risk of thrombophlebitis of the facial veins and deep damage to internal tissues;
- When boils form on the face, inflammation may progress and transform into meningitis.
The most dangerous consequence of the disease can be considered sepsis, characterized by numerous abscesses in the internal organs and leading to death.
Forecast
Furuncles in adults and children are a common occurrence. It can appear as a result of various reasons. The patient's age does not matter. Experts do not recommend waiting until furunculosis goes away on its own. You need to go to the hospital, only a doctor will tell you whether the boil is contagious or not, and how to deal with it in order to achieve complete healing.
The prognosis for this disease is disappointing if treatment is approached carelessly. Incorrect therapy will lead to serious complications. If it was not possible to prevent the development of furunculosis, then it is necessary to undergo full treatment. The further development of Staphylococcus aureus depends on its effectiveness.
Prevention of infection with furunculosis
To avoid becoming infected with staphylococcus, doctors recommend following personal hygiene rules and proper nutrition. A person should include as much protein food (mainly of animal origin) in their diet as possible. You need to enrich your menu with fiber by consuming enough fresh fruits and vegetables.
You will need to limit your intake of fats and sweet foods. It is also recommended to exclude allergenic foods from the diet, for example, chocolate, eggs, citrus fruits and seafood. It is not recommended to consume salty and spicy foods.
It would be useful to systematically take special vitamin and mineral complexes that will improve immunity and prevent the development of boils.
In addition, a healthy lifestyle and frequent walks in the fresh air will protect against infection. Particular attention should be paid to the fact that if a small boil appears, it should under no circumstances be squeezed out.
In such a situation, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible. Only he will be able to diagnose and prescribe the required treatment. Another important rule is disinfection of the skin after cosmetic procedures, for example, hair removal.
It is important to resort to them not only at home, but also in beauty salons.
Source: https://xn--80ahsaqcbqq.xn--p1ai/bolezni-kozhi/mozhno-li-zarazitsya-furunkulom.html
Is it possible to get infected with furunculosis?
There is no clear answer to the question of whether chiria and boils are contagious to other people. Numerous medical studies have shown that the likelihood of infection increases with close contact with a patient, a tendency to pathology, or the presence of provoking factors in a healthy person. Some types of staphylococci can survive in an open environment for several weeks. The disease does not occur in people with strong immunity. The skin performs a protective function. Prevents the entry and penetration of staphylococci. Bacteria and skin have the same positive charge. It is difficult for microorganisms to gain a foothold on the skin. The strength and constant renewal of the stratum corneum of the skin prevents the internal penetration of staphylococci.
Infection occurs when microorganisms enter the skin of a weakened body by air. Through microcracks and abrasions quickly penetrate into the underlying structures.
Close contact with a sick person leads to the development of pathology. Several boils may appear on the skin at the same time. The pathological condition is called furunculosis. The risk of infection increases several times.
The disease develops in healthy people with predisposing factors:
- Working in a workplace with hazardous working conditions causes another person to become ill. Dust particles get on the skin and cause microcracks. If there is close contact with a sick person, the potential victim has a chance of becoming infected. A similar situation is with people who have scratches and microtraumas on their bodies.
- Constant stress and poor nutrition negatively affect the immune system. A person becomes infected with furunculosis and other bacterial infections from the carrier of the disease.
- People with dermatological skin problems (eczema, dermatitis) are recommended to avoid contact with a patient with furunculosis for 2 weeks. Skin diseases are often accompanied by itching. The patient constantly scratches the pathological areas of the body. Creates a gate for the penetration of staphylococcus. The same applies to patients with diabetes and various metabolic disorders.
- Hypo- and vitamin deficiency negatively affect the immune system. First strengthen the body's own defenses, then help patients with boils.
Pathology poses a danger even to the sickest. Pus flows from the boil and enters neighboring areas of the body. Furunculosis develops. New chiryaks complicate the course of the disease. In the absence of antibacterial therapy, chirias unite into fused lesions. A carbuncle or abscess appears. Both diseases require immediate surgery and long-term antibiotic therapy.
Features of chiryak treatment
Treatment of a boil on the abdomen is carried out similarly to the treatment of similar neoplasms in other parts of the body. At the stage of infiltration formation, the use of ointments and other drugs that accelerate the maturation of boils is indicated. In the early stages, it is possible to use local antiseptics. This allows you to stop the inflammatory process and the growth of pathogenic flora in the hair follicle.
After the boil on the abdomen has matured, drugs are indicated to draw out the pus and necrotic core, as well as local antiseptics. For single abscesses, general antibiotics are not used, but for multiple abscesses, they are used as prescribed by a doctor.
Compresses with ointments
Compresses, bandages with ointments are used at all stages of treatment of a boil in the abdominal area. At the first stage - promoting the maturation of the abscess, at the second - drawing out pus, preventing secondary infection, at the third - accelerating the epithelization of the wound.
Drugs of choice:
- Vishnevsky's liniment is based on natural birch tar, xeroform antiseptic. Apply under a bandage 2-3 times a day. Promotes the maturation of boils on the abdomen, reduces the severity of the inflammatory process. At the second stage, it is used to accelerate the outflow of pus. Not indicated during wound epithelization.
- Ichthyol – based on ichthyol. Used in the first stage of a boil located on the abdomen. It has an aseptic effect, helps reduce pain, and accelerates maturation.
- Levomekol – based on chloramphenicol. This ointment is effective after the discharge of pus and necrotic core. It contains an antibiotic and prevents secondary infection of the wound and neighboring areas.
- Local antiseptics - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Dimexide solution, hydrogen peroxide are indicated at the stage of opening the apex of an abscess on the abdomen. They are used to clean the wound and prevent infection of healthy tissue.
- Alcohol-containing antiseptics - fucorcin, brilliant green, iodine solution - are indicated in the initial stages of treating a boil located on the abdomen. They penetrate deeply into the skin and can suppress staphylococcus in the early stages.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgery is indicated. The surgeon will open the hair follicle, remove the pus and shaft, clean the wound and apply a bandage with drainage.
Additionally, he will tell you the rules for caring for a wound after a boil in the postoperative period, prescribe antiseptics and healing agents
Only a specialist should treat an internal boil in the lower abdomen. Diagnosis is required; this neoplasm can be benign or malignant. After removal, the tissue is sent for analysis to rule out cancer.
Traditional treatment
A boil on the abdomen in folk medicine is treated with the same drugs that the doctor will suggest after examining the boil. This is Vishnevsky's liniment, Ichthyol ointment.
In the recipes of folk herbalists there are various means that accelerate the ripening and spontaneous opening of the boil.
Popular home treatments:
- Garlic gruel - applied to a boil located on the stomach, under a bandage. Once opened, the product is not used.
- Flatbreads made from flour, butter and eggs - used at the ripening stage. After opening, alcohol tinctures are indicated for treating the wound.
- Aloe leaf – fresh – apply to the boil under a bandage. Apply until the wound is opened and healed.
- Baked onions and laundry soap in equal proportions - a bandage with gruel is applied once a day for 24 hours. After opening the abscess, treat the wound with an antiseptic solution.
Ways of transmission of boils
Are boils and styes contagious to another person? Infectious diseases are dangerous. Furunculosis is transmitted in various ways:
- a healthy child cannot become infected from a sick mother. Breastfeeding provides the baby with a strong immune system. The risk of infection is present in premature, weakened children;
- A decent number of diseases are transmitted through sexual contact. If the boil is localized in the groin or genital area, a healthy sexual partner cannot become infected. In the presence of predisposing factors, the boil becomes contagious;
- staphylococci inhabit public places (baths, swimming pools, clinics). Many people think that infectious agents attack from the air. The disease is never transmitted by airborne droplets (through kissing, talking);
- heredity does not affect the risk of boils;
- contact transmission is possible when working with contaminated instruments, catheters, and dressings.
Prevention of infection
A boil is an unpleasant, painful formation on the skin. With proper and timely treatment, the pathology goes away in a couple of weeks. Often the boil is complicated by abscesses, phlegmon, and sepsis. Simple measures will help you avoid infection and complications of the disease:
- Hand hygiene after processing chiria is the main measure to prevent the disease. Along with hygiene procedures, you need to disinfect your hands with antiseptic agents.
- To prevent the spread of infection, it is necessary to apply a gauze bandage to the inflamed area.
- You cannot use the patient’s bath items and hygiene products.
- It is advisable to do daily cleaning.
- During the period of illness, it is necessary to maintain a balanced diet. Include animal proteins, fiber, fruits, and vegetables in the patient’s diet. You can’t eat sweets, chocolate, citrus fruits, fish, eggs.
- People with reduced immunity need to drink a complex of vitamins and minerals every six months.
- A healthy lifestyle, absence of bad habits, walks in the fresh air, gymnastics are the main prevention of inflammatory and chronic diseases.
- You cannot self-medicate. Timely diagnosis and treatment of a boil will help avoid unpleasant consequences.
- If you have diabetes or obesity, do not start the pathological process, visit your doctor annually.
There are many ways to prevent the occurrence of a boil.
Avoid stress, maintain your immunity and illnesses will not bother you! The article has been verified by the editors
Causes
The disease can be caused by simple trauma to the skin or scratching it. Boils are often the result of failure to comply with basic personal hygiene standards. The most likely cause of boils is weakened immunity, which occurs against the background of diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- alcoholism;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- anemia;
- frequent hypothermia and overheating;
- hypovitaminosis.
Usually the disease occurs in the spring, when the body lacks vitamins and microelements.
This disease is also dangerous because it can be contracted from another person. Knowing the main symptoms of illness will help you avoid this. A timely detected disease and timely prescribed treatment will guarantee the health of other family members and everyone around.
Nervous system disorders can lead to boils