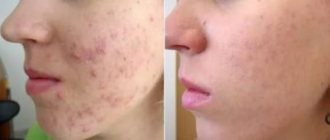
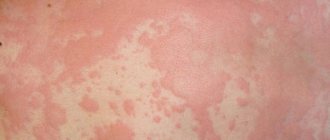
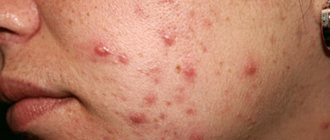
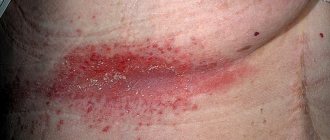
Scabies ointment is the main method of treating the disease, which is also used as a preventive measure.
You can become infected after physical contact with a carrier of the disease. The incubation period lasts 1-4 weeks. The causative agent of scabies is a microscopic mite that lives inside the skin and lays larvae there.
Symptoms of typical scabies:
- red-pink rashes on the arms, stomach, legs;
- severe itching at night;
- erosive and ulcerative rash due to infection in scratching;
- straight or zigzag white stripes up to 8 mm in size.
The disease is transmitted only between people. The disease with typical symptoms can be treated at home, but the Norwegian form requires urgent hospitalization.
Features of medicines for scabies mites
All drugs for the treatment of scabies perform two tasks at once:
- destroy parasites;
- alleviate the patient's condition, relieving symptoms and promoting skin healing.
To do this, the products must have antiseptic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic properties, and in addition, contain substances that cause the death of ticks. All modern medications used to treat scabies mites can be divided into 3 categories:
- high sulfur content;
- synthetic derivatives of balsamic products;
- drugs with a pronounced acaricidal effect.
Remedy for scabies
A separate line can be taken of traditional medicine, which acts as an auxiliary therapy, making treatment more effective.
Prevention
You can protect yourself from scabies, you just need to follow prevention. To avoid getting infected you need to:
- Treat the entire body once with an anti-scab medication - Spregal, Permethrin, Benzyl benzoate;
- Use only personal belongings, do not take other people’s things;
- After contact with a carrier of scabies, change clothes, bed linen, take a shower;
- Clean with disinfectants;
- Boil clothes and spray with A-Par
During treatment you need to visit the doctor 1-2 times a week. After completing treatment for scabies, you need to undergo another examination to confirm recovery. Pregnant women and children need to select the drug with caution.
Types of medications for scabies
Products for the treatment of scabies are available in the form of:
- ointments;
- tablets;
- sprays and aerosols;
- lotions, solutions and emulsions.
Each form has its own characteristics that must be taken into account when making a choice in favor of one or another product.
Ointments
Ointments for scabies are prescribed more often than other dosage forms. This is due to their ease of use and high efficiency. But such means also have disadvantages. They have a persistent unpleasant odor, they are difficult to wash off, and stain clothes, towels and bed linen.
The most popular ointments for scabies for treating humans:
- Benzyl benzoate;
- Sulfuric ointment;
- Lindan;
- Wilkinson's ointment;
- zinc ointment.
An undoubted advantage of ointments is their low cost.
Pills
Few of us, when choosing how to treat scabies, think about tablets. This is due, firstly, to the fact that for most people it is much more common to treat skin pathologies with topical agents, and secondly, to the fact that tablets are quite expensive and not easy to get. The most commonly used are Ivermectin and Butadione, which not only have a detrimental effect on ticks, but also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Sprays
Anti-scabies spray is not the most effective, but a fairly common form of medication. Most often prescribed:
- Spregal;
- A-Par;
- Para-Plus.
They are chosen primarily because of ease of use. Unlike ointment, it is easy to spray on any part of the body yourself, and it does not leave stains on clothes. But in terms of effectiveness, sprays are inferior to ointments and creams, while having a higher price.
Liquids
Lotions and emulsions are another fairly broad category of drugs for scabies. Most often they are applied to the skin for a short time, after which they are washed off with water. Often, limiting the exposure time is associated with the high toxicity of liquid products. For the same reason, they are not prescribed for the treatment of children.
Spray Spregal
Causes of the disease
By scratching infected areas of the body with nails, a person only helps the mite spread. The disease can cover the entire body, except for the hair on the head, where parasites are not so willing to settle. Ticks most often select warm areas and corners such as the skin between the toes, under the breasts, near the navel or waist area.
The main signs of the disease are itching, which usually appears a month after infection. There are many ways that scabies can be spread, and they are not at all limited to being in dirty conditions. Most often, infection is transmitted from one person to another during intimacy or sleeping in the patient’s bed. Children quite often get this disease through playing together.
Video description of the causes of scabies infection:
List of effective drugs
The most popular medications against scabies act quickly, destroy the pathogen and eliminate the symptoms. The following will list some of the products that, according to experts and patient reviews, show the best results in the treatment of skin pathologies:
Spregal
Spray against scabies mites contains a powerful nerve agent. Moreover, the product is non-toxic, it is allowed to be used to treat children, as well as women during pregnancy and lactation. The product is effective and, according to the manufacturer, after a single treatment it destroys not only ticks, but also eggs. However, doctors still recommend re-treatment after 3 days.
Benzyl benzoate
One of the most popular remedies against scabies. It has an antiparasitic, antipruritic, anesthetic effect. Destroys active parasites, but not eggs, so two treatments are required, 3 days apart. The product is quite strong and has a number of side effects. It can be used to treat scabies in adults and children (from 3 years of age), but only as prescribed by a doctor.
Butadion
In cases where a person does not have the opportunity to use topical agents, tablets are prescribed to treat scabies. The active substance of the drug “Butadione” effectively helps to get rid of the causative agent of scabies, but has a number of serious contraindications, including pregnancy.
Sulfuric ointment
As the name implies, the main active ingredient of the drug is sulfur. Treatment with sulfur ointment has several advantages:
- low price;
- ease of use;
- fast action (with regular use, the parasites disappear within a few days).
But there are also disadvantages. The ointment is poorly absorbed, smells unpleasant, and leaves stains on the fabric that are difficult to remove. In addition, the instructions for use indicate that the use of sulfur ointment can lead to complications; it is contraindicated for children under 6 years of age, pregnant and lactating women.
Zinc ointment for scabies
Zinc ointment is used not only for scabies; this universal remedy helps in the treatment of many skin diseases. The active ingredient is zinc oxide, which is safe for the human body. The drug does not contain allergens, is odorless, has an anti-inflammatory and healing effect, and relieves itching.
The use of zinc ointment relieves the symptoms of scabies, but does not kill the mites, so it is usually used in combination with acaricidal drugs.
Zinc ointment
Permethrin
Permethrin is used to treat scabies in the form of ointment, lotion and spray. The drug is applied to the skin using a cotton swab. They should not be used on the face, neck, or areas covered with hair. The product is prohibited for pregnant, lactating women and children under 5 years of age.
Medifox
The basis of this remedy against scabies mites is permethrin. The presence of auxiliary ingredients in the composition reduces the aggressive effect of the acaricide on the skin, so Medifox does not cause irritation. The drug is available in the form of a concentrate, which must be diluted with warm water.
Lindan
This anti-itch remedy comes in lotion and powder form, which is convenient for use in hot climates. One treatment is enough to eliminate parasites. Contraindications include pregnancy, lactation, age under 3 years, the presence of scratches, open wounds, and other skin diseases on the body.
Crotamiton
When treating scabies, this drug is often prescribed in the form of a lotion or cream. Crotamiton is rubbed into the skin twice with a break a day. The popularity of the product is due to the fact that it not only fights parasites, but also eliminates itching and discomfort. The drug is prescribed to adults and children over 12 years of age.
Esdepalletrin
A spray based on synthetic pyrethrin, penetrating the upper layer of skin and scabies, helps quickly get rid of adult mites and larvae. The drug is used once, after application, it should not remain on the skin for more than 12 hours. The product has virtually no side effects, but it is contraindicated for nursing mothers and people with asthma.
Vishnevsky ointment
The main ingredient of this product is birch tar, which is a natural antiseptic and is used to treat a large number of skin diseases. Vishnevsky ointment is an inexpensive drug that disinfects, helps relieve inflammation, eliminates itching and burning, and promotes skin healing.
Vishnevsky ointment
Solutions according to Demyanovich
This method is over 70 years old, and it still remains one of the most effective and frequently prescribed for the treatment of scabies. The technique consists of sequential treatment of the affected areas of the skin with two solutions:
- 60% sodium thiosulfate solution.
- 6% hydrochloric acid solution.
The method is based on the acaricidal effect of substances (sulfur and sulfur dioxide), which are released during the reaction of two solutions. The use of solutions according to Demyanovich has disadvantages, including labor intensity and a high probability of developing dermatitis.
We follow medical recommendations
To treat the disease at home, you must strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, which include doing the following:
- Familiarization with the instructions for use of the medicinal product.
- Avoid using hot showers using a washcloth.
- Trimming nails before water procedures.
- Apply the medication at night due to the fact that mite activity is increased at night.
- Rubbing the drug in is done with dry hands. If the medicine has a liquid consistency, then it is applied to the damaged area using a sponge. This recommendation applies most to the face. So that the drug does not get on the mucous membranes.
- Applying ointment to the facial area requires measures to prevent it from getting on the face and eyes.
- If the medication gets on the mucous membranes, eyes or genitals, it is recommended to rinse them under running water.
- After applying the medicine to the damaged area, hands require soap and water.
- Regular change of bed linen is mandatory.
- When washing individual laundry, you need to add soda to the washing powder. The laundry is pre-soaked for an hour.
- Items that cannot be washed or boiled must be treated by exposure to frost. Mattresses and pillows are treated with a disinfectant spray.
What should you consider when choosing?
Anti-scabies medications differ in composition, release form, duration of treatment, and effect on the human body. To achieve the best results, when choosing a medicine, you need to pay special attention to certain factors. The product must meet the following requirements:
- act quickly without requiring long-term use;
- suitable for the patient’s age (some drugs cannot be used to treat children);
- be convenient to use;
- have a detrimental effect on ticks at any stage of development;
- do not contain highly toxic compounds;
- act on the upper layers of the skin where parasites live, without penetrating deep into the skin;
- have no odor or have a faint pleasant aroma;
- do not stain clothes.
In addition, the list of side effects and possible complications should be as short as possible.
Symptoms
Scabies has characteristic symptoms that allow it to be distinguished from other types of dermatological diseases. The main signs of infection with this disease are the following:
- The presence of severe and unbearable itching, an exacerbation of this symptom usually occurs in the evenings or at night, when subcutaneous mites are most active. The main reason is not bites, but the release of large amounts of waste products by parasites, which cause an extremely acute and difficult to tolerate allergic reaction of the human body.
- The presence of characteristic and clearly visible scratching on the affected areas of the skin.
- Skin rashes in the form of a pink or red rash; in advanced stages of the disease, they can take on the appearance of a crust covering the skin.
You can also diagnose scabies by looking at the places on the body that are most susceptible to various skin rashes. There are a number of patterns that virtually always remain unchanged:
- Regardless of the patient’s gender, the areas between the fingers and their lateral surfaces are primarily affected.
- In half of infected men, the genitals and the area around them are affected, as well as the area where the wrist joints are located.
- In approximately 20–25% of patients, regardless of gender, the feet and body are affected. In some cases, the rash can spread over the entire surface of the arms and legs.
- In some women, the mammary glands are affected.
Symptoms usually appear within the following periods of time after infection:
- After 7–10 days, if this is the patient’s first case of this disease. In some cases, up to 1.5 months may pass before the first symptoms appear if subcutaneous mites undergo a long process of adaptation to the new environment into which they find themselves.
- After a few hours or one day, if the disease is recurrent or has relapsed due to insufficient treatment measures. However, the likelihood of repeated infection with scabies is not particularly high, since after suffering the disease, a person develops a protective reaction of the body, as a result of which some mites die even without taking any measures.
Read more: Vitamins in turnips
Therapy using folk remedies
Scabies is one of the oldest diseases, so over the years people have discovered many treatment methods using different foods and herbs. Most of the ingredients may now be in the refrigerator.
One of these methods is treatment with dairy products. The recipe receives positive reviews; it contains milk or kefir with the addition of black powder; it can be obtained from hunters.
The ratio is one to three, that is, 3 tablespoons of kefir to one spoon of gunpowder. This mixture should be placed in a warm place and stirred regularly for a couple of hours. Then, when the mixture is ready, apply to the areas where the rash has formed and preferably tie it with gauze overnight.
To prepare the following ointment you will need elecampane root, sulfur, pork lard and birch tar. Initially, finely chop the root, heat the pork lard and add the root before the mixture boils. Then boil this mixture for another couple of minutes and reduce the heat, keep it on this heat for 15 minutes.
Strain the warm mixture through cheesecloth and let it brew, then add the remaining ingredients to the semi-finished mixture and pour into a jar, in which you need to stir regularly. When a homogeneous mass is formed, it can be used.
It is necessary to spread it on the areas affected by parasitic mites. Repeat this procedure 3 times a day for a couple of hours.
A simple folk method is to use laundry soap. To prepare a special anti-scabies soap, you need laundry soap, garlic and onions. You need to rub a piece of laundry soap on a grater, heat the shavings over a fire until a viscous mass is formed, to which chopped garlic and onions are added.
Doctor: Olga Shishkina ✓ Article checked by doctor
Scabies: symptoms, photos, first signs in adults and children
Scabies is a parasitic skin disease. Symptoms of scabies cause a person a lot of problems, in addition, the very awareness of the fact that microscopic parasites have settled under the skin becomes a reason for psychological discomfort
Therefore, it is very important to know how scabies is transmitted and how to avoid infection with mites. Symptoms and treatment of the disease are described in this article.
What it is?
The term “scabies” comes from the verb “to itch,” which is explained by the leading symptom of the disease - severe itching that annoys the patient.
Scabies: photo of a mite under the skin
Interestingly, the first descriptions of scabies were made by ancient Greek healers. Researchers classified the disease as a skin pathology, calling it “psora.” True, the causative agent of scabies could not be isolated in Ancient Greece due to its microscopic size. The first assumptions about the parasitic nature of the disease were put forward in the Middle Ages. This hypothesis was confirmed at the end of the 17th century, when the microscope was invented.
Scabies is a social disease. In particular, a significant increase is recorded in times of war and natural disasters, when people have to group in limited areas, saving their lives. In such difficult times, up to a third of the population can become infected with ticks. The number of cases also increases significantly during the cold season. This is explained by the characteristics of the causative agent of scabies, whose peak fertility is observed in winter and autumn. In addition, with the onset of cold weather, people sweat more, and sweat creates excellent conditions for ticks to reproduce.
ICD-10
In the International Classification of Diseases (the system used by doctors to code diseases), scabies is assigned the code B86.
Causes
Infection with scabies occurs at the time of contact with a sick person or in the case of using objects that have mites on them.
An adult individual outside the host’s body remains viable for 36 hours: this time is quite enough to find a new host. Having penetrated the epidermal layer of the skin, the mite moves into them, resulting in the formation of subcutaneous passages.
Symptoms and first signs
First signs: photos
The disease has no incubation period: immediately after entering the human body, the female begins to make passages under the skin and lay eggs. If it is not an adult tick that has entered the body, but larvae, the incubation period can be about 5 weeks: this is exactly how long it takes for the larva to turn into a mature individual.
The symptoms of the disease are determined by two factors: the direct activity of the tick and the body’s reaction to the products of its vital activity.
Scabies on hands: photo
The main symptoms indicating the presence of the disease include:
- severe itching. Itching tends to intensify at night, which is associated with an increase in mite activity in the dark;
- characteristic scratches on the skin, which the patient leaves on himself, trying to cope with the unbearable itching;
- due to sleep disturbances, the patient experiences neuropsychic exhaustion;
- Scabies and a rash appear on the skin of an infected person. The moves look like straight or broken lines with a white or gray tint;
- in some cases, small bubbles with transparent contents appear. Most often, rashes can be seen between the fingers, on the wrists, on the feet, on the stomach and on the buttocks.
In clinical practice, differential signs indicating that a patient has scabies rather than another skin disease include:
- Ardi's symptom: rash in the elbow area;
- Gorchakov's symptom: the appearance of crusts in the elbow area;
- Michaelis symptom: the appearance of a rash in the intergluteal area. In this case, a rash may also appear on the sacrum;
- Sezari's sign: rash between the fingers.
In children
A characteristic feature of scabies in children is that the rash is localized mainly on the scalp, as well as on the feet and palms. Scabies can be detected by the characteristic blisters that form at the bite sites.
If a child has a high sensitivity threshold, he may not complain of itching. In this case, the disease can proceed completely unnoticed. However, the passages will still be visible on the skin, which helps make the correct diagnosis.
Scabies can also appear in an infant. Detecting the disease in this case is problematic, since infants are prone to various types of rashes.
Zinc ointment
Zinc ointment relieves all unpleasant symptoms caused by scabies mites
This medication is not used to eliminate the scabies mite, but to relieve all the unpleasant symptoms that it causes on the surface of the skin. Almost all patients are prescribed ointment, as it can quickly eliminate itching and dry out the skin, which allows wounds and scratches to heal. Zinc ointment can be used not only by adults, but also by children.
When used correctly, only in one case out of a thousand can unpleasant side effects occur in the form of swelling and an allergic reaction. To get a really noticeable result, apply a thin layer of medication to the skin in the morning and evening. In the evening, it is better to use zinc ointment just before going to bed. The duration of therapy is 5-7 days, after which it is worth checking the result and determining the possibility of further use of the medication.
Attention! You should check with your doctor about the possibility of simultaneous use of this drug with others, so as not to reduce the effect of several medications.
Methods for diagnosing the disease in adults
The most common localization points for scabies among patients include:
- brushes;
- elbow joints;
- abdominal area;
- buttock area;
- area of the mammary glands (in women);
- hip area.
Scabies can manifest itself not only in the form described above, but also in the form of pathological complications, manifested in the form of skin erosion on the body and arms, the appearance of an allergic crust, and spots. In the event of a secondary infection, suppuration and the formation of pustules may occur.
The most severe form of scabies complication entails lymphoplasia.
Modern medicine identifies several particularly dangerous forms of scabies, including:
- nodular scabies;
- childhood scabies;
- Norwegian scabies;
- pseudo-itch manifestations.
The diagnostic ruling is a strong basis for an accurate diagnosis by a dermatologist. Epidemiological and laboratory data collected as a result of tests gradually confirm the patient’s condition.