06.02.2017
Ringworm in humans is caused by two types of pathogenic microorganisms - Microsporum and Trichophyton fungi.
Therefore, dermatologists use the terms trichophytosis, dermatomycosis, microsporia, and dermatophytosis to diagnose the disease, depending on the pathogen. Microsporum can infect both people and animals, while trichophyton reproduces only on human skin.
Ringworm is classified as a contagious contact disease; its pathogens are transmitted from infected animals and people through contact. Moreover, you can become infected not only by petting a stray animal, but also by sharing household items with a sick person.
You can also pick up lichen fungus in a swimming pool, bathhouse, gym, and even in a hairdresser if they neglect to disinfect instruments.
The causative agents of the disease are highly resilient and can survive in the soil and on various surfaces for quite a long time. A favorable environment for the fungus is humidity and warmth, so a surge in diseases is observed in autumn and spring. More often, dermatomycosis affects children 4 to 13 years old, which is facilitated by weak immunity and delicate skin. In adults, ringworm is diagnosed less frequently, since the microflora on the surface of the skin contains organic acids that can reduce the activity of the fungus.
Even if the fungus gets on the skin of a healthy person, it is not a fact that he will become infected. Following hygiene procedures allows you to easily wash it off your skin.
For dermatomycosis to begin to develop, the following conditions are required:
- weak immunity;
- skin injuries (scratches, abrasions, abrasions);
- heat and high humidity in the room;
- constant contact with an infected animal or person.
Causes of ringworm
Ringworm is a skin infection caused by the fungi Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton.
As a rule, carriers of the causative agents of this disease are young and middle-aged children, as well as animals; a distinction is made between anthroponotic and zoonotic lichen. If a focus of inflammation is detected, the family doctor must immediately notify the SES and seek help from a dermatologist. The source of the anthroponotic variety of ringworm is directly from sick people. Routes of infection:
- direct contact with the patient,
- through objects - combs, hats, gloves, underwear.
There are three forms of this lichen:
- superficial smooth skin,
- superficial scalp,
- chronic.
There are small- and large-focal ringworm.
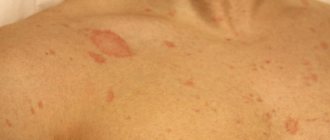
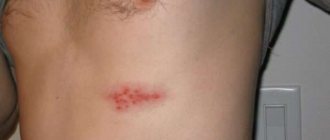
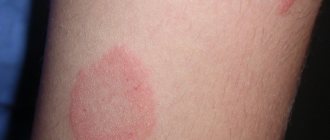
Superficial lichen of smooth skin is characterized by round or oval red inflammatory spots with peeling in the center, along the periphery there is a swollen ridge with nodules, vesicles, and crusts on the surface. The hearth gives the impression of a “seal”. The lesions grow along the periphery, merging into a formation with bizarre outlines. A slight itching bothers me. The course is acute. With rational therapy, the lesions regress within 2-3 weeks.
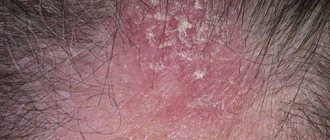
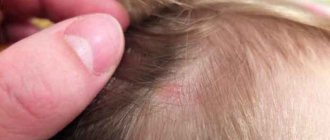
With superficial lichen of the scalp, round or irregularly shaped lesions of various sizes appear with unclear boundaries, mild erythema, and peeling. The lesions are first single, then multiple. Hair in the lesions is broken off at a height of 1-2 mm or at skin level.
Chronic ringworm develops from the previous two forms during puberty, mainly in girls. Interestingly, in boys during puberty the disease can go away on its own. This happens due to changes in the composition of sebum, in which uncylenic acid appears, which has a detrimental effect on fungi.
In the chronic form of lichen, small atrophic bald spots and hairs broken off at the skin level (“black dots”) are observed in the occipital region and temple area. At the same time, on the skin of the buttocks, knee joints, less often the torso, forearms, and face, there are foci of a bluish tint, with slight peeling, and onychomycosis of the fingers (nails are dull, gray, lumpy, crumble and peel off). This form of ringworm often develops against the background of endocrinopathies and dysfunction of the gonads. In some patients, against this background, nodular, granulomatous lesions with abscess formation may occur.
The source of the zoonotic variety of ringworm is livestock (mainly calves), rodents, and pets; the pathogen is transmitted through various objects. There are three forms:
- superficial,
- infiltrative,
- purulent smooth skin and scalp.
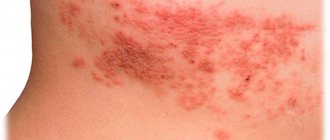
Superficial zoonotic lichen of smooth skin is found on open areas of the skin, inflammatory, red, round spots appear around natural openings, prone to merging, the formation of foci with scalloped edges, peeling on the surface, and a ridge with vesicles and crusts along the periphery.
Infiltrative zoonotic lichen of smooth skin appears as gray spots, round lesions (like a seal), also subject to peripheral growth, but they are infiltrated and swollen. Painful regional lymphadenitis may develop.
Purulent zoonotic lichen of smooth skin is characterized by similar foci, but dense, consisting of deep follicular abscesses; multiple pustules are observed on the surface of the skin; when pressed, pus is released in drops. The lesions are painful on palpation, and regional lymphadenitis develops.
Purulent zoonotic lichen of the scalp is characterized by single and then multiple dense and painful infiltrates, numerous follicular pustules, crusts, and the formation of pus. Lesions with clear boundaries, prone to peripheral growth, fusion and the formation of massive infiltrates, covered with purulent crusts, when compressed or stretched, drops of pus are released on the surface. Regional painful lymphadenitis often develops; Possible increase in body temperature, disturbance of general condition. When such lesions are localized on the upper lip or chin in adult men, the process resembles sycosis (fungal, “parasitic sycosis”). Numerous inflammatory, low-painful nodes resembling boils may appear on the skin of the chin and neck.
Kinds
The disease is classified into several types, which have a similar course and require the same approach to therapy. Depending on the location of the pathology, it is divided into the following forms:
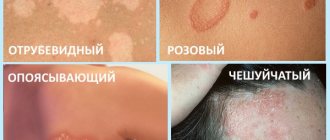
- Erythematosquamous - appears on the shoulders, back, chest and upper abdomen. It is characterized by the absence of obvious itching.
- Follicular - develops against a background of weakened immunity and in the presence of concomitant pathologies, such as diabetes. It is distinguished by the formation of small pustules on the spots and severe itching.
- Inverted - diagnosed in the folds of the skin and in the groin area. Does not cause inflammatory symptoms.
Without proper treatment, any form of pityriasis versicolor spreads over large areas of the skin. Despite this, the disease is not considered dangerous. In some cases, it progresses for several years without causing complications other than aesthetic discomfort.
How to treat ringworm?
Treatment of ringworm is a lengthy process, usually taking 4-6 weeks. If the patient has only one focus of fungal skin infection and generally feels normal, then local therapy through the use of ointments, gels, and disinfectant solutions will be sufficient. Multiple fungal overgrowths require a comprehensive, systemic approach, often taking oral medications. The choice of treatment strategy for ringworm depends on the form of the disease and the depth of the lesion. You cannot do without consulting a doctor; self-medication often leads to chronicity of the process.
Therapy for ringworm has several goals - to alleviate the course of the disease and destroy its causative agent, and also to prevent the addition of a secondary infection.
Treatment of ringworm requires the use of antifungal drugs orally - these are griseofulvin, lamisil, orungal (taken according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor). Local therapy is more common - antifungal ointments (lamisil, orungal, exoderil), 2-5% iodine solution, 3% salicylic ointment .
Treatment will not be effective enough if, in parallel with taking medications, you do not observe hygiene measures and do not adhere to a food diet.
For purulent forms of lichen, manual hair removal is advisable. To eliminate acute inflammatory phenomena, clean lesions from manure, and limited infiltrates, disinfectant lotions and applications of grated potatoes are applied every 2-3 hours. Subsequently, a simple sulfur ointment or official antifungal ointment is applied to the cleaned lesions.
If prescribed by a doctor, creams containing hormones may be used.
Ointments are considered the most effective form of topical preparations, since they have a dense consistency compared to creams and gels and take longer to absorb.
For ringworm that occurs in a chronic form, immunomodulatory and vitamin therapy is necessary, in particular taking vitamins B and C.
Contraindications for use
Almost all ointments for lichen have contraindications. Each product has its own, but there are a number of general limitations that you should pay special attention to:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- children under one year of age;
- skin damage.
Some ointments (especially hormonal ones) cannot be applied to large areas of the epithelium or used for too long. Failure to comply with this rule may worsen the course of the disease and provoke complications.
Like any other drugs, these drugs have their contraindications:
- It is prohibited to use the composition if you are individually intolerant to its components, in particular parabens and undecylenates;
- Do not apply the product to wet areas of the skin, ulcers or blisters;
- many drugs are prohibited for use by children under two years of age;
- It is prohibited to apply the drug to the areas around the eyes.
No studies have been conducted on the use of the drug in pregnant and lactating women. However, after using the products, no negative effects on the body were noted either. Therefore, in this case, you need to consult a doctor to make the most optimal decision.
What diseases can it be associated with?
Ringworm develops solely as a result of infection with fungal spores; no previous diseases are noted. Children, pregnant women and elderly people, people with immunodeficiency conditions, metabolic disorders due to their weakened immunity can be called more prone to infection.
In severe forms of ringworm, which are accompanied by the formation of an infiltrate and the release of pus, the development of lymphadenitis is possible. Untreated lichen for a long time becomes chronic with frequent relapses; there is a risk of secondary infection with the subsequent development of all kinds of dermatoses and eczema.
Treatment for ringworm at home
A patient with ringworm may need hospitalization if there are many lesions on the skin and hairy areas of the body. Treatment of ringworm can also be done at home, but considerable attention should be paid to sanitary and hygienic measures and the direct hygiene of the patient and his cohabitants. The point is that the fungus, along with skin particles, disperses around and persists for months, so there is a risk of re-infection. The following measures to prevent this are recommended:
- if lichen has developed on the body, then the patient should wear knitted underwear, and if on the head - a scarf or a tight-fitting knitted cap; both must be changed daily;
- wash the patient’s underwear and clothes separately from other things, first disinfect them, and then boil them and hot iron them;
- the patient should shower daily using antifungal shampoos; if the doctor recommends not to wet the skin lesions, then during the shower the damaged areas must be covered with plastic (food) film;
- exclude the patient’s contact with carpets, soft toys and other things that are difficult to clean;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning in the room where the patient spends most of his time, as well as in common areas;
- Personal hygiene products and things that the patient actively uses are constantly treated with disinfectants.
The diet requires attention, since food serves as a source of strength for recovery and supports the immune system:
- You should actively consume fresh vegetables and fruits - sources of vitamins;
- you should lean on meat and sea fish - a source of protein and polyunsaturated fatty acids;
- fermented milk products are useful because they restore normal microflora in the intestines and minimize the risk of developing allergic reactions;
- You should avoid products that contain obvious flavorings and dyes;
- You should avoid fried and spicy foods.
To strengthen the immune system, it is advisable to take vitamins B and C.
What medications are used to treat ringworm?
The following drugs have a therapeutic effect on ringworm:
ointments
- sulfuric - has a drying and healing effect;
- sulfur-tar - has an antifungal and disinfectant effect;
- salicylic - has antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects;
- Lamisil - stops the growth of fungi; applied for 5-6 weeks;
- mycosporus - destroys fungal cells; applied for 4-6 weeks;
gels
- exifin - applied 1-2 times a day, rubbed until completely disappears from the surface of the skin; applied within 3-4 weeks;
- mycogel - applied 2 times a day in a thin layer; applied within 3-4 weeks;
solutions (convenient for use on the scalp)
- Vokadin is an antifungal and bactericidal drug;
- iodicirin - promotes rapid healing and detachment of scales;
- nitrofungin is an antifungal drug used until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear;
tablets - have a systemic effect, are highly effective, however, they also have a number of side effects; used in case of presence of several foci of ringworm
- griseofulvin - take 8 tablets per day with meals with a teaspoon of vegetable oil until the first negative test, then the dose is reduced and the drug is gradually discontinued;
- Lamisil - taken 1-2 times a day for 6 weeks;
- orungal - taken 100 mg once a day for 15 days.
Before applying medications to the skin, it is recommended to clean the damaged areas; for this, use:
- furatsilin,
- rivanol,
- potassium permanganate.
Active substance and release form
Lamisil is a non-toxic, broad-spectrum drug produced in Switzerland. Used against lichen and fungal diseases. The active ingredient is terbinafine. Produced in the following dosages and dosage forms:
- tablets packed in blisters of 10 pieces, dosage - 250 mg;
- gel or cream 1% - commercial name - “Lamisil dermgel”;
- "Lamisil" spray for external use 1%, in containers of 15 and 30 ml;
- A 1% film-forming solution, commercial name "Lamisil uno", is used externally.
Treatment of ringworm with traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers a wide variety of recipes for ringworm, but not all of them are highly effective. Discuss with your healthcare provider the advisability of using the following:
- plantain - grind fresh plantain leaves in a blender, squeeze out the juice; combine 1 glass of juice with 1 tbsp. ash and 1 tsp. alcohol; use 5 times a day for a week;
- chamomile - 20 grams of dried chamomile flowers, brew 300 ml of boiling water, strain after half an hour; use for wiping foci of lichen on the skin or wash your hair with a decoction for 7-10 days of treatment;
- beets - boil medium-sized beets for 40-50 minutes, peel, grate on a fine grater; add an equal amount of buckwheat honey, stir, store in the refrigerator; use three times a day for a week;
- black raisins - steam a handful of raisins with boiling water; Crush the steamed raisins into a paste and apply it to the lichen lesions twice a day; the effect will become noticeable on days 3-5, but continue treatment until symptoms disappear completely.
Description
Tinea versicolor, bran lichen, and sweating lichen are the names of the same disease. Pityriasis versicolor is a dermatosis of the skin caused by the yeast-like fungi Malassezia. The main difference: it is not transmitted from a sick person to another person. The infection has no painful symptoms other than an aesthetically unattractive appearance of the skin.
The fungus is localized on the upper half of the body (arms, shoulders, neck, chest), as well as on the scalp. The sores are dark brown in color and are prone to peeling and the formation of scaly crusts. The color of the rash may vary depending on the patient's skin type, as well as the time of year. On light skin, lichen appears in the form of brown or yellow spots. In dark-skinned people - a pink rash. Since the infection disrupts the structure of the skin, the sores do not darken in the sun, but appear in the form of light spots, significantly different in color from healthy and tanned skin.
The disease can develop over a long period of time. If pityriasis versicolor is left untreated, it can lead to the formation of large pockets of infection. In many cases, tinea versicolor appears due to a person's genetic predisposition to the fungus. In this case, it will not be possible to cure pityriasis versicolor forever, but by using modern treatment methods, you can make sure that the infection goes away for many years.
Treatment of ringworm during pregnancy
The risk of contracting shingles during pregnancy increases because a pregnant woman is more vulnerable to any infections. Transmission of ringworm usually occurs:
- in contact with animals,
- in hairdressing salons,
- in preschool and educational institutions.
It is important to take preventive measures so as not to subsequently face the problem of finding acceptable ways to get rid of the fungus:
- do not use things that have been in contact with sick people or people you don’t know;
- avoid close contact with sick people;
- do not contact with unfamiliar or suspicious animals.
Ringworm during pregnancy brings significant discomfort to a woman. Ignoring the disease can lead to chronicity of the process, so it is necessary to treat it immediately after detection.
Most drugs for the treatment of ringworm are applied topically, are not absorbed into the bloodstream, and therefore are not dangerous to the fetus. However, treatment of lichen should not be carried out by the patient himself; consultation with a doctor is indicated, especially if the fungus has developed in the expectant mother.
Side effects
A latent fungal infection may worsen.
The main side effects are associated with allergies:
- itching;
- burning;
- redness.
Symptomatic therapy is not needed - after stopping the medication, the discomfort disappears. In case of overdose, nausea, vomiting, and headache develop. If they occur, gastric lavage and taking Atoxil or activated carbon are recommended. Afterwards, you should visit your doctor to clarify the dosage of Lamisil or change the medicine.
Which doctors should you contact if you have ringworm?
- Dermatologist
- Infectious disease specialist
Diagnosis of ringworm begins with examining the affected areas under the rays of a special lamp - the skin and hair affected by fungi will become emerald green. It is advisable to scrape the affected area of the skin; it is sent to the laboratory, where it is examined under a microscope and becomes material for inoculation on nutrient media.
When diagnosing anthroponotic lichen, the clinical features and course are taken into account; hair, scales, and nails are examined for the presence of fungi. When diagnosing a zoonotic disease, the same thing applies; the presence of lichen in domestic animals is additionally established.
Anthroponotic lichen is differentiated from microsporia, rubrophytosis, inguinal epidermophytosis, infiltrative-suppurative epidermophytosis, seborrheic eczema, pink lichen of Zhiber; zoonotic - with carbuncles, boils, common sycosis, rubrophytosis, infiltrative form of microsporia, chronic generalized candidiasis.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - s
| Treatment of salmonellosis |
| Treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis |
| Treatment of pulmonary sarcoidosis |
| Treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma |
| Treatment of uterine sarcoma |
| Treatment of Ewing's sarcoma |
| Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| Treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| Treatment of seborrhea |
| Treatment of sepsis |
| Treatment of heart failure |
| Treatment of anthrax |
| Treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome |
| Treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome |
| Treatment of Gilbert's syndrome |
| Treatment of Parhon's syndrome |
| Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome |
| Treatment of empty sella syndrome |
| Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome |
| Treatment of Sjögren's syndrome |
| Treatment of sinusitis |
| Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus |
| Treatment of systemic scleroderma |
| Treatment of systemic sclerosis |
| Treatment of syphilis |
| Treatment of scoliosis |
| Treatment of somatoform disorders |
| Treatment of spinal stroke |
| Treatment of spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis |
| Treatment of laryngeal stenosis |
| Treatment of tracheal stenosis |
| Treatment of stenosing ligamentitis |
| Treatment of tetanus |
| Treatment of stomatitis |
| Treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| Treatment of subdural hematoma |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.