Last update: 03/18/2020
A proper understanding of how the skin and the sun interact helps to avoid two extremes - excessive desire to tan and complete isolation from the sun's rays. Both of these options are unacceptable: in the first case, exposure to the sun on the skin can lead to early aging, wrinkles and even cancer, while excessive protection from the sun's rays can result in depression, apathy, brittle bones and other health problems. Therefore, it is so important to understand exactly what effect the sun has on the skin, and in what doses it can be beneficial and in what doses it can be harmful.
Historical background: when did sunbathing begin to be considered beneficial to health?
Carefully protecting your skin from the sun was a social norm a century ago. Until the beginning of the twentieth century, tanning was treated with great suspicion: women tried in every possible way to protect their skin with mittens, dresses and blouses with long sleeves, and summer umbrellas. Aristocratic pallor was one of the main signs of belonging to the highest circles of society, while tanning was the prerogative of peasants, farmers and other commoners.
The situation began to change after the First World War. At that time, many city women were forced to go to the countryside to do field work, because due to the lack of men, there was not enough labor. In addition, around the same time, Dr. Auguste Rollier proposed a new method of treating tuberculosis through sunbathing.
One of the unwitting popularizers of tanning was Coco Chanel. One day her skin got sunburned, but high society considered it a new fashion for tanning. The so-called “healthy tan” became the hallmark of successful and wealthy people who could afford not to pore over papers in offices, but to travel and laze on the beach. Another reason for the popularization of prolonged exposure to the sun, dark skin and tanning were Egyptian and African motifs, which became fashionable in European art in the 20s of the twentieth century.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of sun fungus, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Before you start sunbathing after swimming, you need to dry your skin well with a clean towel;
- If you sweat heavily, you should pre-treat problem areas with talcum powder. Also, wiping the skin folds and armpits with a decoction of oak bark will not hurt;
- You should avoid visiting the solarium;
- On the beach you need to use sunscreen;
- It is best to choose clothes made from natural fabrics.
Following these simple recommendations will protect a person from becoming infected with fungus.
Sun exposure to the skin: is it always beneficial?
To understand the complex relationship between skin and the sun, we need to understand what sunlight and its rays are. The sun's rays are divided into three categories:
- Ultraviolet rays A. This type of rays is considered the least harmful to the skin. Their effect on the skin is difficult to detect with the naked eye, and until recently it was considered completely safe. However, recent studies prove the opposite: ultraviolet A rays contribute to early aging of the skin, the formation of wrinkles on its surface, and a decrease in elasticity. In addition, penetrating to the dermis layer, these rays destroy elastin and collagen fibers and can also reduce the protective functions of the skin.
- Ultraviolet rays B. The greatest danger from exposure to this type of rays on the skin occurs from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m. It is during this time period that it is strictly not recommended to be in direct sunlight. Unlike A rays, B rays cause sunburn on the skin. It is under their influence that melanin is produced and tanning occurs. Like A-rays, they can cause premature aging of the skin, its roughness and roughness, the appearance of wrinkles, and can also cause the development of cancer. This happens because the intensity and wavelength of B rays is sufficient for them to interact with DNA molecules in the skin.
- Ultraviolet rays C. The degree of their radiation is considered the most dangerous to human health. Fortunately, C-rays do not reach the Earth's surface thanks to the ozone layer. However, if its destruction and the appearance of new ozone holes continue, humanity may fully experience the danger of solar radiation. Residents of Australia and New Zealand have already felt the negative impact of these rays. There is an increase in cases of skin cancer, and the reason for this is believed to be the violation of the integrity of the ozone layer. And, despite the fact that the ozone hole is not over Australia and New Zealand, but over Antarctica, these are the countries that suffer from it the most.
As you can see, the sun's rays can cause great harm to the skin. However, we should not forget about their positive properties:
- Sunlight promotes the production of vitamin D in the body. It is necessary for better absorption of phosphorus and calcium, which are necessary for the strength of bones and muscles, as well as for rapid tissue regeneration after wounds.
- Sunlight has a beneficial effect on a person’s general condition, his emotional background and mood. Therefore, during the winter months, when the days get shorter, many of us feel low energy and depressed.
- The sun's rays have a beneficial effect on many vital processes in the human body: breathing, blood circulation, metabolic processes.
- UV light therapy is widely used in the treatment of many skin diseases.
So, the harm of the sun to the skin cannot be called absolute. If you sunbathe wisely and use protective equipment, you can not only avoid getting sick, but also improve your health. But at the same time, you need to take into account the characteristics of your body and your own belonging to one or another phototype.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine knows how to treat solar lichen. This treatment at home is recommended for use at the initial stage of pathology development, when the spots are small in size.
- Sea buckthorn oil helps speed up skin regeneration and stop the spread of fungus. This product should be rubbed into stains twice a day. Sea buckthorn oil helps both cure sunburn and prevent the spots from reappearing. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to use it once every three days for two weeks after the symptoms disappear.
- Apple cider vinegar compresses are used to treat any mycoses. Vinegar should be mixed with water in equal proportions. Then a compress is generously moistened in the product and applied to the skin for half an hour. The procedure should be repeated three times a day; there is no need to wash off any remaining product.
- Rosehip decoction helps improve the protective function of the skin and accelerates regeneration. It can be used both to treat fungus and to accelerate the restoration of pigmentation in affected areas of the skin. To prepare the decoction, add three large spoons of dried berries to two glasses of water and cook over low heat for 20 minutes. After the medicine has cooled, soak a cotton swab or gauze compress in it and apply it to the skin for 30 minutes. The procedure is carried out in the morning and evening.
- Rosehip oil also helps speed up skin restoration. The product should be rubbed into the stains twice a day.
Sensitive skin and the sun: why do some people burn and others tan?
In 1975, American dermatologist Thomas B. Fitzpatrick identified six skin types and determined their response to sunlight. The Fitzpatrick classification is currently considered the main one; it is by it that you can determine your phototype.
- Type 1: Scandinavian. People with Scandinavian skin type live mainly in Finland, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Iceland, but we must not forget that many people from these countries live today in other countries - often in those where the level of solar radiation is much higher. People belonging to this type of appearance usually have milky white skin, light eyes, blond or red thin hair, and freckles. The sensitivity of the skin to the sun in people of the Scandinavian phototype is maximum: after spending only a few minutes under its direct rays, they can get sunburned. That is why achieving an even tan is almost impossible for them.
- Type 2: light European. Blonde-haired and light-skinned residents of northern and central Europe usually have fairly light eyes and are much less likely than Scandinavians to have freckles. Sunburned skin is a fairly common occurrence for them, but still less than for representatives of the first type.
- Type 3: Central European. People with ivory skin, light brown or light brown hair and light brown or hazel eyes belong to the Central European phototype. They tan easily, but if exposed to direct sunlight for a long time, their skin will burn in the sun.
- Type 4: Mediterranean. Dark-skinned people with olive, velvety skin tones, dark brown eyes and dark brown or black hair almost never get sunburned. The tan applies easily and evenly to their skin and lasts a very long time.
- Type 5: Asian. Staying in the sun in summer is almost not dangerous for the skin of people belonging to this phototype. Quite strong natural pigmentation of yellowish or brownish skin in itself looks like a light or more intense tan.
- Type 6: African. Chocolate or almost black skin color, dark brown eyes and black hair are the distinctive features of representatives of this phototype. These are the only people whose skin does not turn red in the sun. This is caused by very strong natural pigmentation and high UV protection.
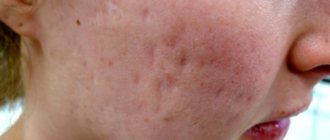
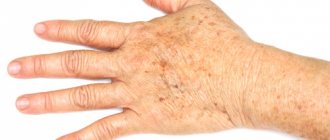
Sun spots on skin
The effect of the sun on the skin of the face and body can manifest itself in the form of light pigment spots. This is usually due to low melanin production. It also sometimes turns out that there is a fungal infection in the body (for example, pityriasis versicolor), which causes small or large areas of a light shade to appear after tanning. Another reason for this reaction lies in the use of certain medications that reduce melanin production.
Skin allergies to the sun
The scientific name for this reaction of the body to sunlight is photodermatosis. Allergies can manifest themselves in the form of burns, blisters and erythema, small rashes, redness, peeling, swelling, and the appearance of scales and crusts on the skin.
Most often, representatives of the first and second phototypes are susceptible to skin allergies to the sun. Therefore, they should always use sun protection for their skin during the summer.
Skin redness in the sun
Red skin from the sun is the first symptom of a sunburn. At the same time, body temperature may increase, swelling and soreness may appear. If redness appears, take a cool shower and apply a special product containing panthenol to the damaged skin. You can also use a common folk method - applying kefir or sour cream compresses to the burnt areas.
The sun dries out the skin: what is the reason and how to fight it?
As mentioned above, ultraviolet rays age the skin, affecting collagen and elastin fibers. As a result, the skin becomes rough and dry. To avoid this, it is necessary to apply protective products to the body that filter ultraviolet rays.
Itchy skin in the sun
If your skin begins to itch after being in direct sunlight, be sure to consult a dermatologist. It is quite possible that this is one of the first signs of photodermatosis.
Diagnostics
Solar lichen is easy to diagnose. Any dermatologist can determine this type of skin lesion. To do this, it is enough to conduct a visual inspection of the problem area on the body. But sometimes experts have doubts about the correct definition of infection. In this case, they ask the patient to undergo a series of diagnostic procedures. To identify sun fungus, the following research methods are required:
- To study skin peeling, a test for Beignet's sign is required;
- To determine the current state of the epidermis, a Balzer test is performed, which involves the use of iodine;
- To identify the type of infectious agent, you will need to submit a tissue sample for PCR diagnostics;
- To more accurately determine the type of pathogen, laboratory diagnostics of skin particles is used;
- Wood's lamp examination is used to identify lesions on the body.
After undergoing a complete diagnosis and receiving its results, it will be easier for the dermatologist to determine the diagnosis for the patient who came to see him.
Several methods have been developed to diagnose beach fungus, or pityriasis versicolor in other words.
How to minimize sun damage to skin?
How to protect your skin from the sun? First of all, avoid being in direct sunlight from 10.00 to 16.00 - at this time UV rays are especially dangerous. It is also recommended to choose suitable protective equipment.
If you already have a rash on your skin from the sun, it itches and causes discomfort, we recommend that you use La Cree restorative cream. It helps fight redness, flaking and itching. Due to the panthenol and avocado oil contained in the cream, skin regeneration occurs, and bisabolol, walnut, string and violet extracts provide an antipruritic effect.
Experts' opinion
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
It has been clinically proven that as a result of using the cream:
- Dryness and flaking of the skin goes away;
- The skin's own moisture is preserved;
- The skin becomes protected from wind and cold.
Consumer Reviews
tararkova (irecommend.ru)
Magic emulsion for your skin.
Good day to all.
During the period of breastfeeding, I developed an allergy, which was accompanied by itching and flaking of the skin, and since most medications were prohibited, the dermatologist recommended several moisturizers to choose from, from which I chose La-Cri Emulsion. I have never met this company, and most likely would not have paid attention to it if not for chance.
The emulsion is white, a little runny, every time I use it, more product comes out than needed, so its dispenser is not convenient. Its aroma is not very pleasant, but not annoying.
At first I applied this Emulsion only to areas with allergies, and then I began to apply it to my face, since with its help I got rid of the symptoms of the disease in just a few days.
This emulsion perfectly moisturizes and nourishes, relieves itching and irritation. There were no negative consequences after it. I recommend this Emulsion, I give it 5 stars, despite the inconvenient dispenser.
Advantages
- actively moisturizes and nourishes the skin
- absorbs quickly
- light texture
- relieves itching and redness
- economical to use
murka2610 (irecommend.ru)
“Hello everyone!
Today I want to tell you about the wonderful cream for sensitive skin “La-Cri”! With the birth of my baby, I became more attentive to all perfume and cosmetic products, including creams
Sources:
- Yagodka Valentina Stepanovna, Medicinal plants in dermatology and cosmetology, Naukova Dumka publishing house, 1991
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, publishing house: Notabene, 2017
- Churolinov Petr, Herbal medicine in dermatology and cosmetics, Medicine and Physical Education Publishing House, 1979