Hemangioma is a benign tumor whose cells do not transform into cancer. A node develops in places where blood vessels accumulate. The tumor grows slowly and can disappear on its own, leaving no traces. Therefore, removal of the hemangioma is required in extreme cases when the patient has some discomfort.
Large formations compress nearby tissues and disrupt the functioning of the organ, which affects the patient’s well-being. More often, the disease develops in children in the first months after birth. In adults, neoplasms rarely occur. The choice of method for removing hemangioma depends on medical indications and the pathological process occurring in the diseased area. Each method has pros and cons, which the doctor takes into account when choosing, excluding the occurrence of complications.
When to delete or not to delete
Hemangioma is a vascular node that forms on the skin, bone tissue and parenchymal organs. The disease is considered congenital, as it is often diagnosed in newborns in the first months after birth. A child may already be born with a hemangioma. During the first year of life, the neoplasm actively grows. The node then lies dormant for several years. By the age of 10, education passes on its own without a trace.
The disease is benign. But in the process of proliferation, atypical cells gradually destroy healthy tissue, which is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the organ. Therefore, it is recommended to remove the hemangioma, preventing the development of negative consequences.
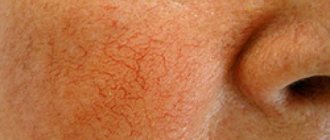
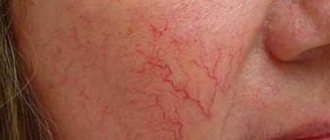
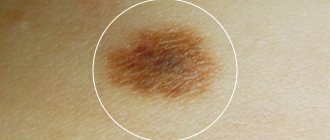
The disease can be recognized by the shape of the node and color. The neoplasm is formed asymmetrically, with a bright red tint. Occurs on the skin, on the mucous membrane and in the internal layers of the organ. According to their structure, the following types of hemangioma are distinguished: capillary, cavernous, capillary-cavernous, cellular and intermuscular.
Hemangioma in adults
The tumor is removed for medical reasons or due to cosmetic discomfort. In the absence of active growth and other accompanying signs, treatment is not applied - doctors prefer to control the disease through regular diagnostic procedures. Urgent treatment is required if there are signs:
- the formation rapidly increases in size and changes color;
- there is bleeding and ulceration on the surface of the tumor;
- the node is located near vital organs - the facial nerve, in the area of the auricle, etc.;
- the disease is accompanied by external deformations of the face or internal organ;
- there is a risk of malignant degeneration of the disease.
In case of such symptoms, the pathology should be removed. But in some cases the procedure is prohibited:
- the presence of an acute illness associated with infection;
- exacerbation of chronic pathology;
- febrile state of unknown etiology;
- hemangioma is covered with purulent, eczematous and other suspicious neoplasms;
- diseases of the heart muscle, kidneys or lungs.
Methods for removing a node:
- use of medications;
- mectoral or radical resection;
- cryodestruction;
- laser therapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- irradiation with gamma rays.
The doctor selects the method of treating the disease according to medical indications after conducting a detailed examination and assessing the degree of damage to the body.
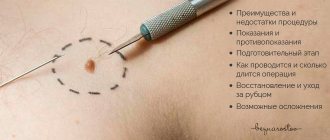
Preparing for removal
The preparation process depends on the procedure method. Before a traditional removal operation, the patient is sent to the laboratory to donate blood for a general clinical analysis of blood and urine.
Coagulability and Rh blood group, HIV with hepatitis and syphilis are detected. Adults will need to undergo fluorography of the lungs and an electrocardiogram of the heart. Additionally, consultation with an oncologist, cardiologist, dermatologist or other specialist is recommended, depending on the location of the node. It is necessary to identify possible complications after local anesthesia or general anesthesia. The clinic may require additional examinations, depending on the surgeon performing the removal.
The procedures of cryodestruction, laser therapy, and electrocoagulation do not require complex diagnostic measures. The patient needs to donate blood and urine to study the indicators of basic elements, coagulation and serious pathologies. You will also need to get a report from a therapist or pediatrician. It is prohibited to take anticoagulants 7 days before surgery.
Before carrying out any procedure, it is forbidden to eat or drink water for 12-16 hours. The operation is performed on an empty stomach and intestines. Additionally, sometimes the intestinal cavity is cleansed by taking a laxative or an enema with saline solution. Immediately before the procedure, the surgeon and anesthesiologist talk with the patient.
Contraindications
Preliminary examinations are necessary to identify possible contraindications to the procedure. Experts do not recommend intervention in the following cases:
- Systemic blood diseases (leukemia, hemophilia and others).
- Cerebrovascular accident.
- Hypertension.
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Exhaustion.
- Oncology.
- Liver and kidney failure.
- Epilepsy, psychosis, other nervous disorders.
- Fever and increased body temperature.
- Pregnancy.
Abdominal surgery
Surgical removal of hemangioma is used mainly for damage to internal organs - liver, kidneys, lungs, etc. Excision of atypical cells is carried out with the capture of healthy tissue up to 15-20 mm. If the formation is large, treatment is prescribed to reduce its size. Medications and courses of gamma ray irradiation are selected for the patient.
Small nodules formed in places of regular mechanical injury are surgically removed - on the back, in the armpit, on the foot, arm, etc. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia due to the painful process. After removal, the patient requires medical care. The obtained biological samples are sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
The downside of the operation is the pain of the procedure and residual deep scars that require additional cosmetic correction. Therefore, the method is used for tumors located in closed places and internal organs.
The advantage of this method is the radical removal effect, i.e. the tumor is excised completely, preventing recurrence of the disease.
The operation is performed mainly in adults with a diagnosis of acquired hemangioma with suspected oncology. The method is rarely used for childhood tumors. In a child, the node is excised in a more gentle way.
Before the procedure, a thorough examination is carried out, taking into account possible complications and consequences. Rehabilitation of the patient is carried out under medical supervision in order to identify negative consequences in the early stages.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the formation begins in the doctor's office. When examining the patient, the doctor assesses the condition of the nevus, what it looks like, asks about concomitant pathologies, and whether growth of the formation is observed. First of all, it is important for the dermatologist to exclude the malignant nature of the origin of the neoplasm. To do this, a scraping is taken from the nevus, and a histological examination is performed, which will show the presence or absence of cancer cells. If the doctor suspects the formation of a hemangioma on internal organs, the patient is referred for ultrasound, CT or MRI diagnostics. If the liver is damaged, angiography is performed to evaluate the functioning of the organ’s vessels.
Excision of hemangioma using cryodestruction
Cryodestruction involves freezing the tumor with liquid nitrogen. Used for small sizes up to 20 mm - this prevents the formation of deep scars after surgery.
The procedure lasts several minutes - atypical holes are frozen with liquid nitrogen at a low temperature, leading to the destruction of diseased tissue. Within a short period of time, a healthy layer of skin forms at the site of the node. For a positive result, 1-3 sessions are performed with an interval of 2-3 days.
The surgical site is subsequently treated with a solution of potassium permanganate. It is permissible to carry out the procedure on an outpatient basis, because no pain or blood loss. The child or adult goes home after the operation. The patient does not need to undergo a bunch of numerous diagnostic measures, which speeds up recovery.
The method is not used to treat tumors on the spine or near vital organs. It is quite suitable for treating tumors on the face and other visible areas.
Carrying out the procedure in children requires a special approach and special conditions to avoid unpleasant consequences:
- the time of exposure of the hemangioma to liquid nitrogen should not exceed 30 seconds;
- a node on the mucous membrane is excised for no more than 15 seconds;
- multiple nodule formations can be removed in one session, but the total area of exposure should not be more than 10 cm2;
- in the area of the perineum and buttocks, the maximum area of excision is 5 cm2;
- deep damage to the organ requires a series of courses to avoid injury and swelling - the time interval between sessions is 2-3 weeks;
- the process of cryodestruction begins from the peripheral area, gradually moving towards the center of the pathology.
The area exposed to liquid nitrogen becomes swollen within 2-3 days. This is especially noticeable in the eyelid area, lips, and mucous membranes. On the fourth day, the destroyed vessel becomes covered with a crust, under which a healthy layer of epithelium begins to form. The skin is completely restored within a month.
Cryodestruction is characterized by a high percentage of complete recovery (more than 95%) and minimal trauma to the skin. After removal there are practically no scars left. The scar remains when treating a node with deep growth. Complications of procedural intervention are diagnosed in isolated cases.
For the treatment of cavernous and combined hemangioma using cryodestruction, microwave therapy procedures are first prescribed. The completed courses increase the chances of a favorable prognosis for surgery to remove a deep tumor. The combination of two methods preserves the integrity of the muscles and facial contour without damaging the facial nerve and avoids bleeding of the node. It is allowed to be used to treat pathologies in infants.
Laser therapy
Laser removal of hemangioma has been used quite often over the past 20 years. The method is considered effective and gentle. The procedure is carried out mainly in private medical centers. Allowed for children and adults.
Before and after laser hemangioma removal procedure
The procedure shows the advantages:
- there is no pain during removal - the patient only feels a slight burning sensation;
- The operation takes several minutes;
- the tumor is removed in one session;
- the targeted effect leaves no marks or scars;
- the process does not require general anesthesia, local anesthesia is sufficient;
- it is possible to remove tumors on the face and mucous membranes - on the lip, tongue, head, etc.
The disadvantage is the impossibility of influencing seals with a large affected area and the cost of the procedure. The disadvantages include a contraindication for newborn children.
The doctor calculates the dosage, session time and course quantity individually for each patient. The age and well-being of the patient, as well as the pathological processes of the disease, are taken into account. If more than 3 sessions are required, the interval between them is 1 month.
It will not be possible to remove a tumor in the spine due to its deep growth. The laser beam penetrates tissue up to 4 mm, which is not enough to treat deep tumors. The method is used mainly for the treatment of capillary hemangioma.
After removal, a dense crust forms at the site of the node, which disappears on its own after 2-3 weeks. A healthy layer of dermis is restored at the site of the lesion.
Rehabilitation period
After diagnosing a hemangioma, removal of the formation can be performed using different methods, however, in order to speed up the healing and recovery process, it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. If removal was carried out using radio wave coagulation, cryodestruction or sclerotherapy, a small scar may form.
If electrocoagulation or laser treatment was chosen for therapy, a small crust forms at the site of the tumor, which disappears after a while. Regardless of how the removal was performed, the procedure for treating the crusts is carried out with an antiseptic until complete healing.
Sclerosing therapy of pathology
Sclerotherapy is suitable if the tumor appears in a hard-to-reach place and is large in size. The method is also effective for treating a node in the area of the auricle or in the oral cavity.
Previously, ethyl alcohol was used as a sclerosant, injected with a special thin needle into the cavity of the hemangioma. For the last 15-20 years, ethoxysclerol or fibro-vane has been introduced, which destroy the structure of the node. Within 7 days there will be swelling at the site of the pathology, gradually dissolving.
The disadvantage of the procedure is pain, therefore it is not used for treating children. The patient may be prescribed a course of painkillers to relieve pain. It is also necessary to carry out several procedures to destroy all atypical cells.
Electrocoagulation
Removal of hemangioma in hard-to-reach places using electrocoagulation is used quite often. Coagulation is the cauterization of the diseased area with high-frequency pulsed electric current. During the procedure, the tissues are heated and the cells are destroyed. The radio wave method must be used to influence the soft tissues of the node in order to provoke their death. A special device is used - Surgitron.
Working with an electrocoagulator
After cauterization, dead tissue falls away and the process of skin restoration begins. The procedure is used mainly in adults, because... there is a certain soreness. The process is characterized by a targeted effect on the tumor, but it is rarely used. After excision, a deep scar remains at the site of the node, which can be removed using cosmetic correction.
X-ray therapy in the treatment of pathology
The disease can be cured using X-rays, which can destroy the atypical structure. The method is used in children from 3 to 8 months, when pathological tissues react sensitively to radioactive exposure to rays. In older people, X-ray therapy is rarely used. The origin of the tumor is benign, but X-ray influence can cause degeneration into oncology.
The procedure consists of dosed exposure to x-rays on the diseased area at a certain time interval. The daily dose and course of therapy are selected individually by the attending physician. The location and pathological parameters of the disease influence. The operation has a number of side effects that can cause a deterioration in the patient’s well-being and provoke serious complications during the development of the node. Therefore, this method is used only when the previous ones did not give the desired effect.
The indication for the procedure is its location in the eye area and the space behind it. They can also be used to excise a large lesion area. The course of irradiation stops when there is no growth of diseased cells and the color changes to a paler shade - this indicates the beginning of involution of the pathological process.
Hemangioma on the eyelid
What it is?
Hemangioma is a benign tumor that develops from a vascular structure, and the causes of which have not been fully investigated. Typically, hemangioma forms in children and newborns from the moment of birth or some time after it. Growth in size does not depend on increasing age in children; heredity and hormonal changes are more important.
The most natural place of occurrence is subcutaneous fatty tissue; sometimes formation occurs in the liver or kidneys; in some cases, the vertebrae of the spine or other bone elements are affected.
Photo 1. What different types of hemangioma look like
Symptoms appear after the tumor has gained a significant size ; before that, they do not appear. Treatment is carried out using surgery, sometimes using a laser. In some situations, the hemangioma itself regresses and disappears, this often happens in children under 6 years of age.
Recovery and possible consequences of the disease
After each method of excision of hemangioma, a rehabilitation procedure is needed. The remaining scar requires special care and monitoring from the attending physician to prevent the development of dangerous symptoms. Cryodestruction, sclerotherapy and radio wave therapy are characterized by a small scar that heals on its own. Laser and electrocoagulation leave the area with the formation of a dense crust, which can also go away on its own when the skin is restored.
Do not treat the operated area with iodine, alcohol, hydrogen peroxide or other products containing acid. It is recommended to use ointments with a softening effect during this period - levomikolev or solcoseryl.
After abdominal surgery, the patient is under daily medical supervision. The wound is treated with a special antiseptic and the condition of the seam is examined. The threads are removed after 1.5-2 weeks. Then you will have to care for the wound at home on the advice of a doctor.
After removal, you should not walk in direct sunlight for a long time. It is prohibited to take hot baths and visits to the bathhouse. Warm showers are allowed. A special diet enriched with plant fiber is required.
Treatment of pathology at home
Small seals on the superficial layers of the dermis can be removed at home. To do this, use kombucha and copper sulfate.
A mushroom compress is applied to the affected area and fixed for 24 hours. After that they remove it and make a new one. Repeat the procedure daily until the node disappears completely.
A solution of copper sulfate is prepared at the rate of 1 tbsp. for a small amount of water. The resulting mixture is rubbed into the seal. The course lasts 10 days.
Before using traditional medicine methods, you should consult your doctor. This will avoid serious consequences.
Use of traditional medicine
How to remove hemangioma at home? The impact on superficially located vascular formations is carried out with lotions and compresses:
- with green walnut juice;
- with onion pulp: grate the onion, apply to the skin in the area of the tumor, apply for up to 10 days;
- with copper sulfate: dissolve 20 g of the product in 100 ml of water, change the lotions up to 5 times a day, the course of treatment is up to 10 days;
- with oak bark: for one tablespoon you will need ½ cup of boiling water, cook in a steam bath for 10 minutes, it is recommended to apply such compresses at least 4-5 times a day for two weeks.
Important. Treatment of vascular tumors located in critical areas (on the face, at the corner of the eyes) is best left to professionals.
If the non-traditional remedies used do not give the desired result, contact the Laser Medicine Clinic. Here they will help you get rid of hemangiomas quickly and effectively, using modern technologies and techniques for removing vascular formations. Call and get a free consultation.
Lyudmila Sergeevna Amyokhina
Head of the Laser Medicine Clinic Physician of the highest category, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, reflexologist
We provide a professional range of procedures in the laser medicine segment. We use modern equipment and widely use effective treatment methods. The staff is staffed by professional doctors of the highest category. Still have questions? Just call us and get a free consultation +7(812)244-36-58.
This is a type of benign tumor. Although it does not cause direct harm, it is still dangerous, since its growth is not controlled. Therefore, hemangioma removal is most often performed. For this purpose, a full range of modern surgical interventions is used. You can try to get rid of the disease by treating hemangioma with folk remedies at home. There is an opinion that the cause of the appearance of hemangiomas is due to a viral process that occurs in the expectant mother during the 5th - 6th week of pregnancy. During this period, the laying of the vascular wall occurs.