When exposed to external factors, thermal injury occurs on the tissues of the body; this can be contact with steam, hot metals, or boiling hot liquids. Open tissue damage occurs when exposed to chemicals or electric current, most often on the arms or legs. The depth of the lesion varies and is divided into four degrees. A remedy for burns with boiling water will reduce pain and minimize traumatic consequences.
Symptoms and distinctive signs of a 3rd degree burn
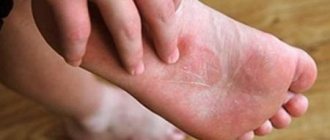
Visually distinguishing a third degree burn injury from other types of injuries is very difficult. To do this, it is necessary to determine the depth of the lesion by the color of the tissue and related signs.
3a
A 3a degree burn is accompanied by destruction of the outer layer of the skin and part of the dermis (deep layer). The functions of the appendages, that is, the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, are preserved. The degree of burn determines local and general symptoms:
- necrosis (death) of tissue in the affected areas;
- formation of blisters on the body;
- vascular changes;
- extensive swelling throughout the entire depth of the injury;
- the formation of a light brown dry crust on the burn.
When palpating (feeling) the area, a person feels severe or moderate pain. A few hours after receiving a burn, dense blisters filled with yellow liquid appear on the skin. When answering the question of how long it takes for a burn to heal, the doctor takes into account the area of the burn and the presence of complications. In the absence of infectious inflammation, the wounds heal within 4-6 weeks. If pathogenic bacteria multiply in the dermis, the treatment period is 2-3 months.
3b
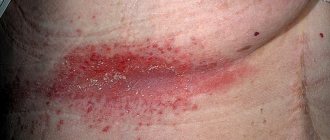
A 3b degree burn is accompanied by damage to the epidermis with the dermis and the tissue underneath - fatty tissue. The depth of damage is determined by the color of the burned tissue.
What does a deep burn look like:
- the skin acquires a dark brown tint;
- blisters filled with blood form on the wound;
- The burn crust becomes brown or dark gray.
With deep burn lesions, hair follicles, exocrine glands (sebaceous, sweat), and sensory receptors are damaged. When palpating the wound, the patient does not feel pain.
If a deep 3rd degree burn is located over a large area, the formation of a burn disease is likely, which makes the process of complete healing difficult.
Independent restoration of soft tissues with such injuries is impossible. Skin transplantation from healthy areas of the body is necessary. Even after surgery, the wound heals very slowly - more than 2-3 months.
What medications can you buy at the pharmacy?
If you go to the pharmacy, they will offer a whole list of medications for burns of any kind (thermal, or received in the sun), the drugs differ in composition and cost. Today, remedies for burns from boiling water are available in a price range for every consumer. The purchased ointment should be universal, suitable for all types of burn injuries.
Since the list of victims may include pregnant women, nursing mothers and children of different ages, pharmaceutical remedies for burns with boiling water should have minimal contraindications.
Regardless of whether it is an ointment or a spray, the drug should be easy to use and safe to store.
The medicine for boiling water burns has several therapeutic properties. First of all, it is an analgesic effect. And the anti-inflammatory will help avoid the formation of infection in open areas of damage. The faster the wound heals, the better, so the medicine should also be endowed with regenerating wound-healing properties.
Causes of burns
The damaging factors for all degrees of burn disease are the same. The main ones include:
- ultraviolet radiation;
- chemical acids;
- alkaline solutions;
- hot metal;
- boiling oil;
- electricity.
Grade 3 is characterized by damage not only to the outer but also to the deep layers of the skin. Therefore, the disease is accompanied by tissue necrosis. If more than 15% of the body is damaged, the burnt person’s body begins to be poisoned by metabolites, that is, decay products of dead tissue.
High temperature and ultraviolet
Most often, third degree burns occur through direct contact with the following factors:
- Flame. Under the influence of fire, the limbs, face, and respiratory organs (mouth, nasal passages) are affected. If the torso is damaged, problems arise related to the removal of stuck-on clothing. Because of this, the risk of septic, that is, infectious tissue inflammation, increases.
- Ultraviolet. Burns caused by ultraviolet radiation are more common in the summer. The damage in 90% of cases is shallow (burn wounds of degree 3a), but they occupy 50% of the entire surface of the body.
- Water vapor Water evaporation provokes shallow burns of the skin, nasal mucosa, and mouth. The epithelium that lines the inner surface of the respiratory tract is often damaged.
The depth of tissue injury is determined by the duration of contact with hot objects, hot water, ultraviolet radiation, etc. The speed of recovery depends on the condition of the burnt person’s skin.
Chemical substances
3rd degree burns when aggressive chemicals come into contact with the epidermis are often accompanied by infectious inflammation. Causes of burns include contact with the following substances:
- Acids. Chemical reagents in 80% of cases do not penetrate the subcutaneous fat layer. At the site of damage, crusts quickly form, which prevent the caustic substance from entering the dermis.
- Alkalis. Alkaline solutions easily penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, causing severe wounds with damage to the fiber.
- Metal salts. As with acids, burns are most often shallow. But chemicals are absorbed into the skin, causing intoxication (poisoning) of the body.
The severity of damage is determined by the degree of concentration of the reagents, as well as the duration of contact with them.
Electric shock
When exposed to electric current, complications often arise, since soft tissues and blood have good electrical conductivity. After contact with conductive objects, two marks are formed on the victim’s body - the exit and entry points of electrically charged particles. The greatest danger to life is an electric shock at a current strength of 0.05 A.
Ionizing radiation
The degree of radiation burn depends on the duration of exposure to ionizing radiation. Its sources include:
- rocks (apatite, zircon);
- medical equipment;
- radon;
- uranium mines, etc.
Not only the dermis and subcutaneous fat tissue, but also internal organs are damaged. The depth of pathological changes in tissues depends on the received radiation dose.
How to give first aid
First aid for a 3rd degree burn is to eliminate contact with traumatic factors and make the victim feel better. In domestic conditions, burns are most often caused by exposure to hot steam, contact with hot iron (iron, frying pan), boiling oil, etc.
Treating a 3rd degree burn at home is impossible, as doctors use a lot of complex measures that can completely eliminate pain, as well as speed up the restoration of damaged skin and deeper layers.
Before you go with the victim to a burn center or call a doctor at home, you need to provide him with pre-medical assistance:
- Cleansing the wound. First, you need to remove clothing from the source of damage as quickly as possible. If it is stuck, you need to carefully cut off the flaps close to the burned area.
- Anesthesia. To alleviate the patient’s condition, it is necessary to give non-narcotic analgesics - Ketorolac, Ibuprofen, Ketanov, etc.
- Treatment. Do not wash burns or apply antiseptic solutions. Before the doctor arrives, the affected area is simply covered with a sterile bandage or napkin.
The victim needs to urgently contact a specialist. Treatment of 3rd or 4th degree burn wounds is carried out only in a hospital.
Further treatment
Treatment of 3rd degree burns involves transplanting healthy tissue into the lesions. After the operation, rehabilitation follows, the duration of which depends on the depth and extent of the damage and the formation of abscesses.
Infusion therapy
For burn injuries of 3rd or 4th degree, detoxification treatment is mandatory. The action of the drugs is aimed at cleansing the patient’s blood and tissues from decay products of burned skin, replenishing the lack of fluid in the body. To do this, the following is administered intravenously:
- Ringer-Locke solution;
- Stabizol;
- Sorbilact;
- Refortan;
- glucose solution.
The volume of the drug is determined by the depth and extent of the damage. Timely infusion therapy prevents burn shock and poisoning.
Painkillers
What to do in case of a burn depends on the depth of damage to the dermis or subcutaneous fat. After surgery, patients complain of pain, so tablets are prescribed:
- Spasmaton;
- Nurofen;
- Paracetamol;
- Citramon-Borimed;
- Ketoprofen.
On the recommendation of a doctor, local painkillers and anti-inflammatory ointments are used, which are applied to the wound - Levomekol, Panthenol, Radevit, etc.
For 3b degree burns, local antiseptics and analgesics should not be used immediately after surgery.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are used to prevent and treat infectious inflammation in burn areas. With a serious degree of tissue damage, the risk of pus accumulation in the wound exceeds 65-70%.
Cooling is carried out not by running water, but by standing water. It is strictly forbidden to use ice for cooling.
To eliminate the infection, use:
- Ceclor;
- Cefazolin;
- Bicillin;
- Ampicillin;
- Gentamicin.
For injuries of moderate severity, drugs with antimicrobial components are used - Levosin, Streptonitol, Argosulfan, Dioxidin, Dermazin.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
For rapid skin healing, anti-burn ointments with dexpanthenol are used. The most effective ointments, sprays and creams include:
- D-Panthenol;
- Dexpanthen;
- Heppiderm;
- Bepanten;
- Pantoderm.
Anti-inflammatory drugs prevent the synthesis of substances that enhance inflammatory reactions (histamine, arachidonic acid). Due to this, the regeneration of damaged cells of the dermis and epidermis is accelerated.
Antiseptic dressings and treatments
Antiseptics are used to treat damaged skin for 3rd degree burns. They are applied under an occlusive dressing to prevent bacteria from entering the wound. For tissue disinfection the following are used:
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Levosin;
- Ichthyol ointment;
- Baneocin;
- Zinc ointment;
- Olazol;
- Mephenate;
- Eplan;
- Ebermin.
Dressings are changed as they become dirty, but not more than 1-2 times a day. If they become wet, treat the burns with Zinc ointment. It dries the tissue and stimulates the formation of crusts.
Sedatives
Depending on the degree of tissue damage, patients experience severe or moderate discomfort in the burn areas - itching, pain, burning, etc. To reduce the sensitivity of pain receptors and improve sleep, sedatives are used:
- Deprim;
- Afobazole;
- Alvogen Relax;
- Phytosed;
- Persen Forte;
- Dormiplant;
- Zelenin drops;
- lily of the valley-motherwort drops.
Sedatives are used for insomnia and increased anxiety only on the recommendation of a doctor. When the sleep-wake pattern is restored, therapy is discontinued.
Other medicines
Additional drugs in the treatment of burn wounds of 3a or 3b degrees are used to accelerate tissue regeneration. Typically, the treatment regimen includes:
- bactericidal ointments – Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Polymyxin;
- antiseptic solutions – Chlorophyllong, Eucalymin, Chlorhexidine;
- immunostimulants – Likopid, B-imunoferon 1b, Alfarekin, Virogel.
After rejection of the burn crust, it is necessary to treat the skin with antiseptics or use sterile dressings for 1-3 weeks.
Review of products to speed up healing
The timely use of medical supplies determines how long it takes for burns to heal. Sprays are usually used immediately after injury to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Ointments and gels are used for long-lasting effect and healing. The solutions are universal, and the patches protect against infection.
Coolants should be used with caution if your face is burned.
- Panthenol is a common first aid remedy, available in the form of a spray and ointment. The ointment is recommended for use after pain.
- Olazol. A domestic product that is more effective than Panthenol due to better absorption and antibacterial action.
- Furaplast. When applied, it forms a durable film. Protects damage from infections if the crust begins to crack. Do not apply to an inflamed or festering wound.
- Solcoseryl. Its use for 1-2 degree thermal burns promotes the growth of skin cells and helps heal damage.
- Boro-plus. Healing cream, completely natural, suitable for children.
To prevent these drugs from entering the esophagus, mild burns of the lips and tongue should be treated with folk remedies. Despite the opinion that this is the last century, they are quite effective. Diluted lavender oil relieves pain and inflammation.
What not to do
For mild injuries, rinse the wound with running water. But if the dermis or subcutaneous tissue is damaged, such actions cannot be performed.
In order not to aggravate the patient’s condition, when providing pre-medical care they refuse:
- washing or cooling burns with running water;
- tearing off stuck-on pieces of clothing from the lesion;
- applying dry cotton wool or cotton wool soaked in antiseptic to the wound;
- treating tissues with bactericidal or analgesic ointments.
For such serious injuries, treatment is carried out only within the walls of the hospital. To heal the tissue, the doctor transplants healthy skin from other parts of the body - back, lower leg, buttocks, etc.
Traditional methods
You can relieve the pain of a burn using various folk remedies.
- Raw potatoes. Grind the pulp, place the pulp in a sterile bandage, and apply to the damaged area. The pain will be reduced due to the starch contained in potatoes.
- Dairy products. Kefir, yogurt, sour cream soothe the skin well and reduce pain. Especially often used for sunburn.
- Egg white. Applied to damaged skin immediately after injury, it eliminates burning sensation well.
- Aloe juice. Soak a bandage in the fresh juice of the plant and apply it to the damaged area. The product disinfects well, reduces inflammation, and promotes regeneration.
- Toothpaste. Used only for minor burns, unless there is an open wound. Mint, which is part of toothpastes, has a cooling and distracting effect, helping to get rid of pain from a mild burn.
Folk remedies can help with very mild skin damage. But they must be used with caution. Self-medication can lead to further tissue damage, wound infection and other serious complications.
Dangerous consequences
Complications are determined by the location and extent of burns on the body. If the germ layer of the dermis is preserved (grade 3a), skin transplantation is not performed. With deeper injuries, dangerous complications sometimes arise:
- purulent arthritis;
- scarring;
- furunculosis;
- sepsis;
- phlegmon;
- gangrene.
Treatment of serious injuries is strictly not recommended at home. With extensive damage, undesirable systemic effects are often observed - burn shock, toxemia (poisoning), septicotoxemia (infectious intoxication). To prevent complications, immediately after receiving an injury, call a doctor at home or go to a burn center.